Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market By Scrap Source (Post-Consumer (Old), and Post-Industrial (New) Scrap), By Alloy Type (Wrought Alloy, and Casting Alloy), By Recycled Form (Billets/Logs, Ingots, Pellets/Granules and Sheets/Rolls), By End-User Industry (Packaging, Transportation (Automotive and Aerospace & Defense), Building & Construction, Electrical & Electronics, Machinery & Equipment, and Others) – Global Analysis & Forecast, 2025–2030
Industry Outlook
The global Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market size was valued at USD 5.18 billion in 2024, and is expected to be valued at USD 5.64 billion by the end of 2025. The industry is projected to grow, hitting USD 8.58 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 8.7% between 2025 and 2030.
Aluminum UBC scrap recycling stands at the forefront of sustainable industrial practices, reshaping material lifecycles, revolutionizing resource management, and redefining the way we view waste. This essential sector of the circular economy focuses on developing efficient processes capable of transforming discarded beverage cans into valuable raw material, simulating a continuous loop of resource utilization.
From advanced sorting technologies and energy-efficient melting to strategic collection networks and closed-loop manufacturing, UBC recycling's applications are diverse and far-reaching, promising to transform the way we consume, produce, and engage with the environment around us. As this industry continues to advance rapidly, its potential to drive progress and shape a more sustainable future is both exciting and profound.
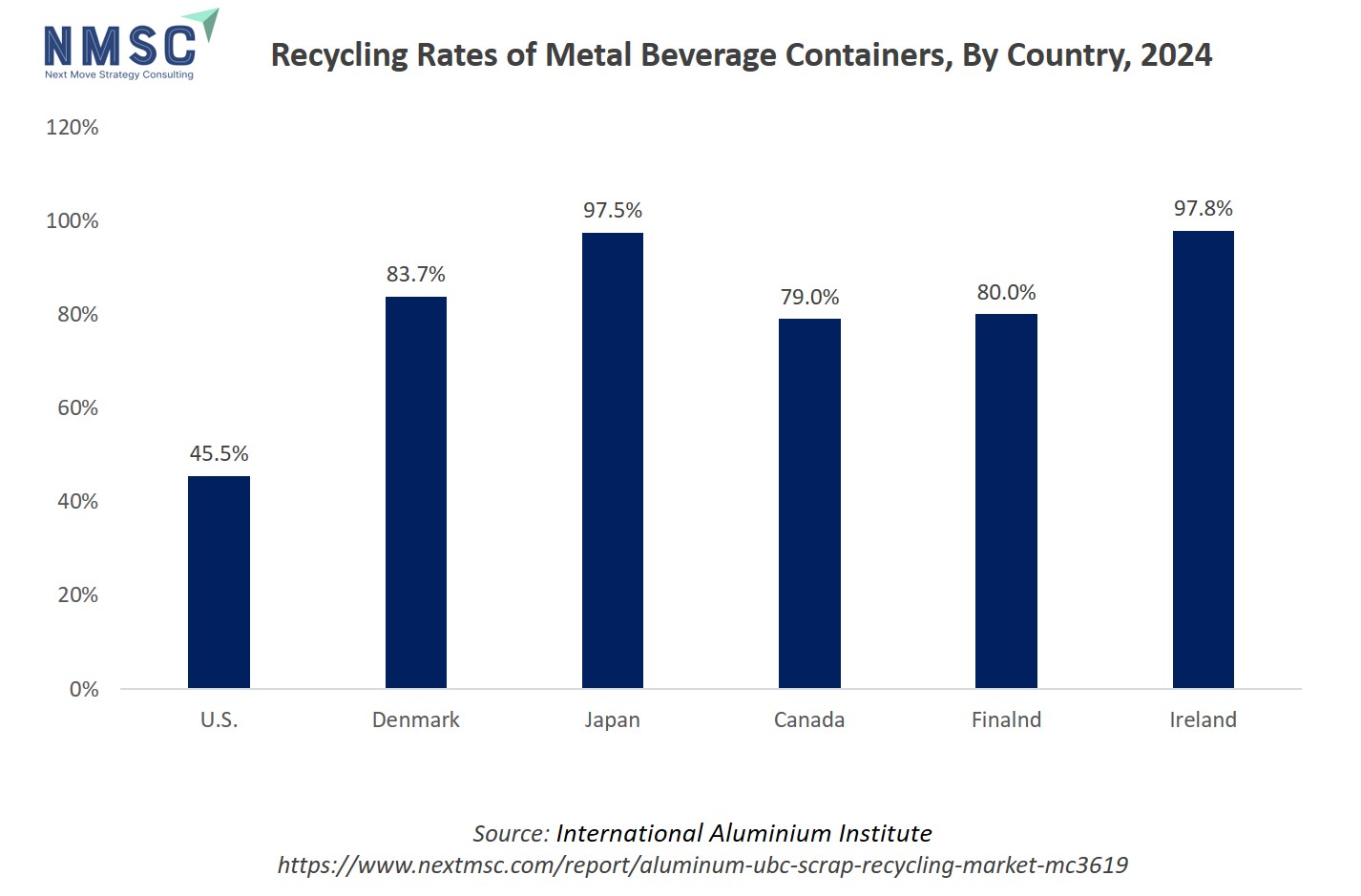
The above chart shows the percentage of metal beverage containers separated for recycling in 2024 across six countries, with Ireland (97.8%) and Japan (97.5%) achieving the highest separation rates, followed by Denmark (83.7%), Finland (80.0%), and Canada (79.0%), while the U.S. lags at just 45.5%. This significant variation impacts the aluminum Used Beverage Can (UBC) scrap recycling market, as higher separation rates directly increase the supply and quality of UBC scrap available to recyclers, thereby fueling the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market growth, enabling efficient recycling operations, and supporting investments in recycling infrastructure; meanwhile, countries like the U.S. with lower rates face constraints in feedstock supply, which can hinder the scale and cost-effectiveness of UBC recycling and limit the environmental and economic benefits that aluminum recycling offers.
What are the Key Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Industry Trends?
How is Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Reducing the Industry’s Carbon Footprint?
Aluminum UBC scrap recycling significantly reduces the industry's carbon footprint by drastically cutting down on energy required. Producing new aluminum from recycled scrap uses approximately 95% less energy compared to raw materials, leading to a 95% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. This makes recycled aluminum a critical component for lowering environmental impact. The efficiency also encourages governments with incentives like low-carbon product credits, pushing companies to certify recycled content under carbon-label programs.
