Low-Code Application Platform (LCAP) Market By Offering Type (Platform Core/Solution, and Services), By Platform Type (No-Code, Low-Code, and Pro-Developer), By Organization Size (SMEs, and Large Enterprises), By Deployment Mode (Public Cloud, Private Cloud and On-Premises), By Application Type ( Web-Based, Mobile-Based, and Others), By Industry Vertical (BFSI, Government and Public Sector, Telecommunications / IT / Infrastructure and Others) – Global Analysis & Forecast, 2025–2030
Low-code Application Platform Industry Outlook
The global Low-Code Application Platform Market size was valued at USD 36.81 billion in 2024, and is expected to be valued at USD 49.43 billion by the end of 2025. The industry is projected to grow, hitting USD 215.97 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 34.3% between 2025 and 2030.
The low-code application platform industry is expanding rapidly as businesses prioritize agility and faster time-to-market for digital solutions. By reducing the reliance on traditional hand coding and offering visual, drag-and-drop interfaces, no-code platforms empower both developers and business users to build applications more efficiently.
Research indicates that by 2025, a large majority of new applications will be created using low-code or no-code technologies, highlighting the shift from niche adoption to mainstream enterprise strategy. This growth is fueled by rising digital transformation initiatives, persistent IT talent shortages, and the need for scalable solutions across industries.
At the same time, the low-code application platform industry is diversifying in terms of adoption. Large enterprises continue to lead with platforms such as Microsoft Power Apps, OutSystems, Mendix, and Appian, while small and mid-sized firms are increasingly leveraging solutions like Zoho Creator for cost-effective innovation.
Integration with cloud ecosystems, AI-driven features, and workflow automation tools is broadening the scope of use cases, from process optimization to customer engagement. As governance, security, and compliance practices mature, LCAP is evolving into a foundational pillar of enterprise IT strategies, enabling organizations worldwide to balance speed with long-term sustainability.
What are the Key Trends in Low-Code Application Platform Industry?
How is the Low-Code Application Platform Market Transforming Digital Transformation Programs?
Low-code is no longer a pocket of tactical automation; it’s rewriting how organizations deliver digital products. Industry research widely cited projects that by 2025 a large majority of new applications will be built with low-code tools, reflecting enterprises’ drive to speed delivery and reduce backlog. That shift means digital transformation owners must treat low-code as a mainstream delivery model which integrate platform selection into enterprise architecture, enforce common data contracts, and measure outcomes rather than lines of code. Practically, teams that treat low-code like a first-class capability see faster pilot-to-production cycles and higher stakeholder satisfaction.
How is the Low-Code Application Platform Market Changing Who Builds Software Inside Companies?
One of the most visible trends in the low-code application platform market demand is the rise of citizen developers and cross-functional builders. Surveys show a growing share of low-code activity originates outside central IT as business teams build work-specific apps. Forrester’s The State of Low-Code, Global 2024 says low-code is now a mainstream development approach worldwide, but adoption patterns vary by region.
The report is based on a survey of >2,000 developers and finds North America and much of APAC have largely institutionalized low-code, Europe remains more cautious and efficiency-focused, and APAC skews toward innovation while North America wants both speed and breadth of capability. It highlights that citizen development and fusion teams are common, that organizations still write a lot of traditional code (especially in North America), and that treating low-code as a first-class part of enterprise architecture is increasingly important.
How is AI (Including Generative AI) Changing Low-Code Application Platforms and Outcomes?
Generative AI and assistive AI are rapidly being embedded into low-code tooling, from autocomplete for logic flows to auto-generated UI and data mapping because AI shortens iteration cycles and lowers the bar for non-technical users. Recent surveys and industry reports show firms are pushing AI into tooling and workflows to extract faster business value, with leadership and governance being the critical adoption barrier, where about 78% of companies using AI in at least one function and 71% already leveraging generative AI.
That means low-code vendors that combine trustworthy AI with developer extensibility will stand out. For companies, the immediate action is to pilot AI-augmented modules for two high-value use cases, e.g., invoice processing, customer onboarding with strict metrics on accuracy and error handling and build an AI-policy checklist (data lineage, retraining cadence, fallback flows) before scaling.
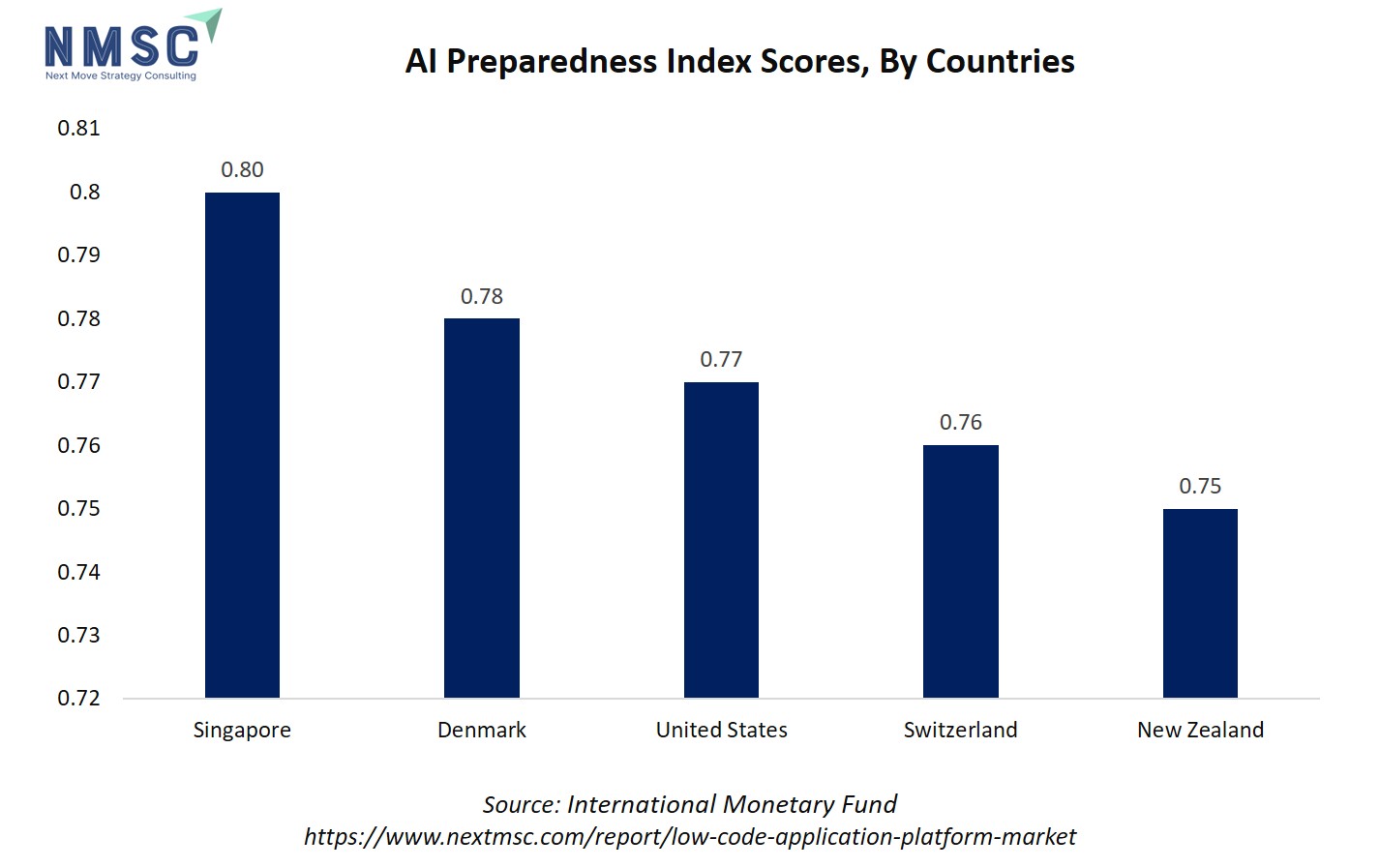
The chart illustrates the AI Preparedness Index (AIPI) scores of the top five countries, with Singapore leading at 0.80, followed by Denmark (0.78), the United States (0.77), Switzerland (0.76), and New Zealand (0.75). This ranking highlights each country's readiness to adopt and integrate AI technologies based on digital infrastructure, human capital, innovation capacity, and regulatory frameworks.
