India Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) Market By Power Capacity (Small < 20 MW, Medium 20–100 MW, Large > 100 MW), By Application/Service (Renewable Integration & Firming, Energy Arbitrage, Ancillary Services, T&D Deferral, Microgrids & Islanding), By Discharge Duration (0–2 h, 2–4 h, 4–8 h, >8 h), By Installation (Front-of-Meter, Behind-the-Meter), By Business Model (Utility-Owned, Third-Party/IPPs, Customer-Owned, PPP) – India Analysis & Forecast, 2025–2030.
Industry: Energy & Power | Publish Date: 20-Oct-2025 | No of Pages: N/A | No. of Tables: N/A | No. of Figures: N/A | Format: PDF | Report Code : EP3588
Industry Outlook
The India Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) Market was valued at USD 306.3 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 386.5 million by 2025. Looking ahead, the industry is projected to expand significantly, reaching USD 1237.3 million by 2030, registering a CAGR of 26.2% from 2025 to 2030.
The market is being driven by rising electricity demand, increasing renewable energy capacity, and heightened awareness of climate-related challenges such as extreme weather events and grid instability. Investments in advanced battery technologies, AI-driven energy management systems, and smart grid integration are supporting innovation, operational efficiency, and enhanced energy reliability.
Regulatory frameworks, including central and state-level energy storage incentives, renewable integration policies, and grid stability mandates, are further shaping market dynamics, ensuring robust system standards and compliance. The India BESS market is evolving with a strong focus on scalable storage solutions, optimized risk and performance assessment models, and streamlined digital monitoring and control systems, reflecting India’s rapidly modernizing energy landscape and the growing demand for flexible, technology-enabled energy storage solutions.
What are the key trends in the India Battery Energy Storage System Industry?
Are large-scale tenders fuelling the growth of India Battery Energy Storage System Market?
Yes, the India BESS industry is witnessing rapid expansion, largely driven by government-backed large-scale tenders. According to the Central Electricity Authority, the country will require a total of 411.4 GWh of energy storage by 2031–32, with 236.2 GWh expected from battery energy storage systems and 175.2 GWh from pumped-hydro storage projects.
This surge is propelled by the growing share of solar power in India’s energy mix: solar generation peaks during the day but drops sharply in the evening, while electricity demand remains steady, highlighting the critical role of storage systems in ensuring grid stability and energy reliability.
Are policy and fiscal support accelerating the India BESS market?
Yes, the India BESS market growth is being rapidly accelerated by both large-scale tenders and strong government support. The Central Electricity Authority estimates that the country will need 411.4 GWh of energy storage by 2031–32, with 236.2 GWh expected from BESS and 175.2 GWh from pumped-hydro storage, driven by the growing share of solar power and the need to balance daytime generation with evening demand.
To support this growth, the government has introduced several policies and incentives, including US$1.09 billion in viability gap funding for 43.2 GWh of BESS capacity, waivers on inter-state transmission charges for BESS projects co-located with renewable energy plants commissioned by June 2028, and a Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) program worth USD 2.18 billion to support domestic manufacturing of 50 GWh of Advanced Chemistry Cell batteries. These measures, combined with large-scale tenders, are driving rapid adoption, attracting domestic and international players, and strengthening India’s energy storage ecosystem.
Is technology diversification happening in the India BESS sector?
Yes, lithium-ion batteries remain the backbone of the India BESS market trends, driven by their high efficiency and falling costs. At the same time, pumped hydro energy storage (PHES) continues to be vital for large-scale, grid-level storage requirements. Meanwhile, emerging solutions, such as flow batteries and second-life EV batteries, are gradually being deployed in specialized applications where longer life cycles, higher reliability, and low degradation are critical.
Rising Corporate and Industrial Demand for Reliable Power
In India, industries and commercial consumers are increasingly turning to battery storage technology to ensure uninterrupted operations and optimize energy costs. With rising peak electricity tariffs and the need to maintain consistent power supply, companies are deploying BESS solutions to manage peak demand charges and avoid costly downtime.
Additionally, as more corporations commit to sustainability goals, on-site integration of renewable energy with storage systems is gaining traction, allowing businesses to store excess solar or wind power for use during non-generation hours. This growing adoption is not only helping enterprises enhance energy reliability and cost efficiency but is also creating new revenue opportunities for BESS developers, further accelerating the market’s growth across industrial and commercial segments.
What are the key market drivers, breakthroughs, and investment opportunities that will shape the India Battery Energy Storage System Industry in next decade?