For example, a major player like Novelis demonstrates this impact by recycling over 2.3 million metric tons of aluminum scrap and more than 82 billion used beverage cans each year. This large-scale recycling effort directly contributes to significant carbon emission reductions globally. Companies can then leverage these certifications to secure favourable agreements with beverage brands that are committed to meeting their net-zero carbon goals.
How are Deposit-Return Schemes (DRS) Shaping Global UBC Recovery Rates?
Deposit-Return Schemes (DRS) are critically enhancing global UBC recovery rates by establishing effective collection infrastructures and directly incentivizing consumer participation. The core objective of DRS is to leverage a refundable deposit as a financial driver, compelling consumers to return used beverage cans. This mechanism not only significantly boosts collection volumes but also improves the purity of collected materials, vital for efficient recycling processes.
Indeed, a 2024 International Aluminum Institute assessment highlights that well-structured DRS programs, already operational in the UK, Japan, South Korea, and Spain, can boost UBC collection rates. They published a report recommending deposit-return systems, policy and investment reforms in 140 countries to raise UBC recycling. It estimates that landfilled cans in the U.S. could replace about 18% of U.S. aluminum imports. This has incentivized beverage producers to collaborate with policymakers on deposit levels and reverse-vending infrastructure. Producers and recyclers should engage proactively in DRS policy design to maximize feedstock quality and consistency.
How is Digital Traceability Transforming the UBC Scrap Supply Chain?
Digital traceability is fundamentally reshaping the UBC scrap supply chain by instilling unprecedented transparency and trust throughout its various stages. By enabling precise tracking of materials, from collection to re-melt, it enhances efficiency, ensures quality, and strengthens accountability across the entire value chain. This transformation is pivotal for building confidence in recycled content and optimizing material flows.
According to Resource Recycling, Inc., 2025, traceability tools are a crucial solution to build trust in recycled materials, offering third-party verified proof of content. They significantly enhance the effectiveness of EPR programs, promoting accountability. Key technologies like geospatial solutions and blockchain provide essential supply chain visibility. This global movement is further propelled by initiatives such as Europe's mandatory Digital Product Passports.
How is Aging Infrastructure Impacting Recycling Efficiency in the United States?
Aging infrastructure significantly impedes recycling efficiency in the United States, creating bottlenecks and reducing the overall effectiveness of material recovery. This deterioration manifests in various ways, from outdated sorting machinery that misidentifies materials to unreliable equipment causing operational delays. Consequently, valuable recyclables are often lost to landfills due to contamination or the inability of facilities to process them efficiently.
According to the Aluminum Association, the recycling rate for aluminum beverage cans in the United States was 43%. This represents a decline from the average rate of approximately 52% since tracking began in 1990. The organizations attribute this decrease significantly to aging recycling infrastructure and a passive approach to recycling policy, underscoring the challenges faced in maintaining and improving recycling efficiency.
What are the Key Market Drivers, Breakthroughs, and Investment Opportunities that will Shape the Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Industry in Next Decade?
The aluminum UBC scrap recycling market is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by rising sustainability goals, circular economy adoption, and regulatory pressures. With demand for recycled aluminum growing across packaging, automotive, and construction, collection and processing are accelerating, especially in urban regions with high beverage can consumption. Recyclers are expanding capacities and diversifying technologies to serve small scrap dealers, large processors, and end-use manufacturers, balancing both cost efficiency and high-quality output. At the same time, volatile raw material prices, energy costs, and environmental compliance requirements are shaping strategic choices. The market is witnessing increased collaboration between recyclers, smelters, and packaging companies, with asset-light and partnership-led models emerging as preferred approaches. Technological advances in sorting, shredding, and energy-efficient smelting are redefining operational performance. Despite this progress, profitability challenges and uneven collection rates persist, creating opportunities for innovative business models and investments.
Growth Drivers:
How are Regulatory Mandates Accelerating Recycling Volumes?
Regulatory mandates such as deposit-return systems (DRS) and extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs are significantly boosting aluminum UBC recycling volumes. According to the Container Recycling Institute, implementing a national DRS could increase UBC recycling rates by up to 85%, adding nearly 815,000 more tons of recycled material each year. Organizations like the U.S. Aluminum Association and the Can Manufacturers Institute are actively supporting these policies to establish a consistent, nationwide recycling framework. These efforts are aimed at improving material recovery, reducing landfill waste, and ensuring a steady supply of recycled aluminum for manufacturers.
Country-Wise Government Initiatives for Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market:
|
Country |
Initiative/Policy |
Focus Area |
|
Ireland |
Re-Turn Deposit Return Scheme |
Charges deposit on cans/bottles, refunded on return to boost recycling |
|
United Kingdom |
Joint Policy Statement on DRS |
Sets design and timeline for national deposit return scheme |
|
European Union |
Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation |
EU circularity measures mandate higher recovery and DRS/EPR adoption for cans |
|
Brazil |
Federal Decree No. 12.106/2024 |
Provides fiscal incentives to strengthen recycling value chains |
|
Canada |
Modernised Deposit-Refund Systems |
Expanded eligible containers and infrastructure upgrades to improve UBC collection |
|
India |
Draft Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Rules |
Draft packaging waste EPR rules tighten obligations on producers for can recovery |
How do Federal/State Policy Priorities Enhance Collection and Recycling Infrastructure?
Federal and state policy priorities are playing a critical role in strengthening aluminum UBC recycling infrastructure across the United States. The Aluminum Association’s 2025 policy roadmap emphasizes expanding deposit-return and extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs to support domestic manufacturing, conserve energy, and reduce reliance on imports. States like Oregon and Maine are leading efforts by drafting packaging EPR legislation that includes aluminum beverage cans. These initiatives are not only improving collection rates but also encouraging private investment in recycling systems. The Association also calls for clear, consistent national policies to create a stable supply chain for recycled materials, which is essential for long-term economic and environmental gains.
Growth Inhibitors:
How is Low Material-Collection Density Limiting Supply Continuity?
Low material-collection density directly constrains the supply continuity of UBC scrap for re-melters, acting as a significant restraint on the aluminum recycling industry. This low density refers to the insufficient volume of high-quality UBCs collected per geographic area or per capita, especially in regions relying predominantly on less efficient collection methods like traditional curbside recycling without strong incentives.
What Opportunity Do Advanced Remelting Technologies Offer for Differentiated Value in UBC Recycling??
