How Advanced Tech is Shaping 3D Printing
Published: 2025-09-16

In today's fast-paced industrial world, implementing flexible and responsive production methods is critical. 3D printing, also called as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing product design prototyping and even industrial manufacturing. It became an essential technology across various industries such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods for creating complex structures. This technology also reduces waste materials in production processes and speeds up the production time.
Modern additive manufacturing systems are integrated with these advanced technologies to utilize smart sensors and connectivity to improve capabilities. These technologies include real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. They lead to a reduction in costs while improving the quality of products. Among the most exciting advancements are innovations such as nano-scale 3D printing, 4D printing, artificial intelligence (AI), and bioprinting. This blog explores how additive manufacturing has brought transformation in various industries, providing advantages, latest progressions, and prospects across various sectors. Let us look into them.
1. Nano-Scale 3D Printing
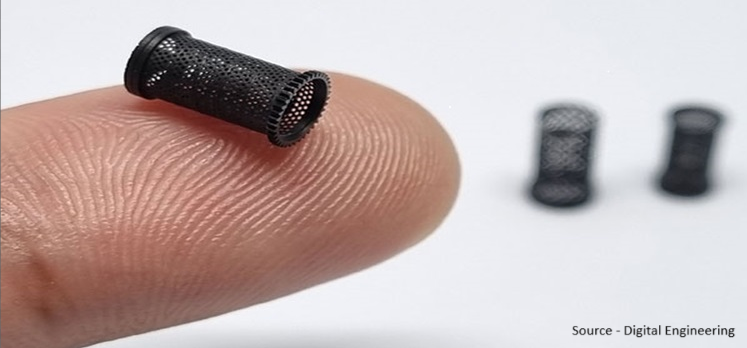
The emerging field of nanoscale 3D printing aims to expand the boundaries of additive manufacturing by producing structures with sizes as tiny as a fraction of a human hair's width. Researchers are overcoming challenges in this field by creating innovative materials. One such material is a new composite developed at Stanford University that incorporates metal nanoclusters to form small lattices that are both strong and lightweight. Innovations in printing methods such as the Multiphase Direct Ink Writing technique developed at Arizona State University are facilitating quick and accurate nanoscale 3D printing. These technologies create a wide range of applications, ranging from improved lightweight protection in satellites and microelectronics to major breakthroughs in biomedical engineering in which precise control over nanoscale materials is essential. In the future, we anticipate to witness more advancements in nanoscale 3D printing as the field progresses.
2. 4D Printing
4D printing is an advanced technology that enables objects to alter their shape and characteristics over time in reaction to the external factors, such as temperature, moisture, or electric current. One of the leading manufacturers of 3D printers and filaments Zortrax and the European Space Agency (ESA) created 4D printing technology for the space sector. The goal of the project was to develop lightweight structures such as antennas and sensors that can be deployed without requiring additional deployment mechanisms. The completion of this project creates chances for Zortrax to work on more advanced projects with ESA, enhancing 4D printing technology and preparing electrically-activated 4D printed parts for space missions. This transforms the way deployable structures are created and utilized in the space sector, allowing more efficient, lightweight, and versatile options for different space uses than before.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is changing the landscape of 3D printing as every stage of the manufacturing process incorporates AI technology. Aibuild, a top provider of AI-based software for additive manufacturing, released an updated version of its platform. This new version integrates the entire manufacturing process in a single AI-powered cloud platform. It has features including, full automation, an AI copilot for autonomous suggestions and actions, compatibility with a wider range of AM hardware and materials, and easy cloud access. AI algorithms are able to efficiently assess the 3D model, constantly compare it to the printing process, and make immediate changes to improve the result. This has been demonstrated through the collaboration of Aibuild with WASP. This collaboration aims to incorporate WASP's CEREBRO hardware as a digital twin on the Aibuild platform. This integration of AI and 3D printing will revolutionize the 3D printing sector, leading to advancements, improved functionalities, and increased flexibility to address the changing needs.
4. Bioprinting
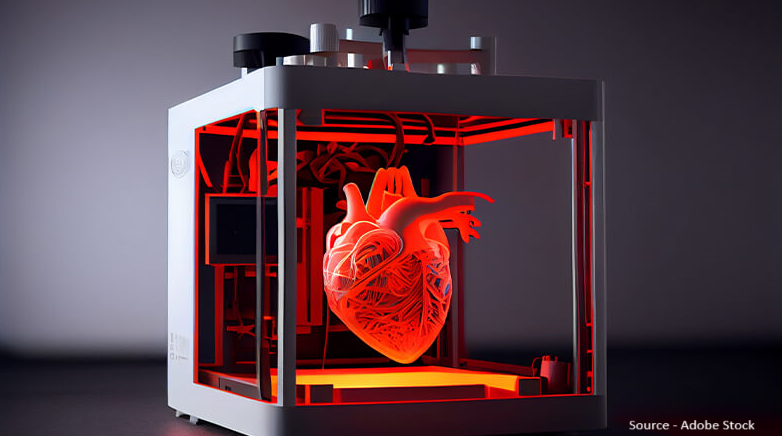
3D bioprinting, a new technology utilizing 3D printing methods to create tissue structures using cells, biomaterials, and biological components, is transforming the organ transplant industry. The ARPA-H PRINT program is a major advancement in the field as it uses 3D bioprinting to produce customized and immune-matched organs as needed. At present, there is a critical lack of donor organs, with more than 120,000 individuals waiting and only 45,000 transplants taking place yearly in the U.S. The PRINT program aims to combat this issue by creating kidneys, livers, and hearts using the patient's cells or a biobank. This eliminates the necessity for immunosuppressive medications and increases organ accessibility. If it proves to be effective, this new method of using 3D bioprinting has the potential to revolutionize organ transplants and have a significant impact on the medical field by cutting down on waiting periods and preserving lives. The main elements of 3D bioprinting, such as pre-bioprinting, bioprinting, and post-bioprinting, will be essential for the success of the PRINT program. This technology is a major advancement that can revolutionize the organ transplant market and enhance patient results.