The India battery energy storage system market is undergoing a period of transformation, fuelled by rising electricity demand, climate-related challenges, and the adoption of smart-grid and distributed energy technologies. Expansion of urban centers, coupled with increasing integration of renewable energy sources, is driving the need for flexible, reliable, and digitally enabled storage solutions.
At the same time, sustainability initiatives and government-backed green energy policies are encouraging developers and utilities to incorporate eco-efficient and resilient features into BESS deployments. However, the market faces headwinds. Regulatory complexities, limited awareness of energy storage benefits, and initial high investment costs remain persistent barriers.
Nevertheless, innovations such as AI-powered energy management systems, IoT-enabled performance monitoring, and digital-first grid integration platforms are creating new growth avenues. Companies that align their solutions with evolving regulations, embrace automation, and offer scalable, reliable, and tech-enabled storage solutions are likely to capture significant market share in the coming decade.
Growth Drivers:
Do Expansion of Microgrids and Distributed Energy Systems Boost Market Growth?
The rising deployment of microgrids in industrial zones, remote areas, and smart cities is significantly boosting the India battery energy storage system market demand. BESS enables these microgrids to operate independently from the main grid, ensuring reliable power supply in regions with unstable or intermittent connectivity. By storing excess renewable energy generated on-site, such as solar or wind, microgrids reduce dependence on fossil-fuel-based backup power, lower operational costs, and enhance energy resilience.
Additionally, distributed energy systems equipped with smart grid storage provides critical services to the main grid, including peak shaving, frequency regulation, and voltage support, helping utilities manage load fluctuations more efficiently. This trend is further supported by India’s push toward rural electrification, smart city initiatives, and industrial parks, all of which are driving localized energy storage adoption and creating new market opportunities for BESS developers.
Does EV Sales Impact the Market Growth?
The rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India is creating significant opportunities for second-life battery applications in stationary energy storage. Repurposing EV batteries for BESS reduces costs, supports sustainability, and helps scale storage capacity without relying solely on new battery production.
Beyond storage, EV growth is contributing to India’s broader energy and environmental goals. In 2022, India recorded CO₂ emissions of 36.8 Gt, and EV adoption helps reduce this footprint while enhancing energy security by lowering dependence on imported fossil fuels. With over 1,054,938 EVs sold in 2022, India aims for 30% of all vehicles to be electric by 2030. This rapid growth not only supports renewable energy integration and grid stability but also drives economic opportunities.