Advanced re-melting technologies represent a significant opportunity for the aluminum recycling industry, allowing producers to create differentiated value through enhanced product quality, reduced environmental impact, and improved resource efficiency. These innovations are crucial for meeting growing demand for sustainable materials and achieving circular economy goals. A prime illustration of this capability is seen in Constellium's recent achievement of recycling end-of-life commercial jet aluminum into new, high-performance aerospace material. This breakthrough showcases how specialized remelting processes can transform complex scrap into demanding applications, offering superior product quality and a drastic 95% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to primary aluminum. This innovation not only diversifies the market for recycled aluminum but also provides critical, low-carbon solutions for industries like aerospace aiming for greater sustainability.
How the Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market is Segmented in this Report, and What are the Key Insights from Segmentation Analysis?
By Scrap Source Insights
Is Post-Consumer or Post-Industrial Supply Dominating the Market in 2025?
Based scrap source type, the market is segmented into post-consumer UBC scrap and post-industrial UBC scrap.
Post consumer UBC scrap accounts for the majority of feedstock, roughly 60% of total scrap intake globally, driven mainly by packaging streams, while post-industrial scrap supplies the remainder. UBC collection gaps persist: the US recycling rate fell to 43%, whereas jurisdictions with deposit return schemes show much higher recovery; ten DRS states representing 27% of the population account for 515 of cans recycled. Major recyclers raising recycled content targets are increasing demand for post-consumer UBCs.
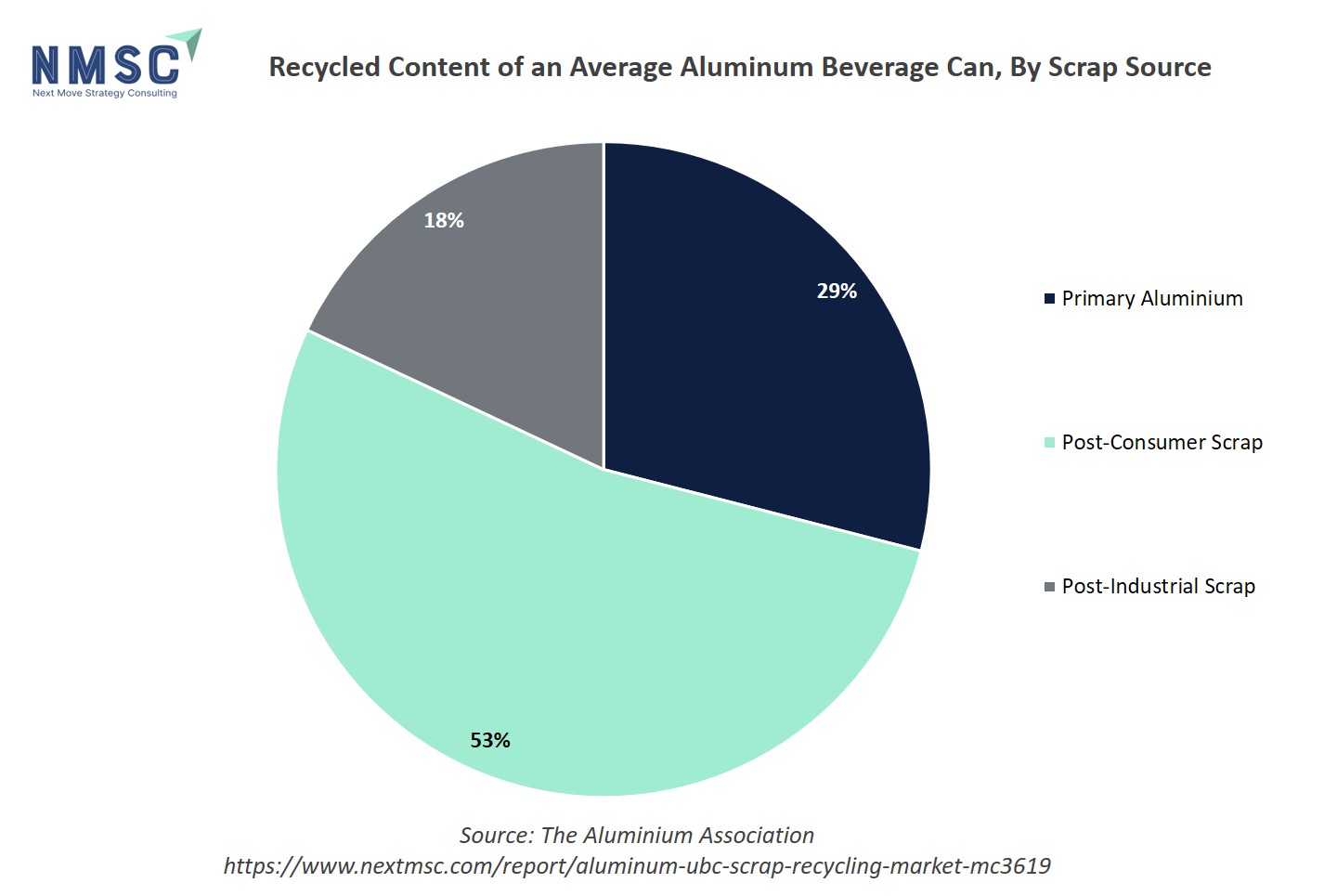
The above chart reveals that an average aluminum beverage can contain 53% post-consumer scrap, 18% post-industrial scrap, and only 29% primary aluminum. This high proportion of recycled content demonstrates the strong circularity and sustainability of aluminum cans, largely due to robust Used Beverage Can scrap recovery and utilisation. The dominance of recycled material lowers production costs, saves substantial energy (up to 80% versus primary production), and encourages continued investment in UBC scrap recycling infrastructure and programs, directly supporting market growth as demand rises for greener packaging and closed-loop supply chains.
By Alloy Type Insights
Which Alloy Type is Driving the UBC Recycling Market in 2025?
Based on alloy type, the market is segmented into wrought alloy and casting alloy.
Wrought-alloy UBCs (can stock) dominate the 2024 UBC recycling stream because pervasive collection systems, deposit-return schemes and the cans’ near-direct remeltability deliver higher, more stable feedstock value for can makers and recyclers. Whereas, Casting alloys remain important as a separate scrap stream (notably from automotive castings that account for ~40–50% of aluminum scrap use) but do not meaningfully form the UBC feedstock.
By Recycled Form Insights
How Does the Recycled Form Influence the UBC Aluminum Scrap Market?
