Real Estate Market by Property Size (Small, Medium, Large), by Property Type (Residential, Commercial, Land, Industrial), by Business Type (Buying, Selling, Leasing, Renting, Real Estate Investment), by Ownership (Owner-Occupied Properties, Rental Properties, Co-ownership), by Property Value (Affordable Housing, Luxury Housing, Ultra-Luxury Housing), and by End User (Individual Buyers, Business Entities, Government, Institutional Investors) – Global Analysis & Forecast, 2025–2030
Industry: Construction & Manufacturing | Publish Date: 25-Nov-2025 | No of Pages: N/A | No. of Tables: N/A | No. of Figures: N/A | Format: PDF | Report Code : CM452
Industry Outlook
The global Real Estate Market size was valued at USD 22.64 trillion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 25.26 trillion by 2025. Looking ahead, the industry is projected to expand significantly, reaching USD 33.61 trillion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 5.87% from 2025 to 2030.
The real estate market is witnessing robust expansion globally, shaped by the steady rise in urbanization and evolving lifestyle preferences. As cities continue to grow and attract populations from rural and suburban regions, the demand for residential, commercial, and mixed-use developments is surging. This transformation is redefining how urban spaces are designed, encouraging compact, sustainable, and technology-integrated developments that cater to the needs of a modern, mobile, and connected population. The influx of people into urban centers is also driving the need for smarter housing solutions, efficient public infrastructure, and proximity to employment hubs, creating immense opportunities for developers to innovate and optimize land use. Real estate firms that embrace smart-city concepts, digital property management systems, and sustainable materials are better positioned to meet these shifting consumer and policy demands.
At the same time, rapid urban expansion and infrastructure modernization are unlocking new avenues for investment across housing, logistics, and commercial real estate. Governments worldwide are prioritizing urban renewal and sustainable development, paving the way for large-scale projects that improve connectivity, enhance living standards, and support economic growth. For real estate developers and investors, aligning with these infrastructure rollouts and targeting emerging metropolitan corridors presents strategic advantages. Those who focus on early land acquisition, adaptive building designs, and integrated community planning capture long-term value as cities evolve into dynamic, high-density ecosystems that balance growth with sustainability and livability.
What are the Key Real Estate Industry Trends?
How is the Real Estate Market Responding to the Global Housing‐Affordability Squeeze and Rising Urban Demand?
Housing shortages and affordability pressures are central concerns across OECD and global policy agendas: cross-country analysis shows a meaningful rise in price-to-income and rent burdens for low-income households, with many OECD countries reporting that a large share of low-income owners or renters spend over 40% of disposable income on housing. That squeeze pushes demand toward higher-density, mixed-use and modular construction solutions while also expanding the role of public-private delivery models and inclusionary zoning. For operators and cities the practical move is to combine supply-side acceleration with demand-side tools to preserve affordability without destabilising markets. Real-estate companies should pilot one modular or infill project per market to prove unit-economics and engage local authorities early to reduce approval times quick wins that lower per-unit costs and increase velocity.
How is the Real Estate Market Leveraging Proptech and Generative AI While Keeping Governance and Transparency Front-And-Centre?
The real estate market is undergoing a digital transformation, driven by the growing integration of PropTech solutions and AI-powered analytics across operations. From smart sensors optimizing HVAC systems to predictive models assessing tenant retention and property valuations, digital adoption is reshaping how assets are managed and monetized. According to the World Bank’s 2024 “Digitalization and Governance in Urban Development” report, the convergence of AI and data systems in infrastructure now demands strong accountability, explainability, and procurement standards to avoid bias and data misuse. This evolution signals a dual challenge for property firms achieving operational efficiency while maintaining trust and compliance. Companies that integrate IoT-enabled building data with validated machine learning tools are reporting measurable cost reductions in maintenance and energy consumption. To stay competitive, developers and REITs should establish an “AI & Data Governance Playbook” outlining model-risk thresholds, validation protocols, and third-party audit schedules. Piloting these practices on flagship assets balance innovation with governance, enabling sustainable scalability in a rapidly digitizing market.
How is the Real Estate Market Redefining Spaces to Meet the Hybrid Work and Lifestyle Shift?
The boundary between work, living, and leisure is dissolving and the market is evolving to reflect this change. As hybrid work models become the norm, tenants increasingly seek spaces that balance flexibility, wellness, and connectivity. Traditional office demand is giving way to adaptive spaces offering modular layouts, wellness-certified environments, and integrated digital infrastructure. Residential projects, too, are being reimagined with co-working lounges, smart-home integrations, and community-focused amenities that support both productivity and social interaction. This shift challenges developers and property managers to rethink design philosophies emphasizing multi-use spaces, biophilic elements, and advanced connectivity as standard features. For companies, the actionable opportunity lies in repositioning existing assets to align with the “live-work-play” mindset: converting underused commercial areas into hybrid community hubs or flexible lease models that adapt to evolving tenant needs. Real estate players that embrace this human-centric approach will not only retain occupancy but also strengthen brand value in an increasingly experience-driven marketplace.