The relevance to the sector lies in the fact that countries with higher AI preparedness are more likely to adopt AI-enabled low-code platforms, leveraging features like AI-assisted app development and process automation. High AIPI scores indicate robust ecosystems where organizations can efficiently implement software development solutions, accelerating digital transformation, improving productivity, and driving the low-code application platform market growth. Conversely, these markets are also prime targets for LCAP vendors seeking early adoption of advanced, AI-integrated low-code tools.
How is the Low-Code Application Platform Market Evolving Toward Verticalization and Composability?
Low-code platforms are maturing from generic app builders into industry-aligned, composable toolkits. Vendors and customers increasingly prefer prebuilt vertical components (healthcare workflows, banking KYC flows) and composable building blocks that plug into microservices or enterprise event buses.
Some forecasts also show rapid growth in platform adoption and in the population of low-code developers, supporting more specialized and large-scale deployments which implies that horizontal platforms without domain accelerators struggle to deliver immediate ROI. Actionably, product and GTM leads should prioritize one or two vertical accelerators that map to existing sales motion, e.g., HR/Payroll for a workforce tool vendor and invest in a composable SDK so professional developers can extend platform behavior safely. This hybrid strategy, vertical templates and composability helps capture customer value earlier while leaving room for enterprise-grade extensions.
What are the Key Market Drivers, Breakthroughs, and Investment Opportunities that will Shape the Low-Code Application Platform Industry in the Next Decade?
The low-code application platform market trends is accelerating as organizations chase faster software delivery and measurable business outcomes. Platforms that reduce hand-coding and automate common integrations let small teams and citizen builders deliver business apps quickly, lowering time-to-market and unit cost. Rising cloud adoption, expanding API ecosystems, and persistent developer shortages push more business units to adopt LCAPs, which raises both scale and governance questions as usage spreads beyond central IT.
Vendors are responding with AI features, prebuilt vertical components, and composable architectures to broaden use cases from frontline automation to customer-facing apps. Enterprises that couple platform adoption with shared data models, governance rules, and developer enablement capture stronger ROI; those that don’t risk sprawl and technical debt. For investors and product leaders, the low-code application platform market looks like sustained growth, but winners will balance speed, security, and extensibility.
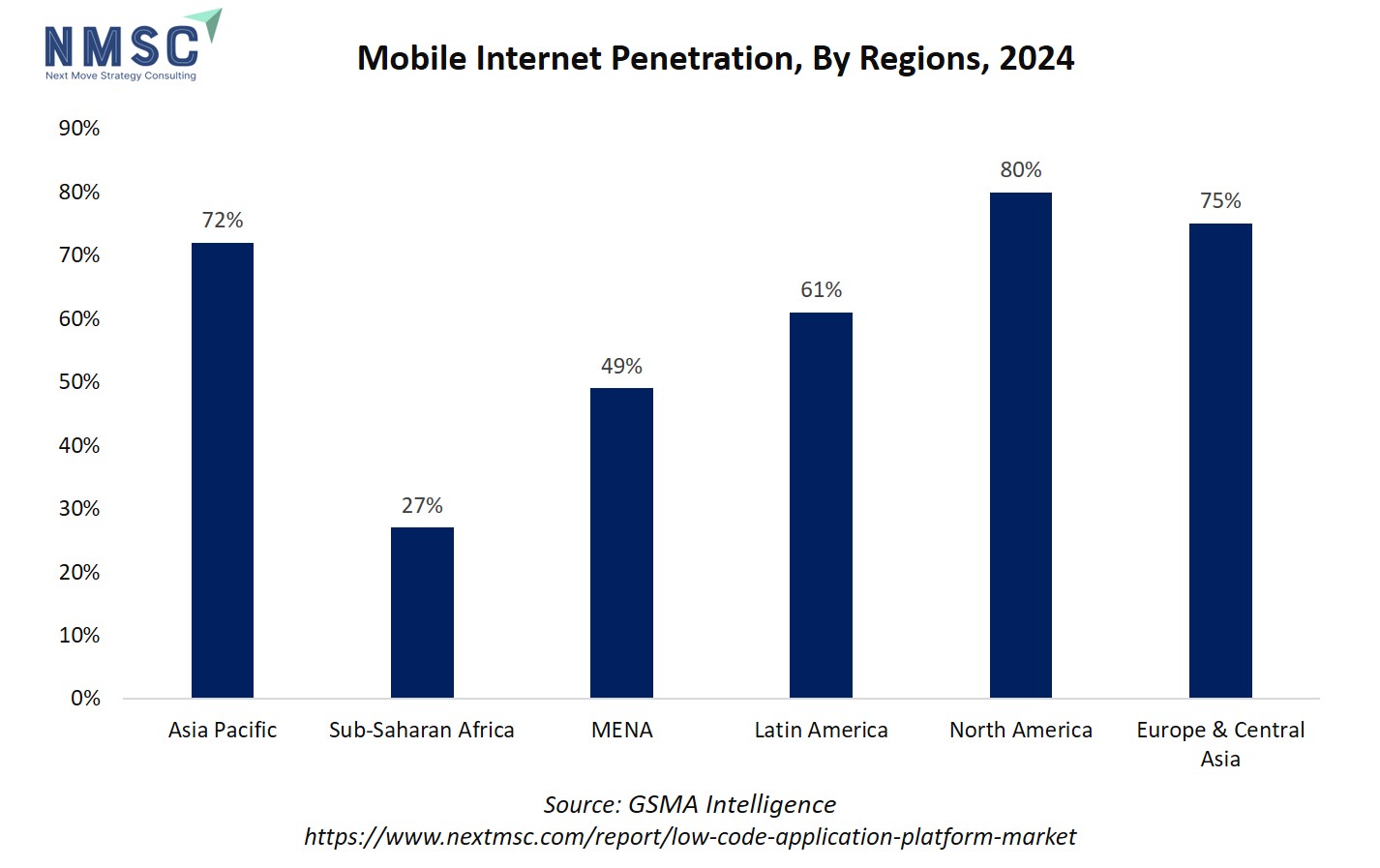
The above chart illustrates the percentage of mobile internet penetration across different regions in 2024. North America leads with 80%, followed closely by Europe & Central Asia at 75% and Asia Pacific at 72%. Latin America has a moderate penetration rate of 61%, while MENA registers 49%, and Sub-Saharan Africa lags at 27%.