Based on recycled form, the UBC recycling market is segmented into billets/logs, ingots, pellets/granules and sheets/rolls.
Post-collection, UBC scrap is converted into different recycled forms, such as billets/logs, ingots, pellets/granules, and sheets/rolls to meet diverse downstream requirements. Billets and ingots are mainly used in extrusion and rolling processes, offering consistent composition and easy remelting. Pellets and granules provide transport efficiency and uniformity for secondary aluminum producers, while sheets and rolls are often used for direct remelting into new can stock. At present, ingots and pellets dominate the market due to their versatility, ease of handling, and strong demand from canmakers and foundries, whereas sheets/rolls remain limited to niche or specialised applications.
By End-User Industry Insights
Which End-User Industries Drive the UBC Aluminum Recycling Market in 2024?
The end-user industry segmentation includes packaging, transportation, building & construction, electrical & electronics, machinery & equipment and others.
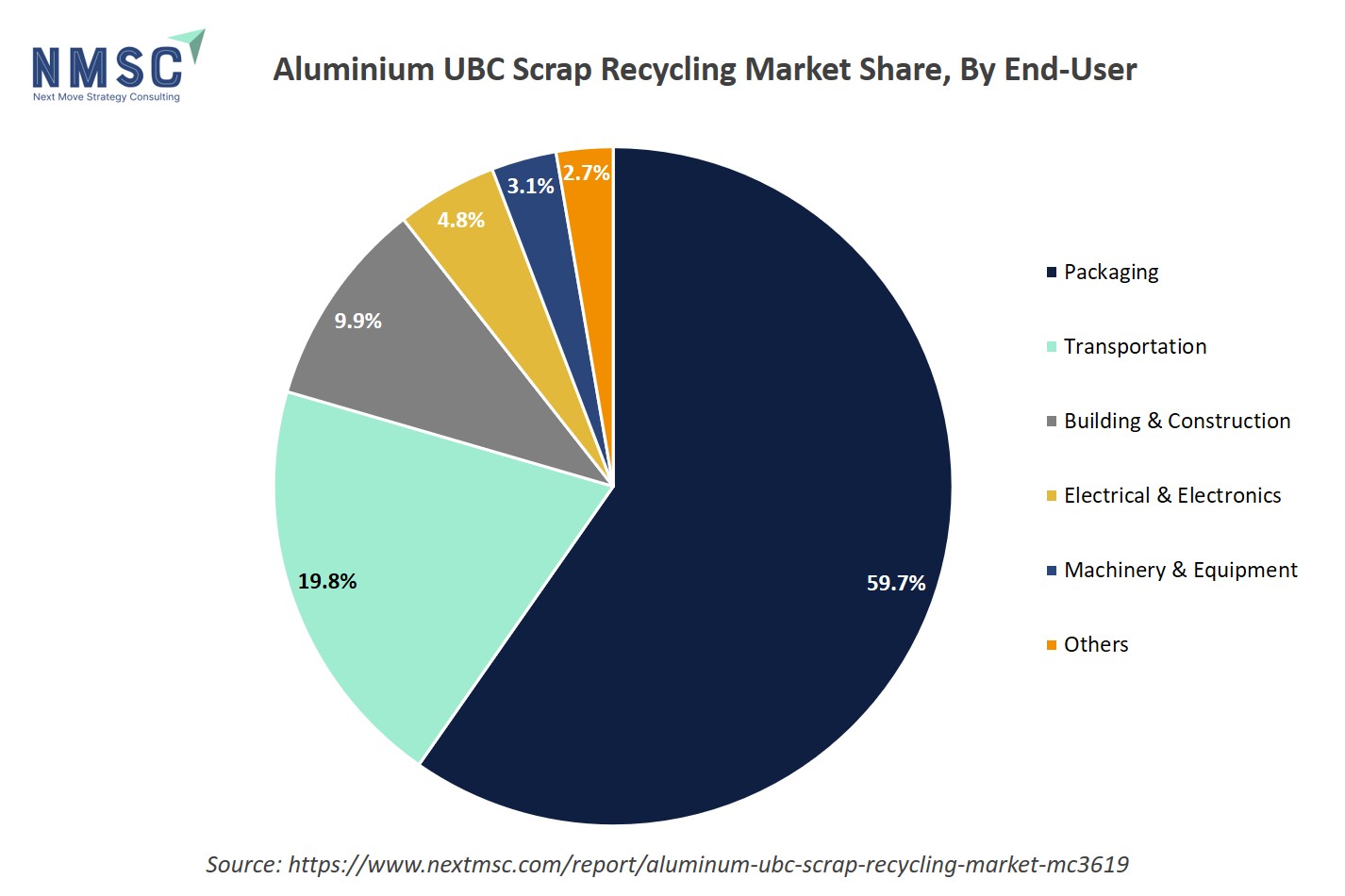
The UBC aluminum recycling market serves a range of end-user industries with varying demand patterns. Packaging is the dominant segment, driven by the extensive use of recycled can stock for beverage cans, supported by established collection systems and high remelting efficiency. Transportation leverages recycled aluminum for automotive parts, aerospace components, and lightweighting initiatives, while building & construction uses sheets, extrusions, and panels for roofing, facades, and structural elements. Electrical & electronics utilize aluminum for wiring, enclosures, and heat sinks. Machinery & equipment and others (consumer goods, specialty products) constitute smaller shares.
Regional Outlook
The market is geographically studied across North America, Europe, the Middle East & Africa, and Asia Pacific, and each region is further studied across countries.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in North America
North America has emerged as a dominant force in the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, driven by its commitment to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. Leading the charge, both the United States and Canada have made public sustainability goals backed by data from respected sources. The Aluminum Association reports that recycling aluminum beverage cans consume just 5 % of the energy required for primary aluminum production, resulting in up to 95 % energy savings, and the U.S. recycling industry saves over 90 million barrels of oil equivalent annually. This unwavering focus on reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions not only strengthens North America's global leadership in aluminum recycling but also positions the region as a model for sustainable industrial practices in the circular economy.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in the United States
The U.S. is strategically enhancing its aluminum UBC recycling ecosystem through industrial-scale investments aimed at revitalizing domestic metal production and boosting material recovery. A prominent example of this movement is Century Aluminum’s Phase 1 award under a Department of Energy grant, highlighting a shift toward modernized, low‑carbon aluminum infrastructure. In March 2024, Century Aluminum was selected by the DOE Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations to receive potential funding of up to USD 500 million as part of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and Inflation Reduction Act. The goal is to build a new green aluminum smelter, the first in over 45 years, leveraging innovative production methods, including significant incorporation of recycled UBC scrap. This investment underscores the U.S. industry’s focus on domestic supply chain resilience, decarbonization, and increased use of recycled materials, all vital to strengthening the aluminum UBC recycling market in America.
