Mexico Waste Management Market by Waste Type {Hazardous Waste (Solid Waste, Liquid Waste, Gaseous Waste), and Non-Hazardous Waste (Food, Paper and Cardboard, Plastic, Glass, Metal, Water, E-Waste, and Others)}, by Service {Collection (Collection and Transportation, Storage and Handling, Sorting), and Disposal (Open Dumping, Landfills, Recycling, and Others)}, by Source (Residential or Municipal Waste, Commercial Waste, and Industrial Waste) – Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2024–2030
Industry: Energy & Power | Publish Date: 17-Oct-2025 | No of Pages: 94 | No. of Tables: 128 | No. of Figures: 73 | Format: PDF | Report Code : EP1242
Mexico Waste Management Market Overview
The Mexico Waste Management Market size was valued at USD 18.75 billion in 2023 and is predicted to reach USD 30.47 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 6.1% from 2024 to 2030.
The Mexico waste management, also known as waste treatment or handling market involves a wide range of services and activities aimed at managing and mitigating the impact of waste generated by various sectors including residential, commercial, and industrial. It includes the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, and disposal of waste materials in a manner that is environmentally responsible and sustainable.
The market also involves the development and implementation of technologies and practices that promote waste reduction, resource recovery, and the safe handling of hazardous materials. Key components of the waste management market include waste collection services, recycling facilities, waste-to-energy plants, landfill operations, and environmental consulting services. As awareness of environmental issues grows, the waste management market continues to expand, driven by growing population and increasing public demand for sustainable waste solutions.
Urban Expansion Driving the Need for Scalable Mexico Waste Management Systems
Mexico’s rapid urban growth is transforming the dynamics of its waste management landscape. As cities expand and urban populations rise, the generation of solid waste becomes increasingly complex, encompassing a wide variety of waste streams from households, businesses, and infrastructure development. This surge in urban waste challenges existing collection and disposal frameworks, pushing municipalities and private operators to modernize their systems. Urban zones, often densely populated and resource-constrained, demand smart, efficient solutions such as digital tracking of waste, automated segregation, and decentralized processing units. In response, there’s a growing push toward enhancing municipal capabilities with integrated waste management systems, aiming to ensure cleaner cities and more sustainable urban living environments.
Policy Backing and Circular Economy Drive Waste Management Growth
Mexico’s regulatory landscape actively supports the evolution of its waste management sector. National action plans and sustainability frameworks have laid the foundation for a transition from landfill-dependent systems to resource-efficient, circular practices. A robust focus on recycling and resource recovery is encouraging municipalities and enterprises to invest in modern waste segregation and processing technologies. These efforts are further reinforced by government mandates promoting product lifecycle responsibility, which has led to the creation of structured recycling channels across urban and semi-urban regions. As a result, there is increasing demand for waste management services that go beyond basic disposal—encompassing reuse, material recovery, and value-chain optimization.
Stringent Regulatory Framework creates Operational Roadblocks for Mexico Waste Management Companies in Mexico
Mexico’s waste management sector is governed by a layered and increasingly rigorous regulatory environment, driven by national sustainability goals and environmental protection mandates. Key frameworks such as the Ley General para la Prevention y Gestion Integral de los Residuos (LGPGIR), state-specific waste levies, and circular economy strategies require companies to comply with strict guidelines on waste classification, hazardous waste handling, extended producer responsibility, and ambitious recycling and diversion targets.
While these regulations aim to enhance environmental outcomes, they often impose significant administrative and operational burdens on market players. Obtaining permits, adhering to reporting requirements, and investing in compliant infrastructure can be time-consuming and costly—particularly for small and mid-sized operators. The frequent updates to waste-related policies and localized regulatory discrepancies further complicate nationwide service delivery. This complex and demanding compliance landscape slows down the rollout of advanced waste processing technologies and limits the ability of businesses to scale operations swiftly, ultimately hindering overall market dynamism.
Adoption of Waste-to-energy Technologies creates Future Growth Opportunities in the Market
Mexico’s waste management sector is witnessing a strategic shift with the increasing integration of waste-to-energy (WTE) technologies such as incineration, anaerobic digestion, and gasification. These solutions play a vital role in transforming non-recyclable municipal and industrial waste into usable forms of energy, helping to reduce the pressure on overburdened landfills.
This transition aligns closely with Mexico’s National Waste Policy Action Plan, which emphasizes circular economy principles and encourages sustainable waste treatment alternatives. Several state-level initiatives are reinforcing this momentum by setting clear targets for reducing landfill dependency and promoting the recovery of organic and high-energy-content waste.
By Waste Type, MSW Holds the Predominating Share in the Mexico Waste Management Industry
Municipal solid waste (MSW), commonly known as household waste includes the everyday items discarded by the public, including food scraps, packaging, yard waste, and household items. Household waste is primarily non-hazardous while industrial waste includes hazardous materials and bulky industrial by-products.
As per research conducted by Next Move Strategy consulting, household waste is the dominating and fastest growing segment in waste type. Around 76% of waste collected in Mexico is generated from household waste.
In contrast to industrial waste that demands specialized handling and treatment due to its diverse and often hazardous composition. Household waste management emphasizes convenience, community participation in recycling efforts, and environmental stewardship through waste reduction and resource recovery initiatives.