High mobile internet penetration directly impacts the growth of the low-code application platform market share. Regions with greater connectivity, such as North America and Europe, provide a ready environment for deploying and scaling low-code applications, supporting faster adoption by enterprises and government bodies.
In contrast, regions with lower penetration, like Sub-Saharan Africa, present untapped potential, where LCAP providers could focus on mobile-first solutions to bridge digital gaps. Overall, mobile internet penetration serves as a strong enabler for LCAP adoption, influencing low-code application platform market strategies and regional growth priorities.
Growth Drivers:
How are developer shortages and time-to-market pressures driving LCAP adoption?
Many organizations face persistent developer shortages and large application backlogs, so they adopt low-code platforms to accelerate delivery of internal tools, customer portals, and automation. By letting business users build standard workflows and enabling developers to assemble reusable components, low-code reduces handoffs and shortens iteration cycles, which improves responsiveness to changing business needs. That said, maintaining velocity requires clear role definitions, centralized component libraries, and escalation pathways for complex cases.
How is AI and cloud integration accelerating the LCAP market?
The infusion of generative and assistive AI into low-code tooling, such as, automatic UI generation, smart mappings, and code suggestions combined with native cloud connectors shortens prototyping and enlarges the set of solvable problems. Business users can now build workflows with embedded intelligence while developers rely on cloud services for scale and reliability.
This capability expands use cases from simple forms to document processing and predictive routing, but it raises governance needs. Artificial Intelligence (AI) outputs must be validated, observed, and have fallback logic. Companies should pilot two high-value AI-augmented apps, instrument accuracy and performance metrics, and codify an AI playbook that sets testing, retraining, and human-in-the-loop rules before broad rollout.
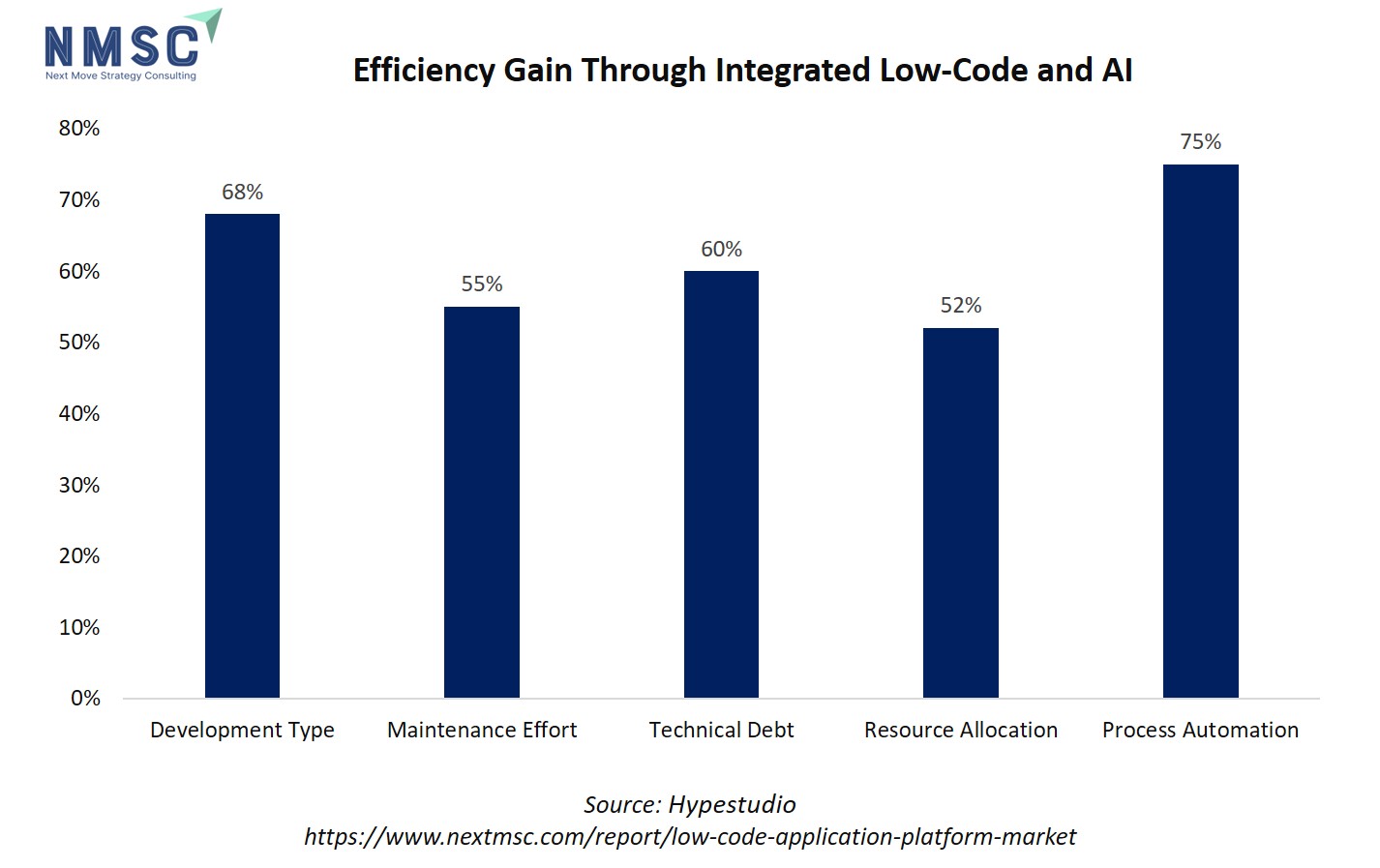
The above chart shows the efficiency gains from integrating low-code and AI, with process automation delivering the highest improvement at 75%, followed by development type at 68%, technical debt reduction at 60%, maintenance effort at 55%, and resource allocation at 52%. These efficiency improvements directly impact the growth of the low-code application platform market by accelerating development cycles, reducing costs, improving scalability, and enabling enterprises to automate complex processes with minimal coding effort. As businesses increasingly prioritize speed, flexibility, and cost efficiency, the demonstrated benefits drive broader adoption of LCAP solutions, fueling strong industry expansion.