What are the Key Market Drivers, Breakthroughs, And Investment Opportunities That Will Shape the Real Estate Industry in the Next Decade?
The real estate market is undergoing a period of dynamic transformation, driven by rapid urbanization, evolving lifestyle preferences, and technological integration across property development and management. As cities expand and populations concentrate around economic and employment hubs, demand for housing, commercial spaces, and mixed-use developments continues to grow. Modern consumers increasingly seek properties that combine sustainability, convenience, and digital connectivity, prompting developers to adopt smart infrastructure, energy-efficient designs, and flexible living models. This shift is also influencing the types of spaces being built prioritizing green buildings, co-living setups, and adaptive reuse of existing structures to meet the needs of both individuals and businesses in fast-changing urban environments.
Nevertheless, the industry faces challenges such as fluctuating interest rates, rising construction costs, and regulatory hurdles that delay project timelines or impact profitability. Despite these headwinds, significant opportunities remain for developers and investors who align with sustainability goals, leverage digital technologies, and anticipate future urban trends. Companies that integrate ESG principles, focus on smart-city partnerships, and invest in resilient, community-driven designs are well-positioned to capture long-term value. The market’s evolution reflects a broader shift toward adaptable, technology-forward, and sustainable spaces that redefine how people live, work, and interact in the built environment.
Growth Drivers:
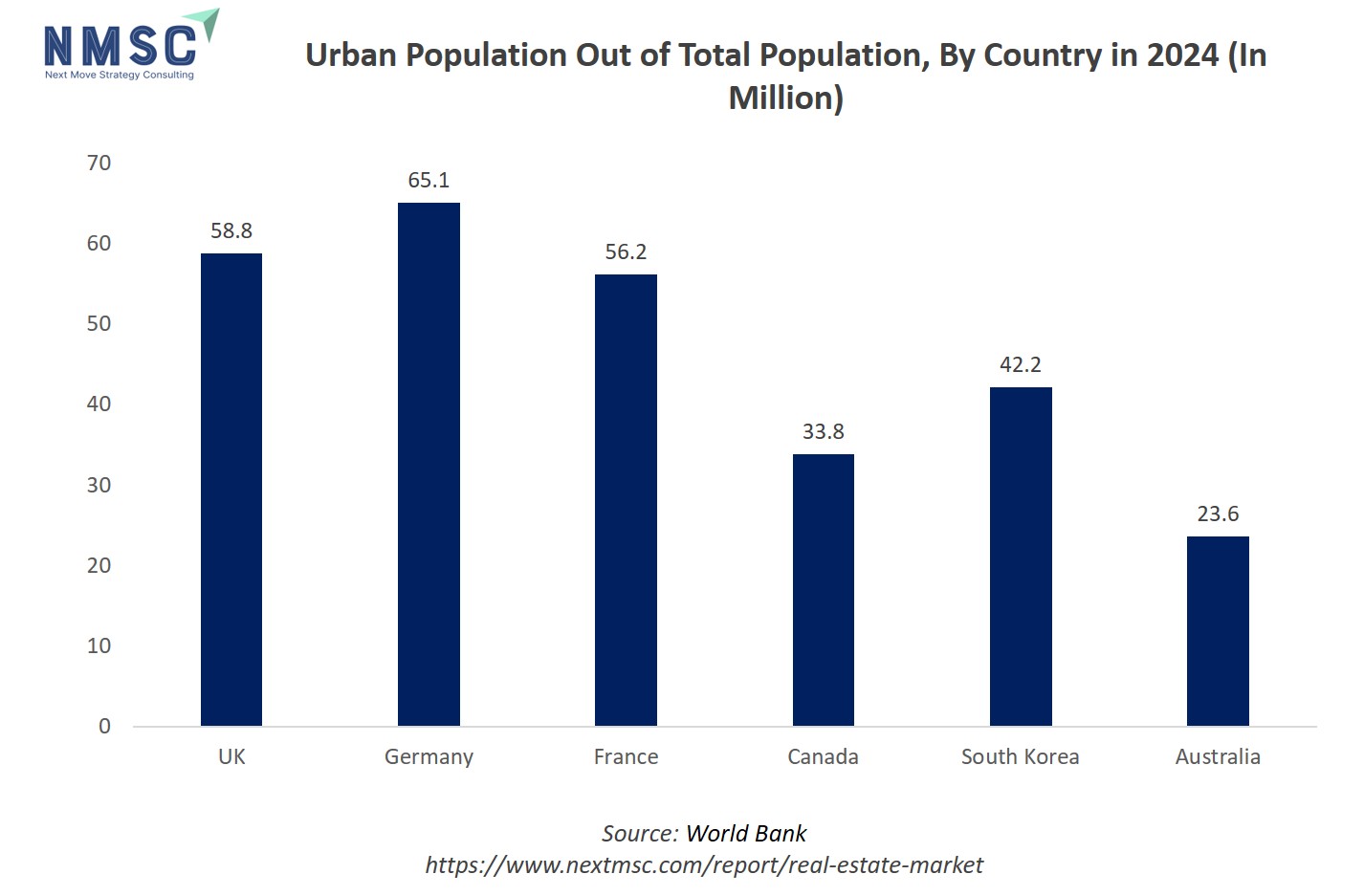
How is the Rising Share of Urban Population Driving Real Estate Market Demand?