The EV ecosystem is projected to create over 50 million indirect jobs by 2030, spanning manufacturing, charging infrastructure development, and renewable energy sectors. By linking EV deployment with stationary BESS applications, India leverages the full lifecycle of batteries, promote circular economy practices, and accelerate the expansion of its energy storage sector.
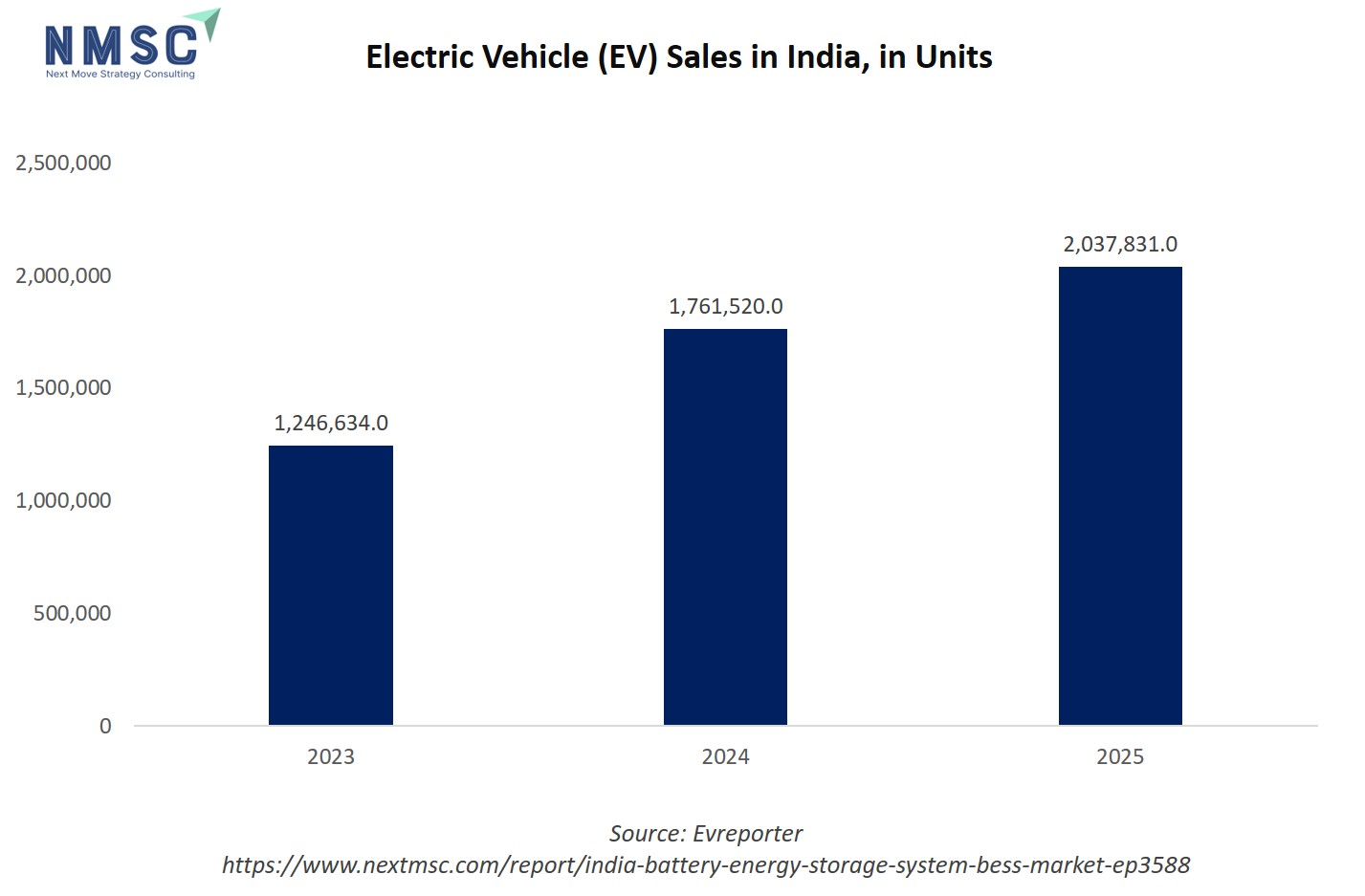
The bar chart of EV sales in India from 2023 to 2025 highlights not just the rapid adoption of electric vehicles but also the rising importance of the India battery energy storage system market. With sales growing from 1.24 million units in 2023 to over 2 million units in 2025, the demand for advanced batteries and storage solutions is scaling in parallel. This surge directly boosts the industry, as large-scale adoption of EVs requires efficient storage technologies for both vehicles and the supporting charging infrastructure.
The sharp growth in 2024 reflects how government incentives and infrastructure upgrades accelerated both EV penetration and investment in domestic battery manufacturing. By 2025, the more moderate growth rate indicates market consolidation, which aligns with the BESS industry’s transition from pilot projects to commercial-scale deployments. Thus, rising EV adoption is acting as a catalyst for India’s BESS sector, fostering opportunities in grid stabilization, renewable integration, and localized battery production.
Growth Inhibitors:
Is high initial capital expenditure hindering BESS adoption in India?
Yes, despite declining lithium-ion battery costs, BESS installations still require substantial upfront investment, including costs for batteries, power electronics, control systems, and civil works. High initial costs deter smaller utilities, commercial enterprises, and independent developers, slowing adoption in certain market segments. Limited access to financing or risk-sharing mechanisms further exacerbates this barrier.
Are limited awareness and technical expertise slowing market growth?
Yes, many potential BESS adopters lack awareness of the operational and financial benefits of energy storage. In addition, India faces a shortage of skilled professionals for designing, integrating, and maintaining advanced BESS systems. Inadequate knowledge of battery lifecycle management, safety standards, and grid compatibility result in hesitation among stakeholders and constrain deployment in regions with high energy storage potential.
How India Battery Energy Storage System Market is Segmented in this Report, and What are the Key Insights from the Segmentation Analysis?
By Power Capacity (MW) Insights
Which power capacity segments dominate India’s BESS market?