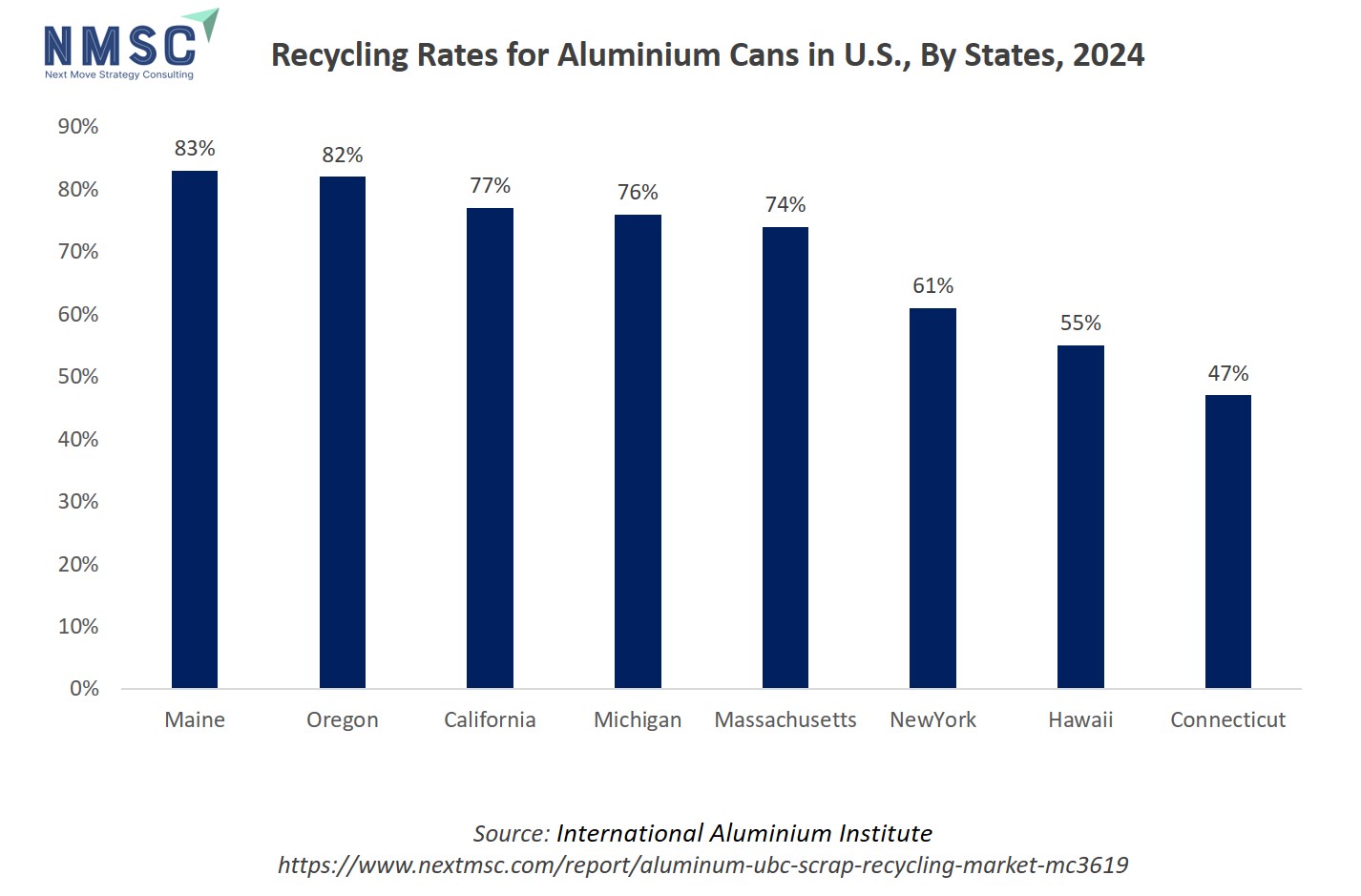
The above chart displays aluminum can recycling rates across various U.S. states in 2024, with Maine (83%), Oregon (82%), California (77%), Michigan (76%), and Massachusetts (74%) leading, while New York (61%), Hawaii (55%), and Connecticut (47%) lag notably behind. States with higher recycling rates provide abundant, high-quality feedstock for the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, supporting efficient recycling operations and economic viability. In contrast, states with lower rates represent untapped potential but also indicate barriers such as lack of infrastructure or incentives. Overall, these disparities directly influence regional strengths and expansion opportunities in the UBC recycling market.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Canada
Canada’s aluminum UBC recycling market is fundamentally driven by province-wide Deposit‑Return Systems (DRS), which place a small refundable deposit on beverage cans. This proven approach materially increases return rates, drastically reducing landfill waste and ensuring a steady flow of high-quality scrap for recyclers. For instance, a 2024 report by Waste and Recycling, highlights that Canadian DRS programs achieved an impressive 76% average return rate for single-use beverage containers in 2023. Within Canada, Alberta led with 85%, followed by Saskatchewan at 84% and British Columbia at 83%. These high return rates illustrate how well-structured DRS programs deliver consistent, clean UBC feedstock, which is essential for maintaining high recycling yields, reducing sorting costs, and minimising environmental impact, all key elements fueling growth in Canada’s aluminum UBC recycling industry.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Europe
The European aluminum UBC scrap recycling industry demonstrates a strong commitment to advancing sustainable practices through significant investment in recycling infrastructure. The region's approach is characterized by a balanced focus on boosting capacity and achieving full circularity, thereby ensuring substantial reductions in carbon emissions. For instance, Novelis's USD 90 million investment in its Latchford facility in the UK serves as a prime example of the region's commitment to boosting its recycling capabilities. This strategic investment is instrumental in creating more robust, localized, and fully circular systems for aluminum UBC scrap.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom's aluminum UBC scrap recycling market maintains a strong position, driven significantly by its high existing recycling performance and proactive industry advocacy. The country emphasizes notable achievements in its aluminum packaging recycling rates, with the beverage can recycling rate maintaining an impressive 81% in 2024, as reported by Alupro (Aluminum Packaging Recycling Organisation). This consistent high performance is supported by ongoing advocacy from industry bodies like Alupro, which actively champions robust policies such as the Deposit Return Scheme (DRS) and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) to further enhance collection and recycling infrastructure across the UK. These combined efforts underscore a robust and forward-looking approach, positioning the UK as a leader in sustainable aluminum UBC scrap recycling industry.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Germany
Germany demonstrates a leading and highly efficient aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, driven significantly by its commitment to technological innovation in sorting, processing, and refining aluminum scrap. For instance, Gerhard Lang Recycling GmbH utilizes TOMRA Recycling's advanced AUTOSORT PULSE system to achieve exceptionally high purity (over 95%, potentially 97%) in sorting aluminum alloy stamping scrap, enabling direct integration into new aluminum production. The country's strategy focuses on maximizing resource efficiency and establishing robust circular economy practices, particularly within its well-established recycling infrastructure.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in France
France demonstrates a rapidly advancing and strategically focused aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, driven significantly by its commitment to technological innovation in sorting, processing, and refining aluminum scrap. A notable example of this advancement is Constellium’s successful deployment of LIBS technology at its Neuf-Brisach recycling facility in France, announced in December 2024. The company reported achieving up to 95% purity in sorting aluminum alloys, commonly used in automotive and industrial applications. This innovation allows Constellium to recycle aluminum scrap without degrading the alloy's integrity, thus preserving its mechanical properties and extending its lifecycle. Such milestone underscores France's role in setting new standards for efficiency and quality in aluminum scrap recycling.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Spain
Spain demonstrates strong progress in the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, driven by early achievement of EU recycling targets. In 2024, the country recycled over 50.7% of total aluminum packaging placed on the market, meeting 2025 EU targets a year ahead of schedule, with nearly 78,297 tonnes of aluminum recovered. This success highlights the impact of civic engagement and well-coordinated selective collection systems in boosting feedstock supply and operational efficiency across the recycling chain.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Italy
Italy showcases an exceptionally advanced aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, driven by its highly efficient and widespread recycling infrastructure. According to CIAL, in 2024, Italy recycled 68.2% of all aluminum packaging surpassing the EU’s 2025 target of 50% and edging beyond the 2030 target of 60% with a 71.7% overall recovery rate including energy recovery, and achieved an 86.3% recycling rate for beverage cans despite a 16% increase in consumption. The robust network of 432 agreements, coverage of 78% population and 70% of municipalities, coupled with strong cooperation among citizens, businesses, and institutions, positions Italy as a leading model in UBC scrap recovery.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, characterized by growing beverage consumption and fast-paced urbanization, which are significantly boosting the generation of aluminum used beverage cans (UBCs). Major economies such as China, India, Japan, and Australia are witnessing an upsurge in on-the-go packaged beverage consumption, especially in dense urban centers, translating to increased UBC recovery potential.
