Innovative Technologies Reshaping the Disabled & Elderly Assistive Device
Introduction
Assistive technology includes devices, equipment, gadgets, or systems specially designed or adapted to support individuals, particularly older people or those with disabilities. This technology helps them in carrying out and executing various tasks. Its purpose is to ensure self-sufficiency and elevate overall quality of life. According to the World Health Organization, about 15% of the world's population suffers from some sort of disability. This technology involves a diverse range of tools, technologies, and software applications tailored to aid individuals with physical, sensory, cognitive, or developmental challenges.
Its goal is to surmount obstacles and facilitate greater participation and inclusion across various facets of life. With the global population rapidly increasing, the elderly demographic is also expanding significantly. This, in turn, presents a substantial opportunity for the assistive technology industry. As per the most recent data presented by Visual Capitalist, in 2022, the global population of individuals aged 65 and above stood at 771 million, constituting 10% of the world's populace. Projections indicate an anticipated increase to 16% by 2050 and a substantial rise to 24% by 2100.
Advancements Revolutionizing the Assistive Technology Industry
Advanced technologies have been implemented to enhance the independence and quality of life for individuals with disabilities and older people. Noteworthy advancements in this field include:
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices facilitate the interconnection and communication of diverse assistive tools, establishing a network that can be managed and supervised from a distance. This includes intelligent home setups, mobility aids, artificial vision systems, interactive sign language, home automation, and linked insoles. Through IoT, the lives of individuals with disabilities are undergoing transformative changes, enabling them to attain their objectives and dismantle societal impediments.
For example, Abode Systems, known for crafting do-it-yourself (DIY) home security systems, revealed a new integration with Google Nest products on its platform. This enhancement enables Abode users to manage their Nest devices, including thermostats, cameras, and doorbells, through the Abode app. The integration of Google Nest products into Abode's platform marks a substantial advancement, particularly beneficial for disabled and elderly individuals. This incorporation simplifies home control for people with disabilities and older adults, facilitating voice commands or gestures for seamless operation.
Wearable Devices: Wearable technology, including smartwatches, fitness trackers, and medical alert systems, are becoming more custom-made to meet the specific requirements of disabled and elderly individuals. These wearable devices provide a collection of features that prove invaluable for this demographic, including monitoring vital signs, tracking physical activity, offering medication reminders, and detecting falls. They guarantee swift aid and proactive healthcare oversight. For example, Medical Guardian, a prominent provider of medical alert systems, recently introduced the MGMove smartwatch. Designed with disabled and older adults in mind, it offers a stylish and user-friendly means to stay secure and connected.
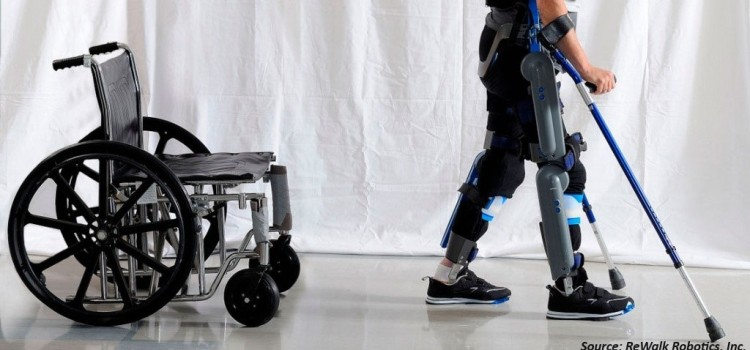
Robotics: Robotics technology holds substantial promise within the realm of assistive technology. Cutting-edge robotic devices, including exoskeletons, can aid individuals with mobility challenges, enabling them to walk or carry out physical tasks autonomously. Additionally, robot companions, including social robots, offer emotional support, help with everyday tasks, and alleviate loneliness, particularly benefiting elderly individuals. For example, Labrador Systems, a robotics company headquartered in California, commenced the deployment of its Retriever Pro robots to a selected group of initial clients. The Retriever Pro is a mobile robot designed to aid older adults in tasks, including retrieving groceries, collecting medications, and offering companionship.
Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR): Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) hold the promise of transforming the landscape of assistive technology. These technologies are progressively utilized to augment accessibility, rehabilitation, and the overall quality of life for individuals with disabilities. Specifically, AR and VR prove particularly advantageous for those with visual impairments. As per statistics provided by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and the American Foundation for the Blind (AFB), nearly half of American adults perceive vision loss as the most significant health issue. Over 23 million adults in the U.S. encounter challenges with their vision, even while utilizing corrective aids, such as glasses or contact lenses.
Companies, such as IrisVision and Acesight, are introducing pioneering offerings personalized for individuals with visual impairments. These products leverage advanced technology to augment vision and offer support. For instance, IrisVision electronic glasses demonstrate the state-of-the-art assistive technology. They hold registration with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a Class-1 medical device. These glasses redefine the paradigm of wearable low-vision aids by integrating a Samsung VR headset with a smartphone.
IrisVision is designed to assist individuals coping with a range of eye conditions, encircling macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, cataracts, and retinitis pigmentosa. The company's device integrates a smartphone, virtual reality headset, and sophisticated algorithms to enable individuals with compromised vision to see and read clearly. It is suitable for use by individuals with visual acuity as low as 20/1000.
Additionally, Acesight, a recent addition to Zoomax's range of wearable low-vision aids, employs augmented reality technology to present a high-definition display that hovers in front of the user's eyes. The device is linked to a controller via a wire, granting the user the ability to personalize the colors and contrast of the display. Acesight is crafted to assist individuals with low vision conditions, such as macular degeneration, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy, which can magnify objects up to 15 times.
Conclusion
Assistive technology is profoundly transforming the lives of individuals with disabilities and older adults and introducing inventive solutions that amplify independence and overall well-being. The escalating numbers of individuals with disabilities and the aging demographic fuel the demand for assistive technology. Breakthroughs in domains such as the Internet of Things (IoT), wearable devices, robotics, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) are granting individuals facing disabilities and older individuals improved access, mobility, and assistance. These technologies are reshaping the execution of tasks, advancing social integration, and elevating the overall standard of living for these individuals. As assistive technology continues its progression and innovation, it is poised to assume a pivotal role in nurturing inclusiveness and constructing a more universally accessible society.
About the Author
 Shyam Gupta is a passionate and highly enthusiastic researcher with more than four years of experience. He assists clients in overcoming difficult business challenges by providing actionable insights through exhaustive research. He has closely monitored several industries, such as ICT & Media, Robotics, and Electric Vehicles. He has a keen interest in writing articles and uses blogs as a medium to share his thoughts. He spends his time reading and painting when not keeping up with industry news. The author can be reached at shyam.gupta@nextmsc.com
Shyam Gupta is a passionate and highly enthusiastic researcher with more than four years of experience. He assists clients in overcoming difficult business challenges by providing actionable insights through exhaustive research. He has closely monitored several industries, such as ICT & Media, Robotics, and Electric Vehicles. He has a keen interest in writing articles and uses blogs as a medium to share his thoughts. He spends his time reading and painting when not keeping up with industry news. The author can be reached at shyam.gupta@nextmsc.com

Leave a Reply