Growth Inhibitors:
What governance, security, and vendor-lock challenges inhibit large-scale LCAP deployments?
Rapid adoption by business units often creates shadow IT, inconsistent data schemas, and uncontrolled integrations that amplify compliance and operational risk. Platforms can also drive vendor lock-in through proprietary components and limited exportability, making migration or multi-vendor strategies costly. These inhibitors slow enterprise-wide adoption despite the technology’s benefits.
The pragmatic response is a lightweight governance model that enforces approved connectors, shared data models, role-based access, and periodic architecture reviews. In procurement and vendor evaluation, insist on portability, open APIs, and an exit plan so enterprises can scale confidently without becoming dependent on a single vendor’s proprietary stack.
Where should investors and vendors place bets in the evolving LCAP landscape?
The strongest opportunities sit at the intersection of verticalization and composability. Industry accelerators, such as healthcare, fintech, manufacturing combined with extensible SDKs, connectors, and marketplaces that enable professional developers to extend low-code platforms. Investors should favor companies with repeatable vertical go-to-market motion, durable recurring revenue, and partner ecosystems.
Vendors should prioritize developer experience, robust APIs, testing frameworks, and clear extension points and build AI-enabled accelerators that shorten time-to-value. Strategic M&A to acquire domain IP or connector portfolios can speed market entry and create defensible recurring revenue that converts pilots into enterprise contracts.
How Low-Code Application Platform Market is Segmented in this Report, and What are the Key Insights from the Segmentation Analysis?
By Offering Type Insights
Which Offering Type is Driving the Low-Code Application Platform Market in 2025?
On the basis of offering type, the market is segmented into platform core/solution and services.
The platform core provides the foundational tools, visual development environments, and integrations that enable organizations to rapidly build and scale applications. Services, on the other hand, include consulting, implementation, training, and ongoing support, which ensure that enterprises can fully utilize platform capabilities. Together, these segments highlight that while the platform delivers technological capability, services drive adoption, user readiness, and long-term return on investment.
By Platform Type Insights
Which Platform Type Rules LCAP Adoption in 2025?
Based on platform type, the market is segmented into no-code platforms, low-code platforms, and pro-developer low-code.
Low code application platforms divide into no code for business users, low code offering visual design plus optional coding, and pro developer low code for deep customization and complex integrations. Government guidance and implementation notes highlight growing public sector adoption and emphasize governance and security when scaling these tools. Analysis indicates that low code leads enterprise adoption because it balances rapid delivery with extensibility, enabling citizen developers while allowing professional developers to extend functionality. No code accelerates simple workflows but has scalability limits, and pro developer low code serves mission critical scenarios with narrower uptake.
By Organization Size Insights
Do SMEs or Large Enterprises Drive the LCAP Market in 2025?
Based on organization size, the low-code application platform market report is divided into small and medium enterprises (SMEs), and large enterprises.
The low-code application platform market, when segmented by organization size, reflects two distinct adoption patterns. Small and medium enterprises leverage these tools to overcome limited IT resources, enabling faster digitization and cost efficiency. Large enterprises, however, dominate adoption due to their complex application needs, larger budgets, and emphasis on governance, integration, and scalability. Public sector studies highlight that while SMEs benefit most from accessibility, it is large organizations that shape market momentum by embedding low code into enterprise-wide digital transformation strategies.
By Deployment Mode Insights
Is Public Cloud the Preferred Deployment Mode for LCAP in 2025?
Based on deployment mode, the market is divided into public cloud, private cloud, and on-premises.
The low-code application platform market by deployment mode spans public cloud, private cloud, and on-premises models, each serving different organizational needs. Public cloud dominates adoption as it offers scalability, cost savings, and accessibility, aligning with global digital transformation and remote work trends. Private cloud is favored in sectors with stricter compliance or data sovereignty requirements, while on-premises persists in legacy-heavy industries needing full control. Government and industry reports underline that cloud-first strategies are now the default, with public cloud driving the broadest adoption across both enterprises and SMEs.