On the basis of power capacity, the India battery energy storage system market report is segmented into small (< 20 MW), medium (20–100 MW), and large (> 100 MW) systems. Small-scale systems currently lead the market, driven by pilot projects, behind-the-meter (BTM) applications, and lower capital requirements. Medium-capacity systems are gaining traction among utilities and renewable developers for applications such as peak shaving, solar and wind output smoothing, and energy arbitrage. Large-scale systems are emerging, supported by government and utility tenders, providing grid-scale energy storage, ancillary services, and transmission & distribution (T&D) capacity firming.
By Technology Insights
Which battery technologies are most widely adopted in India?
Based on technology, the market is segmented into lithium-ion (LFP, NMC/NCA), flow batteries (vanadium redox, zinc-bromine), advanced lead-acid/lead-carbon, sodium-based (NaS, Na-NiCl₂), and emerging technologies (solid-state, Li-S, metal-air). Lithium-ion batteries dominate due to high energy density, declining costs, and faster deployment cycles. LFP chemistry is particularly preferred for large-scale grid applications due to safety and longer cycle life. Flow batteries and advanced lead-acid solutions are primarily used in niche applications requiring long-duration discharge, while emerging technologies are in early demonstration phases but are expected to grow as cost and performance improve.
By Application / Service Insights
What are the main applications driving demand for BESS in India?
The India BESS market share is segmented by application into renewable integration & firming, solar PV smoothing, wind output smoothing, energy arbitrage, peak shaving, load shifting, ancillary services (frequency regulation, voltage support, spinning/non-spinning reserve, black-start capability), T&D deferral/capacity firming, and microgrids & islanding. Renewable integration and firming remain the largest drivers, propelled by India’s ambitious solar and wind expansion targets. Ancillary services and peak shaving are also growing as utilities look to stabilize the grid, optimize transmission assets, and manage demand peaks efficiently.
By Discharge Duration Insights
Which discharge duration segments are most relevant in India?
The market is categorized by discharge duration into 0–2 h, 2–4 h, 4–8 h, and > 8 h. Short-duration (0–2 h) systems dominate, primarily for frequency regulation, load shifting, and peak shaving. Medium-duration (2–8 h) systems are increasingly deployed for renewable firming and energy arbitrage. Long-duration systems (> 8 h) are limited but are gaining attention for utility-scale applications and microgrid support in remote regions, where grid reliability is critical.
By Installation Insights
What installation types are prevalent in the India BESS market?