Applications across Different Industries
The development of nano-scale 3D Printing, bioprinting, AI, and 4D printing in additive manufacturing has greatly influenced the progress in different sectors. Nano-scale 3D printing allows the creation of tiny precise components that are intricate, transforming electronics, photonics, and medical devices in return. Through this technology, highly detailed circuits, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), and implants can be produced. They lead to the advancement of wearable technology, telecommunications, and minimally invasive surgical procedures. It also promotes creativity within drug delivery systems and diagnostic tools, which contributes to effective and personal healthcare solutions at any point in time.
The technology further promotes the industry growth through the improvement of product functions and efficiency with the help of 4D printing, AI, and bioprinting. 4D Printing brings in self-modifying materials that adjust in reaction to triggers, enhancing effectiveness and durability in industries, such as aerospace & aviation, automobile, and textile. AI is transforming the additive manufacturing process by cutting down defect identification time and introducing effective preventive maintenance to lower production expenses and enhance product quality. Bioprinting is transforming healthcare and pharmaceuticals by allowing customized treatments and the experimentation of new drugs and treatments. These technologies are driving the growth and advancement of a new era of innovation and sustainable development.
Future Outlook:
In the future, AI and IoT integration in additive manufacturing will pave the way for an evolutionary and revolutionary change. Based on trends observed over the past year, improvements in AI-based design engineering and IoT-based real-time monitoring of assets will further extend engineering improvement and product differentiation in the future. With the advancement of technologies, the utilization of additive manufacturing as a strategic tool in supply chain networks is poised for higher levels of adoption in the global marketplace.
The focus will remain on the on-demand production and sustainability. Technological improvements in the field of bioprinting and personalized medicine will lead to the transformation of the medical sector. Similarly, architectural breakthroughs would lead to the transformation of cities. AI will be very critical to both education and research through its ability to advance the prototyping process and open possibilities for creativity. In conclusion, innovative AM backed up by AI and IoT is expected to revolutionize industries, open up new avenues, and create a strong foundation for sustainable smart manufacturing in the years ahead.
Furthermore, adopting just-in-time inventories and automating logistics through digital transformation will reduce the costs associated with storage, transportation, and warehousing, thereby increasing profits and competitiveness. The future of 3D printing lies in the continued optimization of the technology in terms of efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability. By embracing this digital integration, companies will be well-positioned to scale up for new markets, align with changing customer needs, and focus on global manufacturing competition.
About the Author
 Supratim Bhowmick is a passionate and highly enthusiastic researcher with over two and a half years of experience. He is dedicated to assisting clients in overcoming challenging business obstacles by providing actionable insights through exhaustive research. Supratim has a keen interest in writing articles and blogs, along with content writing. He consistently endeavors to deliver valuable perspectives in these areas. In addition to his research work, Supratim enjoys traveling and engaging in various sports during his leisure time.
Supratim Bhowmick is a passionate and highly enthusiastic researcher with over two and a half years of experience. He is dedicated to assisting clients in overcoming challenging business obstacles by providing actionable insights through exhaustive research. Supratim has a keen interest in writing articles and blogs, along with content writing. He consistently endeavors to deliver valuable perspectives in these areas. In addition to his research work, Supratim enjoys traveling and engaging in various sports during his leisure time.
About the Reviewer
 Sanyukta Deb is a seasoned Content Writer and Team Leader in Digital Marketing, known for her expertise in crafting online visibility strategies and navigating the dynamic digital landscape. With a flair for developing data-driven campaigns and producing compelling, audience-focused content, she helps brands elevate their presence and deepen user engagement. Beyond her professional endeavors, Sanyukta finds inspiration in creative projects and design pursuits.
Sanyukta Deb is a seasoned Content Writer and Team Leader in Digital Marketing, known for her expertise in crafting online visibility strategies and navigating the dynamic digital landscape. With a flair for developing data-driven campaigns and producing compelling, audience-focused content, she helps brands elevate their presence and deepen user engagement. Beyond her professional endeavors, Sanyukta finds inspiration in creative projects and design pursuits.















Add Comment