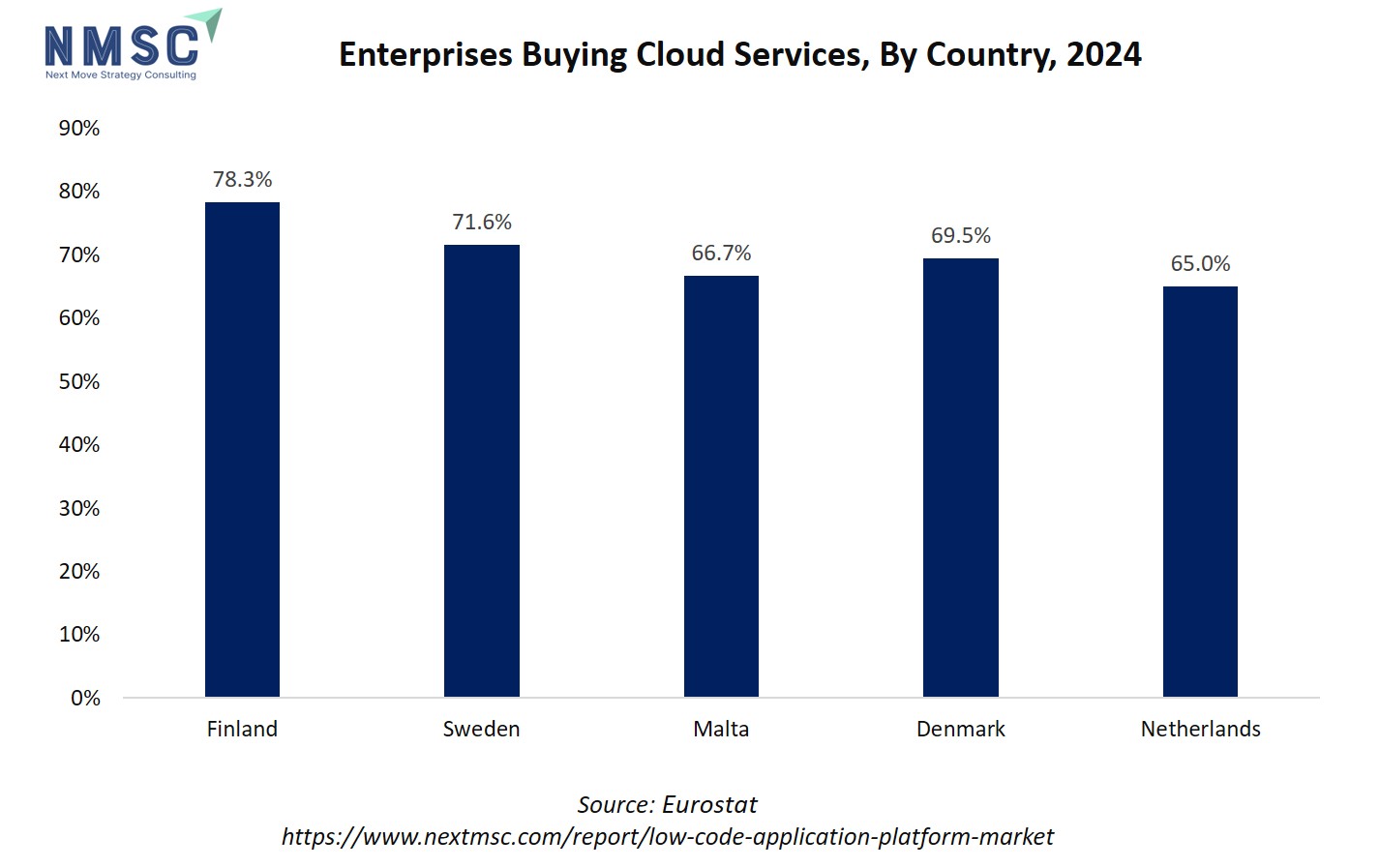
The above chart illustrates the percentage of enterprises purchasing cloud services across five European countries: Finland (78.3%), Sweden (71.6%), Malta (66.7%), Denmark (69.5%), and the Netherlands (65.0%). The data indicates a strong adoption of cloud computing across these regions, highlighting that a majority of enterprises are increasingly relying on cloud-based infrastructure for their IT operations.
LCAPs are predominantly cloud-hosted solutions that enable rapid application development with minimal coding. High cloud adoption in these countries suggests a favorable environment for LCAP deployment, as enterprises are already familiar with cloud-based tools and services. This reduces barriers to adoption, accelerates implementation timelines, and increases the potential for integrating low-code solutions into existing IT ecosystems.
Consequently, countries with higher cloud service adoption rates, like Finland and Sweden, are likely to experience faster growth and higher uptake of LCAPs compared to regions with lower cloud penetration.
By Application Type Insights
Which Application Type Dominates LCAP Use in 2025?
Based on application type, the low-code application platform market is divided into web-based applications, mobile-based applications, desktop / server-side applications, and API-centric / microservices-enabled apps.
Web-based applications dominate because they enable rapid delivery of business tools that are accessible across devices and browsers, supporting both internal operations and customer-facing solutions. Mobile-based applications are expanding quickly, fueled by the need for on-the-go employee productivity and stronger digital engagement with customers. API-centric and microservices-enabled apps are increasingly important for enterprises seeking to modernize legacy systems and achieve seamless system integration. While desktop and server-side apps continue to serve niche or legacy environments, the overall momentum is shifting toward web-first and mobile-first strategies, with microservices providing the backbone for scalability and agility in enterprise architectures.
By Industry Vertical Insights
Which Industry Vertical is Leading LCAP Adoption in 2025?
Based on industry vertical, the low-code application platform market is segmented into banking, financial services insurance (BFSI), government and public sector, healthcare and life sciences, manufacturing, education, retail and e-commerce, telecommunications/IT/infrastructure, and others.
BFSI and government sectors are driving the largest adoption of low-code application platforms due to the critical need for secure, compliant, and scalable solutions that support complex workflows and regulatory requirements. Healthcare and life sciences increasingly leverage these platforms to accelerate patient management systems, digital record keeping, and regulatory reporting, enhancing both efficiency and accuracy. Manufacturing and retail industries focus on operational efficiency, supply chain optimization, and customer engagement through rapid application development. Telecommunications and IT infrastructure organizations adopt low code to streamline service delivery, integrate legacy systems, and support digital transformation. Across all verticals, adoption is closely tied to digitalization priorities, regulatory pressures, and the demand for faster application deployment to respond to evolving market needs.
Regional Outlook
The market is geographically studied across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa, and each region is further studied across countries.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in North America
North America leads in enterprise-grade LCAP adoption because buyers insist on scale, security, and integration with existing cloud estates. Large enterprises treat low-code as a formal delivery model, embedding platform choices in enterprise architecture, setting governance, and funding center-led fusion teams that mix citizen builders with professional developers. AI/automation features and tight integrations with Azure/AWS/GCP accelerate production apps, while a mature partner ecosystem helps migrate pilots into enterprise programs. Those capabilities shorten backlog and time-to-value, but firms still emphasize governance to avoid sprawl. Forrester surveyed more than 2,000 developers globally to gather insights on how low-code is used by both professional and citizen developers in North America, which shows that low-code is now fully mainstream, though implementation styles differ.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in the United States
In the U.S., low-code application platform market adoption is driven by digital transformation urgency, cloud maturity, and a strong enterprise software market. Firms rapidly pilot AI-augmented low-code features (autocomplete, UI generation) to accelerate workflows and customer portals, yet leadership looks for measurable business outcomes rather than proof-of-concepts. Talent shortages and backlog pressures push citizen development, but centralized CI/CD and runtime monitoring remain priorities for scaling. The U.S. market’s emphasis on measurable ROI and governance makes it fertile for vendors that offer enterprise connectors, security certifications, and professional services. Forecast report shows how in the U.S. low-code application platform market is not just growing, but becoming central to enterprise software strategy. It cites that by 2025 roughly 70% of new applications will use low-code/no-code platforms, a shift that implies major demand for platforms that deliver speed plus governance and security.