A notable example comes from Australia, where, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, per capita daily consumption of non-alcoholic beverages reached 387.1 mL in 2023–24, marking a 2.4% year-over-year increase. As urbanization trends mirror across other Asia Pacific nations, such consumption patterns are expected to lead to billions of additional cans entering the recycling stream each year. This surge in urban consumption across the Asia Pacific region is expected to serve as a powerful catalyst for scaling aluminum UBC recycling infrastructure, improving material circularity, and advancing the region’s sustainability goals.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in China
The aluminum UBC scrap recycling market in China is undergoing a strategic shift toward advanced secondary aluminum production, supported by international technology partnerships and government-led innovation models. China's rapid industrial development and increasing beverage can consumption have driven a surge in aluminum UBC waste, creating both a challenge and an opportunity for circular economy solutions.
A relevant example of global collaboration comes from the U.S.-based Century Aluminum, which in 2024 received a Phase 1 contract under the U.S. Department of Energy's grant program. This initiative supports low-carbon aluminum projects and has implications for China, where similar industrial decarbonization efforts are being pursued. While this specific project is U.S.-based, China's engagement with international best practices, such as clean aluminum refining and closed-loop UBC recycling, parallels the strategic intent behind such funding efforts.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Japan
Japan stands out as a global leader in aluminum can recycling, driven by one of the most advanced closed-loop systems in the world. The country has consistently achieved near-perfect recycling rates, with the aluminum can recycling rate reaching 99.8% in fiscal year 2024, the highest level ever recorded. This achievement highlights Japan's strong commitment to environmental sustainability and resource efficiency. A central feature of Japan’s success is its can-to-can recycling model, where used beverage cans are remanufactured into new aluminum cans. According to the Japan Aluminum Can Recycling Association, 2024, 75.7% of recycled aluminum cans were reused in can production, marking a major step toward achieving a fully circular economy. This high-efficiency recycling system not only reinforces Japan’s leadership in sustainable resource management but also sets a global benchmark for circular economy practices in the aluminum packaging sector.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in India
India is emerging as a significant player in the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, driven by a series of regulatory and digital initiatives aimed at strengthening its circular economy framework. A key milestone in this journey is the launch of the National Non‑Ferrous Metal Recycling Portal, introduced by the Ministry of Mines in May 2025 as part of the broader National Framework for the recycling of non-ferrous metals. For example, the portal enables end-to-end traceability by connecting producers, recyclers, and collection agencies on a single digital platform, thereby supporting Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) compliance and promoting transparent, accountable trade practices across the aluminum recycling ecosystem.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in South Korea
South Korea has positioned itself as a regional leader in sustainable packaging waste management through the implementation of stringent regulatory frameworks. According to the G20 Global Partnership on Marine Litter, Republic of Korea (2024), the government has introduced EPR to promote sustainable product design, encourage the use of recycled materials, and introduce Extended Producer Responsibility protocols for packaging. This proactive regulatory approach not only strengthens accountability among producers but also creates a more structured and efficient recycling ecosystem, laying a solid foundation for the long-term growth of South Korea’s aluminum UBC scrap recycling industry.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Taiwan
In Taiwan, leading corporations are actively piloting and scaling advanced recycling processes, reshaping the aluminum UBC scrap recycling landscape with industry-driven innovation. For instance, in December 2024, TSMC rolled out its Aluminum Reimagined initiative at the Southern Taiwan Science Park, in partnership with suppliers. The company developed a breakthrough method to precisely separate aluminum from aluminum–plastic packaging bags producing 0.1 ton of 75% purity aluminum and 0.9 ton of recyclable plastic pellets per ton of waste. This initiative not only demonstrates the potential of corporate-led technological innovation in advancing material recovery but also underscores Taiwan’s growing capacity to integrate high-purity aluminum scrap into its circular economy, setting a strong precedent for sustainable industrial recycling practices.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Australia
The exceptional energy and environmental advantages of aluminum recycling have positioned Australia as an emerging leader in sustainable UBC scrap management. Recycling aluminum uses up to 95% less energy than producing it from raw bauxite ore, drastically reducing carbon emissions and operational costs. This energy efficiency not only aligns with Australia's national climate targets but also strengthens the economic case for scaling domestic recycling infrastructure tailored to aluminum beverage cans.