The continuous rise in the world’s urban population, as highlighted by the World Bank, is profoundly transforming the dynamics of the market. Rapid urbanisation brings with it an expanding need for housing, commercial infrastructure, and public services, placing immense pressure on cities to adapt and grow sustainably. For real estate developers, this migration trend signals an opportunity to invest in mixed-use projects, smart housing, and transit-oriented developments that align with the evolving urban lifestyle. Growing urban populations are also prompting demand for vertical developments, affordable housing, and smart infrastructure integration. Real estate companies that anticipate these shifts gain long-term advantages by acquiring land in emerging metropolitan corridors, leveraging public-private partnerships, and designing flexible, high-density projects that address both livability and scalability in the world’s fastest-growing cities.
How is Infrastructure Investment Need Accelerating Real Estate Market Growth?
Rapid urban expansion and aging infrastructure are generating exceptionally large investment needs, which in turn are driving real-estate growth opportunities across housing, commercial, logistics and mixed-use sectors. For example, one recent report by the World Bank projects that India alone will require USD 840 billion of investment over 15 years in urban infrastructure to meet the demands of a rapidly growing and urbanising population. As infrastructure improves transport, utilities, district services land values, rental levels and development density follow. For developers and investors this means identifying zones where infrastructure rollout is imminent, acquiring land early, and aligning product mix housing, retail, offices to the upgraded environment. By moving ahead of fully realised infrastructure, real-estate players secure value uplift, faster lease-up and premium pricing.
Growth Inhibitors:
What is the Impact of Escalating Commercial Real-Estate Loan Burdens on Market Growth?
The real estate market is increasingly feeling the strain from elevated exposure to commercial real-estate (CRE) loans across the banking system. As reported by the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), banks held nearly USD 3 trillion in CRE loans as of October 2023 about half of the total USD 5.9 trillion in outstanding CRE credit. This high concentration exposes lenders and the broader property market to systemic risks if valuations soften or refinancing becomes difficult. When loan maturities coincide with high interest rates, many borrowers face increased debt-service costs, prompting banks to tighten lending standards and developers to delay or scale down new projects. For the real-estate sector, this means slower capital flow, constrained liquidity, and pressure on asset pricing. Market participants should respond by restructuring debt early, prioritising cash-flow-resilient assets, and adopting conservative leverage strategies to maintain stability amid tightening credit conditions.
How is the Expansion of Digital Infrastructure Unlocking New Growth Avenues for the Market?
The ongoing expansion of digital infrastructure is reshaping the market by introducing new asset classes and redefining value creation beyond traditional property models. The International Telecommunication Union highlights that Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), including broadband networks, data centers, IoT-enabled systems, and integrated urban platforms is becoming the backbone of modern, connected cities. This transformation is driving demand for technologically advanced properties that support connectivity-intensive operations, from data centers and co-working hubs to smart commercial buildings. For developers and investors, this represents an opportunity to reposition assets as “digital-ready” by integrating high-speed networks, energy-efficient systems, and smart automation. Real estate players that align their portfolios with digital infrastructure growth particularly in emerging smart-city zones stand to benefit from enhanced asset resilience, premium rents, and long-term relevance in a rapidly digitizing global economy.
How Real Estate Market Segmented in this Report, and What are the Key Insights from the Segmentation Analysis?
By Property Size Insights
Is the Real Estate Industry in 2025 Shaped by Diverse Plant Sources?
Based on property size, the market is segmented into small, medium and large.