Government AI & Digital Transformation Initiatives by Country
|
Region/Country |
Initiative / Policy |
Focus Area |
|
USA |
GSA's Gemini for Government |
AI Tools for Agencies |
|
Brazil |
AI Investment Plan |
AI Infrastructure & Development |
|
India |
IndiaAI Mission |
AI Development |
|
United Kingdom |
Low Code Community |
Government Digital Transformation |
The above table highlights how government initiatives across key countries are driving the low-code application platform market. In the USA, programs like GSA’s Gemini for Government provide AI tools to agencies, creating a demand for low-code platforms that can integrate AI quickly and efficiently. Brazil’s AI Investment Plan focuses on AI infrastructure and development, encouraging organizations to adopt platforms that simplify AI-driven application development.
Similarly, India’s IndiaAI Mission promotes AI research and skill development, fostering the creation and use of AI-enabled low-code solutions. Meanwhile, the UK’s Low Code Community directly targets government digital transformation, encouraging the adoption of low-code platforms to accelerate application development. Collectively, these initiatives show that governments are enabling environments where LCAP adoption is both necessary and beneficial, validating strong market growth potential.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Canada
Canada’s LCAP adoption mirrors North America’s enterprise orientation but with stronger interest from public sector and regulated industries. Federal and provincial digital programs prioritize interoperability, privacy, and cloud sovereignty, so vendors offering compliance-ready connectors and clear data-governance tooling have an advantage. Canadian organizations often pilot citizen developer programs within business units, then formalize platform governance centrally, this staged approach reduces risk while preserving the speed benefits of low-code. Forrester’s regional work highlights this measured but steady uptake.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Europe
Europe shows heterogenous adoption, Nordics and the UK move faster on innovation, while continental markets emphasize efficiency and compliance. GDPR and strong data-protection regimes push enterprises to prefer platforms that support strong access control, audit trails, and data residency. Vendor success here depends on local templates (industry accelerators) and clear enterprise governance. Forrester’s 2024 mapping shows Europe as cautious but steadily institutionalizing low-code into enterprise architecture rather than leaving it as a departmental tool.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in the United Kingdom
The U.K. balances speed and regulation, public sector digital agendas and fintech growth create high-value LCAP use cases. Many U.K. buyers target customer-facing microapps and rapid regulatory reporting tools, favoring platforms with strong auditability and cloud partnerships. AI features are tested aggressively in customer service and sales automation, but companies often require explainability and fallback flows before broad rollout. That pragmatic posture helps programs scale with governance, turning early wins into multi-team deployments.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Germany
German enterprises emphasize reliability, integration with legacy SAP landscapes, and strict data governance. Low-code wins where it can reduce bottlenecks, internal tools, supplier portals, and manufacturing apps, provided the platform supports enterprise integration patterns and on-premise or hybrid deployment. Vendors that offer strong SAP connectors, localized support, and compliance features tend to gain traction; German buyers prioritize predictable TCO and long-term maintainability over hype.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in France
France is pragmatic. Public sector modernization and telecoms/retail push LCAP pilots for internal automation, but regulatory and procurement norms encourage standardized, secure solutions. Innovation hubs around Paris experiment with AI-augmented low-code for customer experience and citizen services, yet enterprises typically require vetted connectors and certification paths for citizen developers. Platforms that provide vertical accelerators for regulated industries often see faster adoption. Suppliers that provide localized trials, agronomy support, and clear ROI messaging tend to succeed.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Spain
Spain’s market combines public sector modernization and tourism/retail digitization, with low-code used for citizen services, booking/operations apps, and internal process automation. Spanish buyers value platforms that support multilingual UIs, regional data residency, and integration with common ERP stacks. Adoption often starts in operational teams and scales with governance playbooks and reusable component libraries, reflecting a typical Southern-European progression from tactical pilots to governed rollouts.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Italy
Italy’s uptake is driven by SMEs modernizing processes and mid-market firms digitizing supply chains. Low-code appeals because it lowers development costs and shortens delivery cycles; however, limited in-house cloud expertise and funding constraints mean vendors with strong local partner networks, training, and prebuilt templates outperform niche entrants. The region’s pattern is pragmatic adoption via centralized IT oversight of business-led projects.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in the Nordics
Nordic countries adopt LCAPs rapidly, driven by digital-first public services and progressive enterprise IT cultures. High cloud maturity, strong developer ecosystems, and openness to AI pilots accelerate LCAP deployment across government services, healthcare, and fintech. Nordic buyers emphasize sustainability, accessibility, and interoperability, so platforms that demonstrate energy efficiency, compliance, and strong APIs win. This combination of innovation appetite and governance discipline makes the Nordics a hotbed for enterprise-grade low-code use cases.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Asia Pacific
APAC is diverse. China and India show large-scale, fast adoption while Japan moves more cautiously. Rapid digitization, expanding cloud infrastructure, and government digital initiatives propel LCAP uptake across retail, banking, and logistics. Integrating AI with low-code is especially compelling in APAC where automation can rapidly reduce operational costs. IDC and regional research show strong developer population growth and growing demand for citizen development programs, underscoring that APAC will be a major growth engine for LCAP vendors.