In response to these benefits, key industry players are taking action. For instance, in late 2024, Capral Aluminum partnered with Rio Tinto to launch a closed-loop aluminum recycling pilot at the Boyne Smelter in Queensland. The project aims to incorporate at least 20% recycled aluminum into new billet production, highlighting how energy savings can drive innovation in UBC processing. This strategic alignment of environmental impact reduction with industrial innovation underscores Australia’s growing capability to establish a resilient, energy-efficient aluminum UBC recycling ecosystem, advancing both economic sustainability and global leadership in circular resource management.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in Latin America
Environmental education and community engagement have become powerful drivers of aluminum UBC recycling growth in Latin America, particularly in Brazil. By June 2025, Brazil reported a 100% aluminum can recycling rate, a milestone largely attributed to sustained public awareness campaigns and government-backed capacity-building initiatives. For example, the Recicla Latas program trained 955 municipal officials in 2024, equipping local governments with the tools to implement efficient and decentralized recycling systems. This grassroots-level education not only fosters behavioral change among consumers but also enhances municipal recycling infrastructure, creating a well-informed, participatory culture that sustains high recycling volumes and supports long-term market expansion across the region.
Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market in the Middle East & Africa
Raising public awareness is proving to be a powerful catalyst for the growth of the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market across the Middle East, especially in the UAE. A prominent example is the Every Can Counts campaign, launched in February 2024 by a collaboration between Emirates Global Aluminum (EGA), Crown, and Canpack. The initiative is designed to increase aluminum can recycling rates from approximately 80% by 2030, and to 100% by 2050, according to EGA and EEG. Notably, the campaign was piloted at COP28, where it introduced public recycling incentives and mobile collection bins in high-traffic areas such as parks, shopping malls, and event venues. By focusing on out-of-home consumption streams, the campaign addresses a critical gap in aluminum scrap collection, particularly where beverage cans are often discarded rather than recycled.
This targeted engagement not only educates the public on the environmental and economic value of recycling UBCs but also supports the development of a reliable and clean scrap supply chain in the region, reinforcing long-term market growth for aluminum recycling initiatives in the UAE and across the MEA region.
Competitive Landscape
What are the Top Companies in Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market and How They are Competing Against One Another?
The leaders in the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market include major industry players such as Novelis Inc., Ball Corporation, METALUM SA, Norsk Hydro Brasil, Constellium SE, Alcoa Corporation, Tandom Metallurgical Group Ltd, SA Recycling LLC, Kuusakoski, and others who are shaping the global recycling landscape through advanced processing technologies, circular economy integration, and closed-loop supply chains. These companies are aggressively investing in smelting efficiency, alloy purity enhancement, and can-to-can recycling systems to maximize material recovery while minimizing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
The competitive landscape is defined by strategic collaborations with beverage manufacturers, expansions of recycling facilities, and the deployment of AI-powered material sorting technologies to improve scrap quality and throughput. Companies like Novelis and Ball Corporation are pioneering high-purity UBC recycling through vertical integration, while others such as Real Alloy and Kuusakoski emphasize regional supply chain optimization and sustainable sourcing.
Firms are also increasing investments in decarbonization initiatives, with notable moves such as Alcoa’s zero-carbon aluminum smelting process and Norsk Hydro’s Hydro CIRCAL recycled aluminum line. Strategic acquisitions, capacity expansions in emerging markets, and partnerships with municipal waste management systems further characterize the competitive dynamics. Additionally, these companies are reinforcing their market positions through compliance with ESG standards, digital traceability platforms, and public-private recycling awareness programs, all of which underscore their commitment to environmental stewardship and circular economy leadership.
Market Dominated by Major Players and Specialists
The aluminum UBC scrap recycling market exhibits a complex competitive structure with integrated industrial giants competing alongside specialized regional solution providers. The market demonstrates moderate fragmentation, with large material processing companies leveraging their extensive infrastructure, established supply chain relationships, and integrated production portfolios to maintain dominant positions. These incumbents benefit from significant economies of scale in processing technology, logistical networks, and global distribution capabilities. Meanwhile, specialized players are carving out niches in specific collection methods or regional operations, often focusing on efficient solutions in areas like local aggregation, specialized sorting, or direct industrial supply.
The market is characterized by frequent mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships as companies seek to enhance their material processing capabilities and expand their market presence. Large industrial companies are actively acquiring promising collection and processing firms to access robust supply streams and efficient teams, while also forming strategic alliances with industry-specific partners to develop targeted recycling solutions. The competitive dynamics are further shaped by regional players who leverage their local market knowledge and relationships, particularly in emerging markets where understanding specific regulatory environments and local collection needs is crucial.
Innovation and Adaptability Drive Market Success
Success in the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market requires a combination of Success in the Aluminum Used Beverage Can (UBC) Scrap Recycling market is fundamentally driven by a twin focus on innovation and adaptability. This isn't just about scaling operations; it's about pioneering new techniques and quickly responding to a dynamic environment. Innovation is paramount in developing advanced sorting and separation technologies, crucial for achieving high purity levels from mixed scrap and reducing processing costs. It also extends to optimizing melting efficiencies, designing energy-efficient furnaces, and refining alloying techniques to maximize the value derived from recycled material.
Furthermore, innovative logistical solutions, such as improved compaction methods and optimized collection routes, are essential for managing the inherent bulkiness of UBCs. Beyond technology, adaptability is key to navigating the market's inherent volatility. Companies must flexibly adjust to fluctuating global aluminum prices, evolving regulatory landscapes, and shifts in supply and demand. The ability to pivot quickly to comply with new environmental standards, explore alternative scrap sources, or respond to changing consumer preferences for sustainable products ensures sustained competitiveness. In essence, those who continuously innovate their processes and adapt their strategies to external pressures are the ones who thrive and secure market leadership in this vital sector of the circular economy.