BESS installations are classified as front-of-the-meter (FTM) and behind-the-meter (BTM). BTM installations are widespread for commercial & industrial (C&I) customers and renewable developers looking to optimize self-consumption and demand charges. FTM systems are growing in utility-scale projects, co-located with solar or wind farms, and are supported by government tenders and incentives for grid stability.
By Business Model Insights
Which business models are shaping India’s BESS market?
The market is segmented into utility-owned (e.g., DISCOMs), third-party / independent power producers (IPP, lease/PPA), customer-owned (captive/C&I aggregates), and public-private partnerships (VGF, loan guarantees). Utility-owned projects dominate early adoption due to government-led tenders, while third-party IPPs and customer-owned models are rapidly growing, driven by declining battery costs and commercial demand. Public-private partnerships support large-scale infrastructure projects, leveraging financial incentives and risk-sharing mechanisms to encourage faster deployment.
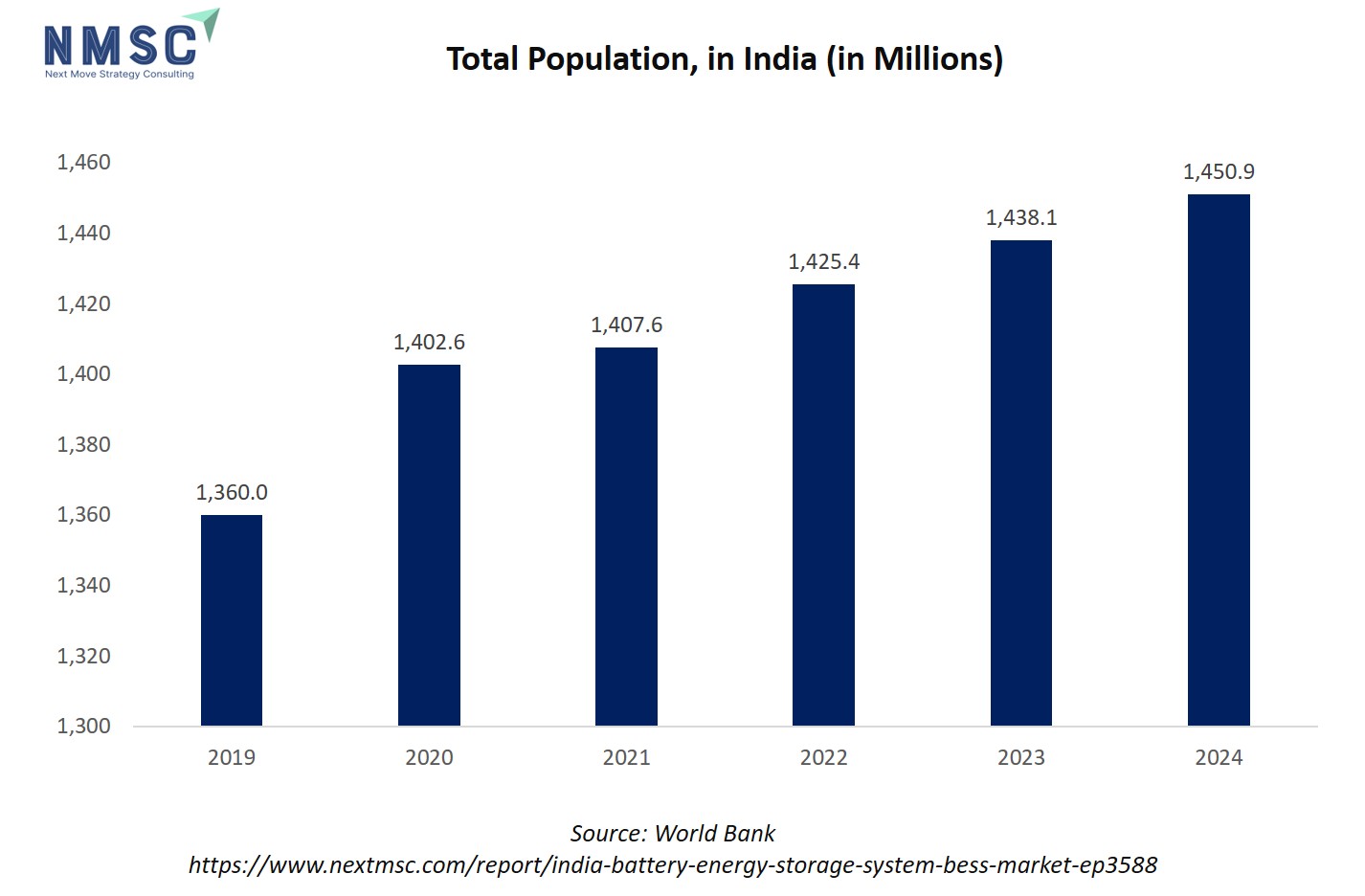
The bar chart of India’s population from 2019 to 2024 shows a steady upward rise year after year. In 2019, the population stood at 1,360 million, increasing to 1,402.6 million in 2020, and 1,407.6 million in 2021. The growth continued with 1,425.4 million in 2022, 1,438.1 million in 2023, and reached 1,450.9 million in 2024. Each bar in the chart is taller than the previous one, reflecting consistent population growth across these years.
This rising population is directly linked to the Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) market in India. A larger population drives higher electricity demand for homes, industries, transport, and digital infrastructure. With this surge, the need for a stable and resilient power supply becomes critical.
Since India is rapidly expanding renewable energy sources like solar and wind to meet growing demand, BESS plays a key role by storing excess renewable energy and supplying it during peak loads or outages. Moreover, population growth pushes urbanization and electric vehicle adoption, both of which require reliable energy storage solutions. Thus, India’s expanding population acts as a structural driver for the India BESS industry, ensuring its long-term growth and relevance.
Competitive Landscape
Which Companies Dominate the Battery Energy Storage System Industry in India and How Do They Compete?
The India battery energy storage system industry is led by major players such as Tata Power Renewable Energy Ltd, Adani Green Energy Ltd, ReNew Power, Fluence Energy, Exide Industries Ltd, Amara Raja Batteries Ltd, Luminous Power Technologies Pvt Ltd, Su-Kam Power Systems Ltd, Virya Energy Solutions, and Hitachi Energy India Pvt Ltd. These companies are driving market growth by expanding energy storage capacity, investing in advanced battery technologies, and offering turnkey solutions for utility-scale and commercial & industrial (C&I) applications. Their strategies increasingly focus on AI-enabled energy management, IoT-integrated monitoring systems, and software-driven predictive maintenance to enhance operational efficiency and grid reliability.