Regional reports from the Asian Development Bank show inclusion and policy coordination are becoming central in Asia-Pacific digital transformation agendas, fostering environments where platforms with citizen-developer programs and secure, local vendor options are likely to thrive. These governmental enablers, policy, infrastructure, regulation are making APAC a rapidly growing and attractive market for low-code application vendors
Low-Code Application Platform Market in China
China’s LCAP market is growing fast with strong local vendor ecosystems and a sizeable addressable market. Adoption is fueled by digital transformation in manufacturing, finance, and government, but foreign vendors face localization and regulatory hurdles. Domestic platforms that integrate with local clouds and offer language/industry accelerators are preferred, and services revenue (implementation/consulting) often outpaces pure platform sales.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Japan
In Japan, enterprises take a cautious approach due to a cultural focus on craftsmanship and legacy system modernization, favoring proven, secure low-code platforms with reliable vendor support. Rising cloud adoption and developer shortages are driving interest in low-code for internal automation, and successful organizations complement these platforms with thorough testing, structured change management, and localized professional services to maintain quality and long-term maintainability.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in India
India is a high-velocity market for LCAP. A large IT services sector, rapid cloud adoption, and an active startup ecosystem drive demand. NASSCOM and local analyses highlight India’s potential to generate multi-billion revenue streams from LCNC platforms, and a growing AI talent pool supports AI-augmented low-code use cases. Cost sensitivity and a thriving partner ecosystem favor vendors offering affordable entry tiers, localized training, and reseller programs. India’s global capability centers also use LCAPs to speed internal tool delivery for global clients. The NASSCOM report highlights India’s low-code market, growing rapidly across BFSI, retail, and SaaS sectors, driving faster development, cost savings, and increased productivity, with projected revenues of ~USD 4 billion by FY25.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in South Korea
South Korea’s corporate sector, especially manufacturing and telecom adopts low-code for rapid operational digitization and customer experience projects. High cloud maturity and strong AI adoption make AI-augmented low-code attractive, but enterprises expect enterprise-grade security and integration with domestic platforms. Local vendors and system integrators play a key role in driving pilots into production, and success often depends on strong QA and performance testing.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Taiwan
Taiwan's low-code application platform market is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as public sector modernization, strong cloud adoption, and a vibrant fintech ecosystem. Their expansion is supported by the increasing demand for hybrid deployment models, robust governance frameworks, and compliance with stringent privacy regulations.
Government agencies are leveraging AI-enabled automation through low-code platforms to enhance service delivery and operational efficiency. Vendors offering localized professional services and training are facilitating quicker enterprise adoption, ensuring that organizations can effectively implement and maintain low-code solutions.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Indonesia
Indonesia shows fast LCAP uptake among fintech, logistics, and e-commerce players as they scale regional operations. Cloud adoption and mobile-first use cases favor low-code for rapid prototyping and regional rollouts. However, uneven developer supply and data-sovereignty concerns mean enterprises prefer vendors with local partners and clear deployment options. LCAPs that offer mobile-native templates and regional connectors typically win the early digital-commerce and microservice integration projects.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Australia
In Australia, the LCAP market is being propelled by public sector modernization, strong cloud adoption, and a vibrant fintech ecosystem. A notable example is the New South Wales Government, which deployed a low-code application in just one week to coordinate multi-agency disaster response across the 300,000-square-mile state. This demonstrates how low-code platforms enable rapid development of critical, large-scale applications, reducing deployment time from months to days.
Such high-profile, practical use cases underscore the value of LCAPs in government and enterprise settings, driving wider adoption. Coupled with demand for hybrid deployments, strong governance, and compliance with privacy regulations, platforms that offer AI-enabled automation and localized professional services are well-positioned to capture the growing Australian market.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in Latin America
The low-code application development platform market in Latin America is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as public sector modernization, strong cloud adoption, and a vibrant fintech ecosystem. The expansion is further supported by the increasing demand for hybrid deployment models, robust governance frameworks, and compliance with stringent privacy regulations.
Government agencies are leveraging AI-enabled automation through low-code platforms to enhance service delivery and operational efficiency. Vendors offering localized professional services and training are facilitating quicker enterprise adoption, ensuring that organizations can effectively implement and maintain low-code solutions.
Countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Chile are leading the adoption of LCAPs, propelled by increasing cloud computing investments and the need to reduce custom development costs. For instance, Microsoft's announcement of a USD 2.7 billion investment in Brazil's cloud and AI infrastructure underscores the region's commitment to digital transformation.
Low-Code Application Platform Market in the Middle East & Africa
In Middle East & Africa, LCAP adoption is accelerating in government, utilities, and finance, where cloud modernization programs and national digital agendas create demand. Sovereignty and compliance concerns mean hybrid or local cloud options are attractive; meanwhile, the push for rapid citizen services drives interest in low-code for faster delivery. Vendors that couple platform capability with local partnerships and implementation support tend to succeed, because many buyers need help translating pilots into sustainable programs.
Competitive Landscape
Which Companies Dominate the Low-Code Application Platform Market and How do they Compete?
The global low-code application platform market is led by established technology leaders such as Microsoft Corporation, Salesforce, ServiceNow, Appian, OutSystems, Pegasystems Inc., and others alongside a growing base of regional innovators like Zoho Corporation, Creatio, and Kissflow. These companies are fueling market expansion through continuous investment in AI-driven automation, cloud-native infrastructure, and enterprise-grade governance capabilities. Their strategies focus on accelerating application delivery, reducing dependency on scarce developer resources, and aligning with enterprise demands for scalability, security, and compliance. With mounting pressure to modernize legacy systems and meet rapid time-to-market expectations, leaders are launching integrated platforms that combine workflow automation, data intelligence, and cross-cloud deployment tools to deliver measurable business agility.
The competitive landscape is being reshaped by AI integration, industry-specific accelerators, and platform consolidation. Major players are strengthening their positions through acquisitions of niche technology firms, ecosystem partnerships, and expansion into high-growth regions across Asia-Pacific and Latin America. At the same time, innovators are embedding low-code capabilities into broader digital transformation platforms, leveraging AI copilots, prebuilt templates, and composable architectures to address sector- and geography-specific needs. As enterprises worldwide shift toward agile development practices, companies that balance ease of use with enterprise-grade scalability are capturing both IT trust and business adoption, positioning themselves at the forefront of the LCAP revolution.
Market Dominated by Low-Code Application Platform Giants and Specialists
The LCAP market is split between giant platform suites, such as, Microsoft Power Platform, Salesforce, ServiceNow, and others that bundle low-code into broader cloud ecosystems and specialist vendors such as, OutSystems, Mendix, Appian, Pega, Zoho, and Creatio that compete on performance, vertical accelerators, or developer experience.
Large vendors win on scale, enterprise connectors, and partner channels, while specialists differentiate with high-performance runtime, vertical templates, or stronger citizen-developer tooling. That dynamic produces a two-tier market where enterprises pick either an integrated cloud play or a best-of-breed low-code stack depending on legacy landscape and speed-to-value needs.