Market Players to Opt for Merger & Acquisition Strategies to Expand their Presence
In the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, Merger & Acquisition (M&A) strategies are pivotal for market players seeking to expand their presence and enhance competitiveness. These strategic moves allow companies to quickly acquire new technologies, secure additional scrap supply chains, and extend their geographical reach. By consolidating operations, firms can achieve greater economies of scale in processing and logistics, reducing costs and improving efficiency. M&As also facilitate the integration of diverse expertise, from local collection networks to advanced material sorting, strengthening overall market position and fostering leadership in the circular economy.
List of Key Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Companies
-
Alcoa Corporation
-
Constellium
-
Granges AB
-
UACJ Corporation
-
AMAG Austria Metall AG
-
Real Alloy
-
Kobe Steel, Ltd.
-
Speira GmbH
-
Stena Metall AB
-
Ye Chiu Group
-
Matalco Inc.
-
CMR Green Technology Ltd
-
Jain Resource Recycling Pvt. Ltd
What are the Latest Key Industry Developments?
-
June 2025 – Constellium, in collaboration with TARMAC Aerosave, achieved a breakthrough in full-circular aluminum recycling for end-of-life aircraft. This significant development showcases their expertise in recycling complex aluminum alloys back into new aerospace materials, reinforcing their broader capabilities in high-value aluminum recycling that could have transferable lessons for UBCs.
-
February 2025 - Norsk Hydro reported in its annual disclosures that it increased post-consumer scrap usage to roughly 451 000 metric tons in 2024 and is on track to expand post-consumer scrap capacity. This demonstrates growing industrial scale uptake of UBC feedstock and supports Hydro’s low carbon product offers. Strategically, the shift underlines competitive advantage from scrap sourcing and processing expertise in meeting customer low carbon requirements.
-
November 2024 – Constellium's new recycling center in Neuf-Brisach, France, qualified its first aluminum coils with Crown Holdings, a major metal packaging leader. This indicates an expansion of their capacity and capability to supply recycled content for the can industry.
-
November 2024 – GME Recycling has developed a revolutionary aluminum decoating system designed to enhance recycling efficiency, particularly for UBCs and other coated aluminum scrap. This closed-loop, auto-thermal system operates with no natural gas usage for organic loads above 5%, significantly reducing energy consumption, lowering costs, and minimizing oxidation for higher-quality recycled aluminum. This is a direct technological innovation impacting UBC processing.
-
October 2024 – Novelis announced its 3x30 program committing to ambitious circularity and decarbonization goals through 2030 including raising recycled content and recycling throughput. This initiative drives capital allocation to new recycling centers and partnerships to secure UBC feedstock and scale remelt capacity. Strategically it signals the largest recycler doubling down on closed loop beverage can recycling and sets a market benchmark for recycled content ambitions.
What are the Key Factors Influencing Investment analysis & Opportunities in Aluminum UBC Scrap Recycling Market Demand?
Investment in the aluminum UBC scrap recycling market is being shaped by a convergence of sustainability targets, policy mandates, and rising demand for low-carbon aluminum. Funding trends indicate strong capital flows into advanced recycling facilities, particularly in regions with supportive regulations such as the European Union and North America, where extended producer responsibility and deposit-return schemes drive reliable scrap supply. Venture and private equity interest is also growing around technology providers offering AI-based sorting, energy-efficient remelting, and traceability solutions.
Valuations are rising for integrated recyclers with closed-loop partnerships involving can manufacturers and beverage brands, reflecting investor confidence in long-term supply contracts and high recycled content demand. Key investment hotspots include Europe, driven by circular economy regulations, and Asia, where rapid urban consumption creates untapped UBC scrap streams. Together, these dynamics present opportunities for strategic M&A, green financing, and joint ventures in scaling global recycling capacity.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
Next Move Strategy Consulting (NMSC) presents a comprehensive analysis of the global aluminum UBC scrap recycling market, covering historical trends from 2020 through 2024 and offering detailed forecasts through 2030. Our study examines the market at global, regional, and country levels, providing quantitative projections and insights into key growth drivers, challenges, and investment opportunities across all major aluminum UBC scrap recycling segments.
Report Scope
|
Parameters |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 5.64 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 8.58 Billion |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 8.7% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Analysis Period |
2024–2030 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2030 |
|
Market Size Estimation |
Billion (USD) |
|
Growth Factors |
|
|
Countries Covered |
28 |
|
Companies Profiled |
15 |
|
Market Share |
Available for 10 companies |
|
Customization Scope |
Free customization (equivalent up to 80 analyst-working hours) after purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Approach |
In-depth primary and secondary research; proprietary databases; rigorous quality control and validation measures. |
|
Analytical Tools |
Porter's Five Forces, SWOT, value chain, and Harvey ball analysis to assess competitive intensity, stakeholder roles, and relative impact of key factors. |
Key Market Segments
By Scrap Source
-
Post‑Consumer (Old) Scrap
-
Post-Industrial (New) Scrap
By Alloy Type
-
Wrought Alloy
-
Casting Alloy
By Recycled Form
-
Billets/Logs
-
Ingots
-
Pellets/Granules
-
Sheets/Rolls
By End-User Industry
-
Packaging
-
Transportation
-
Automotive
-
Aerospace & Defense
-
-
Building & Construction
-
Electrical & Electronics
-
Machinery & Equipment
-
Others
Geographical Breakdown
-
North America: U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
-
Europe: U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Netherlands, and rest of Europe.
-
Asia Pacific: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Indonesia, Vietnam, Australia, Philippines, and rest of APAC.
-
Middle East & Africa (MENA): Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Israel, Turkey, Nigeria, South Africa, and rest of MENA.
-
Latin America: Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, and rest of LATAM.
Conclusion & Recommendations
Our report equips stakeholders, recyclers, manufacturers, policymakers, investors, and sustainability consultants with actionable intelligence to harness the growing potential of the global aluminum UBC scrap recycling market. By combining credible government-backed data, regional insights, and strategic analysis across key growth drivers, from closed-loop production and energy savings to policy innovation and cross-sector collaboration, NMSC’s aluminum UBC scrap recycling market report serves as an indispensable resource for navigating the evolving circular economy landscape and accelerating sustainable aluminum recovery efforts worldwide.

















 Speak to Our Analyst
Speak to Our Analyst