For instance, leading players are deploying real-time analytics to optimize solar and wind integration, energy arbitrage, and peak-shaving strategies across high-demand regions. To remain competitive, these companies are also collaborating with government agencies, renewable developers, and technology providers to co-develop hybrid storage solutions, microgrids, and value-added services that accelerate India’s transition toward a sustainable, decarbonized energy landscape.
Market Dominated by Established Global and Regional Insurers
The India battery energy storage system market is primarily led by global giants such as Tata Power Renewable Energy, Adani Green Energy, ReNew Power, Fluence Energy, and Hitachi Energy India, alongside strong regional players including Exide Industries, Amara Raja Batteries, Luminous Power Technologies, Su-Kam Power Systems, and Virya Energy Solutions. These companies compete by offering scalable energy storage solutions tailored for utility-scale, commercial & industrial, and behind-the-meter applications.
Digital-native and technology-focused players are disrupting the market through IoT-enabled battery management, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and software platforms for real-time energy optimization. Regional and local players maintain strong positions by leveraging strategic collaborations with renewable developers, government initiatives, and financial institutions, enabling bundled solutions such as hybrid storage systems, microgrid integration, and turnkey project delivery.
Innovation and Adaptability Drive Market Success
The India battery energy storage system market is increasingly defined by technological innovation, adaptability, and large-scale renewable integration. For instance, ReNew Energy Global Plc (“ReNew”) announced an investment of USD 2.5 billion to set up one of India’s largest hybrid renewable energy projects in Anantapur, Andhra Pradesh. The project will feature a generation capacity of 2.8 GW, including 1.8 GWp solar, 1 GW wind, and a 2 GWh BESS, making it one of the largest renewable energy complexes at a single location in India.
Market Players Embrace Innovative Offerings and Expansion Strategies
Industry players in the India battery energy storage system market are increasingly focusing on strategic innovations, product expansion, and diversification to strengthen their market presence and meet evolving energy needs. A prime example is Tata Power Renewable Energy Limited (TPREL), a subsidiary of The Tata Power Company Limited and one of India’s leading renewable energy players, which recently signed its first Battery Energy Storage Purchase Agreement (BESPA) with NHPC Limited (NHPC).