By Disposable & Treatment, Composting is Projected to Witness the Highest CAGR Growth Until 2030
Composting involves the biological decomposition of organic waste materials, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, into nutrient-rich compost through microbial activity. Its feature lies in producing a beneficial soil amendment while diverting organic waste from landfills.
According to the analysis of the Next Move Strategy Consulting, composting disposal treatment is the fastest growing segment in the disposal treatment segment with a projected CAGR of 8.9% by 2030.
The advantage of composting is its ability to reduce methane emissions compared to controlled and uncontrolled landfills. However, it requires space, proper management to avoid odor issues, and specific environmental conditions for effective decomposition.
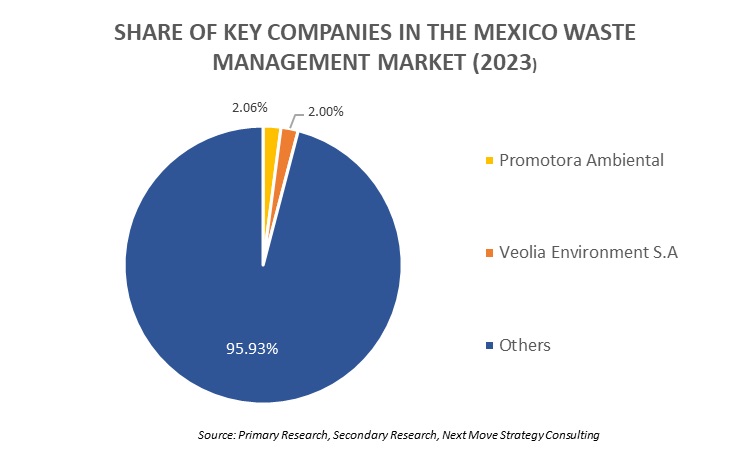
Competitive Landscape
The promising key players operating in the global Mexico waste management industry include Pasa, Broquers Ambiental (Cemex), Veolia, Clean Harbors, Inc, Vls Environmental Solutions, LLC, Mrs, Seche, Comercializadora Century Recycling, Tecnosilicatos De Mexico Sa De CV, Petstar, Cleanmex, Protoss Metales, Remeta S.A. De C.V., Triumvirate Environmental, and Wess Corporate Sa De CV.
These players are engaged in various business expansion merger across various regions to maintain their dominance in the Mexico waste management market.
|
DATE |
COMPANY |
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS |
|
Nov-23 |
PetStar |
PetStar expanded its PET bottle recycling capacity from 58 kilotons per year to 110 kilotons per year by investing USD 167 million. This investment aims to recover and recycle every Coca-Cola PET bottle sold in Mexico by 2027. |
|
Mar-22 |
Veolia |
Veolia North America merged with Suez to form a single entity company while impacting the waste management industry across North America. The merger enhances capabilities in waste management, energy efficiency, and water reclamation, pivotal for advancing environmental goals and supporting carbon neutrality targets by 2030, benefiting municipalities and industries region-wide. |
Mexico Waste Management Market Key Segments
By Waste Type
-
Hazardous Waste
-
Solid Waste
-
Liquid Waste
-
Gaseous Waste
-
-
Non-Hazardous Waste
-
Food
-
Paper and Cardboard
-
Plastic
-
Glass
-
Metal
-
Water
-
E-Waste
-
Others
-
By Service
-
Collection
-
Collection and Transportation
-
Storage and Handling
-
Sorting
-
-
Disposal
-
Open Dumping
-
Incineration/Combustion
-
Landfills
-
Recycling
-
Composting and Anaerobic Digestion
-
By Source
-
Residential or Municipal Waste
-
Commercial Waste
-
Offices and Retail Stores
-
Hospitals
-
Restaurants
-
Other Commercial Sources
-
-
Industrial Waste
-
Manufacturing Waste
-
Construction, Renovation, and Demolition Waste
-
Agriculture Waste
-
Medical Waste
-
Other Industrial Sources
-
Key Players
-
Pasa
-
Broquers Ambiental (Cemex)
-
Veolia
-
Clean Harbors, Inc
-
Vls Environmental Solutions, LLC
-
Mrs
-
Seche
-
Comercializadora Century Recycling
-
Tecnosilicatos De Mexico Sa De CV
-
Petstar
-
Cleanmex
-
Protoss Metales
-
Remeta S.A. De C.V.
-
Triumvirate Environmental
-
Wess Corporate Sa De CV
Report Scope and Segmentation
|
Parameters |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2023 |
USD 18.75 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 30.47 Billion |
|
Value Growth Rate |
CAGR of 6.1% from 2024 to 2030 |
|
Analysis Period |
2023–2030 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024–2030 |
|
Market Size Estimation |
Billion (USD) |
|
Growth Factors |
|
|
Companies Profiled |
15 |
|
Market Share |
Available for 10 companies |
|
Customization Scope |
Free customization (equivalent up to 80 working hours of analysts) after purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional, and segment scope. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |




















 Speak to Our Analyst
Speak to Our Analyst

