Innovation and Adaptability Drive Market Success
Leaders are racing to embed AI, improve UI/UX generation, and add prebuilt industry workflows so customers can deliver production apps faster. Recent moves show vendors layering generative/assistive AI and tighter cloud integrations to shorten build cycles and reduce the need for hand-coding; OutSystems’ Ionic acquisition and Appian’s AI integrations are examples of product evolution toward richer templates and mobile-first capabilities. Firms that invest in extensible APIs, observability, and partner enablement win more enterprise deals because IT teams demand governance, testability, and predictable TCO alongside speed.
Market Players to Opt for Merger & Acquisition Strategies to Expand Their Presence
Mergers and acquisitions have become a key strategy for low-code application platform vendors to expand capabilities and market reach. Siemens’ ~ USD 730 billion acquisition of Mendix enabled it to integrate a high-performance low-code platform with its industrial automation solutions, enhancing its enterprise digital offerings.
Similarly, ServiceNow’s purchase of Raytion bolstered AI-powered search and knowledge management capabilities, while Salesforce’s USD 6.5 billion acquisition of MuleSoft improved integration across enterprise systems. Collectively, these M&A moves accelerate product rollouts, enhance service portfolios, and solidify vendor positions in competitive markets
List of Key Low-Code Application Companies
-
Salesforce, Inc.
-
Microsoft Corporation
-
ServiceNow
-
Zoho Corporation
-
Creatio
-
Kissflow Inc.
-
WaveMaker, Inc.
-
Mendix Technology BV
-
Pegasystems Inc.
-
Caspio, Inc.
-
Rierino Software Inc.
-
Michaels, ross & cole, ltd. (mrc)
-
UI Bakery, Inc.
What are the Latest Key Industry Developments?
-
October 2024- Appian was ranked 1 in the Complex Internal Applications use case in Gartner’s Critical Capabilities for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms report. It was also recognized as a Leader in the 2024 Gartner Magic Quadrant for LCAP.
-
October 2024- ServiceNow has been officially named a Leader in Gartner’s 2024 Magic Quadrant for Enterprise LCAPs for the fifth consecutive year, demonstrating consistency in its vision and execution.
-
October 2024, Microsoft was named a Leader in Gartner's Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms for the sixth consecutive year. This recognition highlights Microsoft's sustained dominance and innovation in the LCAP space, reinforcing the platform's widespread adoption across enterprises.
-
June 2024- Creatio, a no-code CRM and workflow automation platform, raised USD 200 million in a funding round led by Sapphire Ventures, elevating its valuation to USD 1.2 billion. This investment underscores the growing investor confidence in specialized low-code platforms targeting specific business functions.
-
May 2024- Nintex, an automation / workflow / process intelligence vendor, acquired Skuid (a low-code application development platform). Skuid’s strength is enabling business teams to build custom UIs and complex workflows without code. This acquisition gave Nintex stronger front-end app capability in low-code, combining it with its backend automation tools.
What are the Key Factors Influencing Investment Analysis & Opportunities in the Low-code Application Platform Market?
The low-code application platform market is drawing steady investor attention as organizations seek faster and more efficient ways to build applications. Startups offering AI-driven automation and enterprise-grade scalability are especially attractive, with funding rounds often directed toward platforms that reduce reliance on scarce IT talent. Investors see strong growth potential in LCAP because it aligns with the universal demand for digital transformation across industries.
Investment activity is particularly strong in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, where enterprises are rapidly adopting low-code to modernize systems and streamline operations. Countries like the U.S. and India are becoming hubs for both innovation and deployment, making them hotspots for capital inflows.
Strategic acquisitions by larger software companies also indicate consolidation as a key growth path. For investors, the most promising opportunities lie in platforms that combine low-code with AI capabilities, strong compliance features, and adaptable ecosystems to serve diverse global markets.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
Next Move Strategy Consulting (NMSC) presents a comprehensive analysis of the low-code application platform market, covering historical trends from 2020 through 2024 and offering detailed forecasts through 2030. Our study examines the industry at global, regional, and country levels, providing quantitative projections and insights into key growth drivers, challenges, and investment opportunities across all major Low-Code Application Platform segments.
Report Scope:
|
Parameters |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 49.43 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 215.97 Billion |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 34.3% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Analysis Period |
2024–2030 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2030 |
|
Market Size Estimation |
Billion (USD) |
|
Growth Factors |
|
|
Companies Profiled |
15 |
|
Countries Covered |
28 |
|
Market Share |
Available for 10 companies |
|
Customization Scope |
Free customization (equivalent to up to 80 analyst-working hours) after purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Approach |
In-depth primary and secondary research; proprietary databases; rigorous quality control and validation measures. |
|
Analytical Tools |
Porter's Five Forces, SWOT, value chain, and Harvey ball analysis to assess competitive intensity, stakeholder roles, and relative impact of key factors. |
Key Market Segments
By Offering Type
-
Platform Core / Solution
-
Services
By Platform Type
-
No-Code Platforms
-
Low-Code Platforms
-
Pro-Developer Low-Code
By Organization Size
-
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
-
Large Enterprises
By Deployment Mode
-
Public Cloud
-
Private Cloud
-
On-Premises
By Application Type
-
Web-Based Applications
-
Mobile-Based Applications
-
Desktop / Server-Side Applications
-
API-Centric / Microservices-Enabled Apps
By Industry Vertical
-
Banking Financial Services Insurance (BFSI)
-
Government and Public Sector
-
Healthcare and Life Sciences
-
Manufacturing
-
Education
-
Retail and Ecommerce
-
Telecommunications / IT / Infrastructure
-
Others
Geographical Breakdown
-
North America: U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
-
Europe: U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Netherlands, and Rest of Europe.
-
Asia Pacific: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Indonesia, Vietnam, Australia, Philippines, and Rest of APAC.
-
Middle East & Africa (MENA): Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Israel, Turkey, Nigeria, South Africa, and Rest of MENA.
-
Latin America: Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, and rest of LATAM
Conclusion & Recommendations
Our report equips stakeholders, industry participants, investors, policy-makers, and consultants with actionable intelligence to capitalize on Low-Code Application’s transformative potential. By combining robust data-driven analysis with strategic frameworks, NMSC’s Low-Code Application Platform Market Report serves as an indispensable resource for navigating the evolving landscape.

















 Speak to Our Analyst
Speak to Our Analyst
