The project, secured under NHPC’s BESS Tranche-I tender through a competitive bidding route, will serve the Kerala State Electricity Board Limited as the end user and involves setting up a 30 MW / 120 MWh battery storage system at a 220 kV substation. This milestone highlights TPREL’s focus on utility-scale storage solutions, grid stability, and renewable integration.
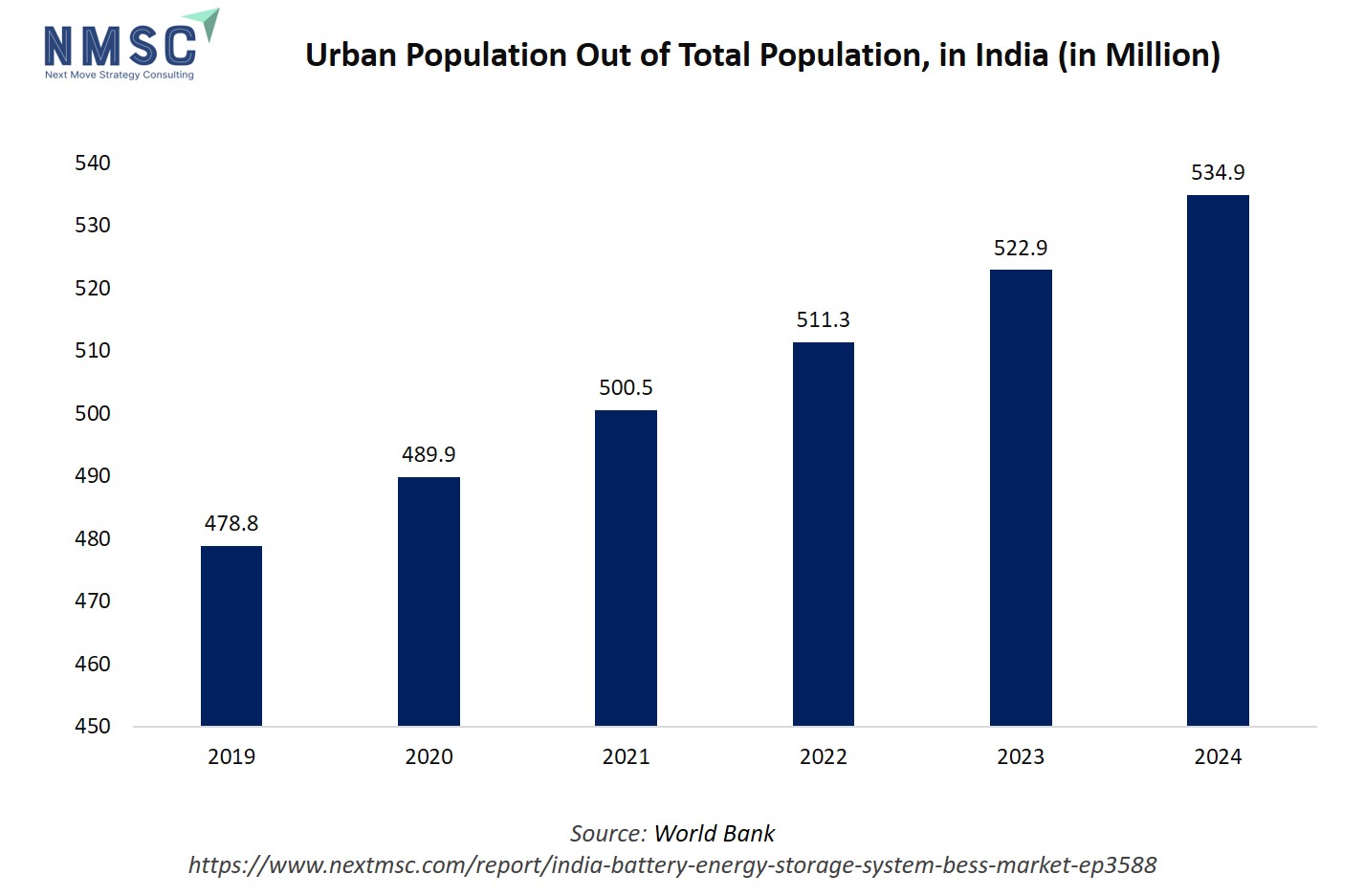
The bar chart showing India’s urban population from 2019 to 2024 highlights a steady and consistent upward trend. In 2019, the urban population stood at 478.8 million, increasing to 489.9 million in 2020 and 500.5 million in 2021. This rise continued with 511.3 million in 2022, 522.9 million in 2023, and 534.9 million in 2024. Each bar in the chart grows taller year after year, reflecting the ongoing process of urbanization in the country.
This steady urban population growth has a direct connection with the India battery energy storage system market growth. As cities expand, electricity demand surges from households, industries, commercial complexes, metro systems, and electric vehicle charging networks. BESS plays a crucial role in meeting these demands by ensuring grid stability, storing renewable energy for urban consumption, and providing reliable backup power during peak loads or outages.
Urbanization also accelerates the push for smart cities, where BESS enables efficient energy management and supports sustainable infrastructure. In essence, the rising urban population drives both electricity consumption and renewable integration needs, making energy management systems (EMS) a key technology for powering India’s rapidly urbanizing future.
Key Players
-
Amara Raja Energy & Mobility Ltd.
-
BYD Energy Storage Co. Ltd.
-
Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
-
Larsen & Toubro Ltd.
-
HBL Power Systems Ltd.
-
Exicom Tele-Systems Ltd.
-
Livguard
-
Okaya Power Pvt. Ltd.
-
NTPC Ltd.
-
Tata Power Company Limited
-
Waaree Energies Ltd.
-
JSW Energy Ltd.
-
Adani Green Energy Ltd.
What are the latest key industry developments?
-
July 2025 - Exide has outlined a growth strategy with a dual focus on lead-acid and lithium-ion battery business. It invested USD 120 million in FY25 in the lithium-ion business and plans another USD 48 million in FY26.
-
July 2025 - Sungrow has launched a next-generation hybrid residential energy storage system; upgrades to its MG Series inverters and a matching battery system will be released in Q4.
-
July 2025 - Exide has infused USD 12 million into its lithium battery arm EESL (Exide Energy Solutions Ltd) to support the development of a 12 GWh greenfield lithium-ion cell/pack manufacturing facility. Commercial production in Phase-1 (6 GWh) is expected by end of FY 2025-26.
-
July 2024 - In India, Fluence has expanded its Digital Services Center (DSC) by building a Remote Monitoring & Diagnostics Center in Bengaluru. This supports its global fleet of battery storage assets.
-
June 2024 - Amara Raja has signed a licensing agreement with Gotion-InoBat-Batteries (unit of China’s Gotion High Tech) for lithium-ion battery cell technology (LiFePO₄) to set up gigafactory facilities in India.
What are the key factors influencing investment analysis & opportunities in the India Battery Energy Storage System Market?
Investment in the India battery energy storage system market is being shaped by several critical factors, reflecting both market dynamics and the growing demand for reliable, renewable-integrated energy solutions. Increasing adoption of solar and wind power, coupled with the intermittency of renewable generation, has amplified the need for utility-scale and distributed energy storage systems, creating attractive investment opportunities.
Funding trends indicate strong interest from venture capital, private equity, and strategic investors in BESS projects that leverage advanced lithium-ion, flow, and sodium-based battery technologies, as well as AI-powered energy management systems and IoT-enabled monitoring solutions. Companies integrating modular and scalable storage solutions, hybrid renewable projects, and microgrid capabilities are particularly attractive to investors due to their potential for high returns and grid resilience benefits.
Valuations of BESS providers are experiencing upward momentum thanks to the deployment of predictive analytics, real-time monitoring platforms, and automated energy dispatch systems, which enhance operational efficiency and optimize energy arbitrage opportunities. Regulatory support from the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), Ministry of Power (MoP), and state-level policies such as Viability Gap Funding (VGF) for storage projects and renewable integration incentives further strengthen investor confidence.
The long-term outlook for the market remains positive, with strategic partnerships, large-scale tenders, technological innovation, and digital transformation fostering growth opportunities across utility-scale, commercial & industrial, and behind-the-meter applications in India’s rapidly expanding energy storage landscape.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
Next Move Strategy Consulting presents a comprehensive analysis of the India Battery Energy Storage System Market, covering historical trends from 2020 through 2024 and offering detailed forecasts through 2030. Our study examines the sector at global, regional, and country levels, providing quantitative projections and insights into key growth drivers, challenges, and investment opportunities across all major segments.
Report Scope:
|
Parameters |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 386.5 million |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 1237.3 million |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 26.2% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Analysis Period |
2024–2030 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2030 |
|
Market Size Estimation |
Million (USD) |
|
Growth Factors |
|
|
Companies Profiled |
15 |
|
Market Share |
Available for 10 companies |
|
Customization Scope |
Free customization (equivalent up to 80 analyst-working hours) after purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Approach |
In-depth primary and secondary research; proprietary databases; rigorous quality control and validation measures. |
|
Analytical Tools |
Porter's Five Forces, SWOT, value chain, and Harvey ball analysis to assess competitive intensity, stakeholder roles, and relative impact of key factors. |
Key India Battery Energy Storage System Market Segments
By Power Capacity (MW)
-
Small (< 20 MW)
-
Medium (20 – 100 MW)
-
Large (> 100 MW)
By Technology
-
Lithium-Ion
-
LFP
-
NMC / NCA
-
-
Flow Batteries
-
Vanadium Redox (VRB)
-
Zinc-Bromine
-
-
Advanced Lead-Acid / Lead-Carbon
-
Sodium-Based (NaS, Na-NiCl₂)
-
Emerging (Solid-State, Li-S, Metal-Air)
By Application / Service
-
Renewable Integration & Firming
-
Solar PV Smoothing
-
Wind Output Smoothing
-
-
Energy Arbitrage (Time-Shift)
-
Peak Shaving
-
Load Shifting
-
-
Ancillary Services
-
Frequency Regulation
-
Voltage Support
-
Spinning / Non-Spinning Reserve
-
Black-Start Capability
-
-
T&D Deferral / Capacity Firming
-
Microgrids & Islanding
By Discharge Duration
-
0–2 h
-
2–4 h
-
4–8 h
-
> 8 h
By Installation
-
Front-of-Meter (FTM)
-
Behind-the-Meter (BTM)
By Business Model
-
Utility-Owned (e.g., DISCOMs)
-
Third-Party / IPP (Lease / PPA)
-
Customer-Owned (Captive / C&I Aggregates)
-
Public-Private Partnership (VGF, Loan Guarantees)
Conclusion & Recommendations
Our report equips stakeholders, industry participants, investors, policy-makers, and consultants with actionable intelligence to capitalize on the transformative India battery energy storage system market potential.

















 Speak to Our Analyst
Speak to Our Analyst

