The large (2000+ sq. ft.) segment in the market represents premium and expansive properties catering primarily to high-income buyers, commercial enterprises, and institutional investors. This segment includes luxury residences, corporate offices, retail complexes, and industrial facilities that prioritize space optimization, advanced amenities, and architectural sophistication. Demand within this category is driven by the growing preference for spacious living and working environments, enhanced design flexibility, and the integration of smart technologies for comfort and efficiency. Developers in this segment focus on high-value locations, sustainability certifications, and long-term asset appreciation, making it a critical driver of prestige and profitability within the broader real estate landscape.
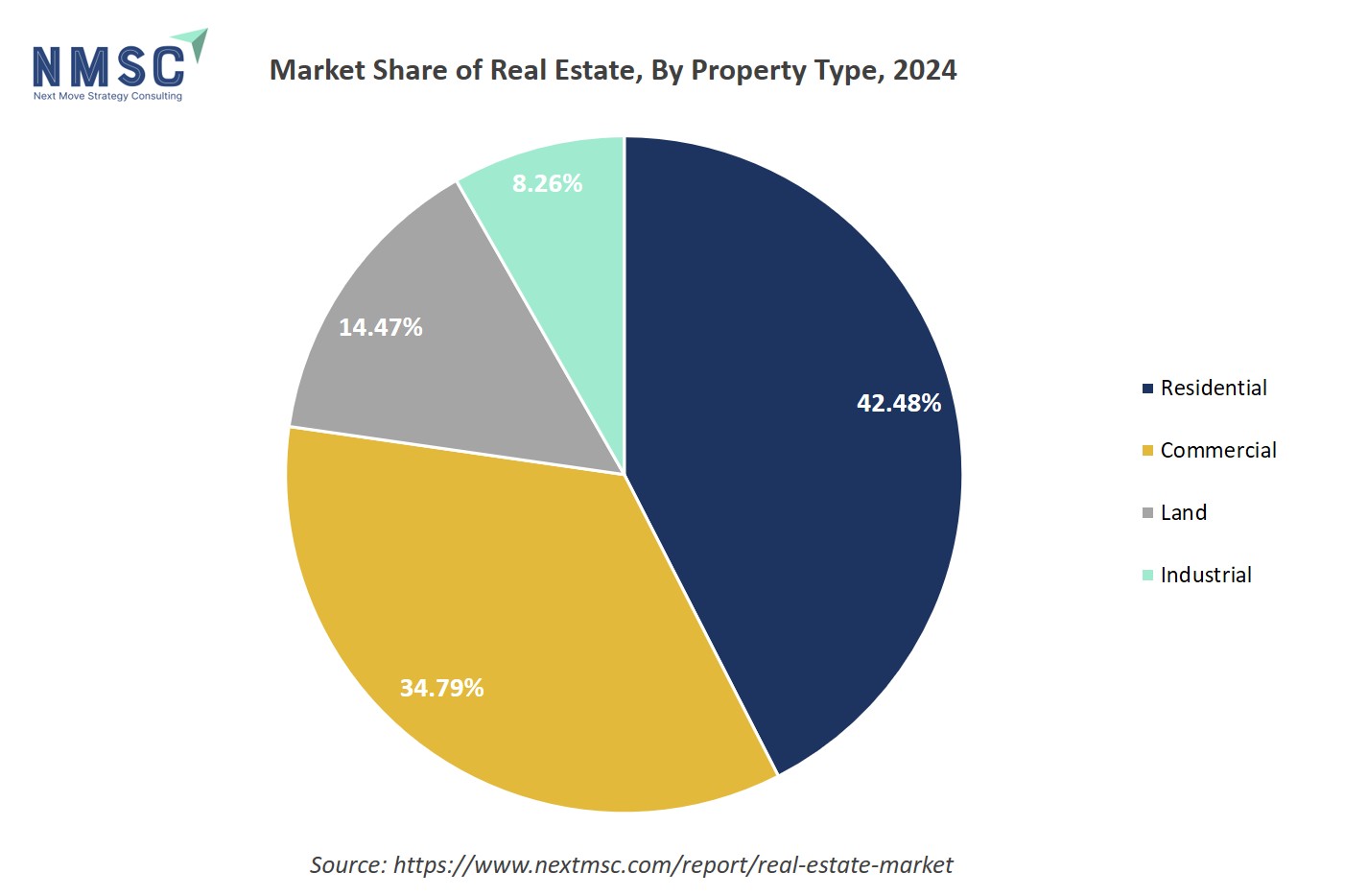
By Property Type Insights
Is the Real Estate Market Trends in 2025 Being Shaped by Product Type?
On the basis of property type, the market is segmented into residential, commercial, land and industrial.
The Residential segment forms the cornerstone of the real estate market, encompassing diverse property types such as apartments, single-family and multi-family homes, condominiums, townhouses, and vacation homes. This segment primarily caters to individual buyers, families, and investors seeking rental income or long-term asset appreciation. Demand in the residential sector is influenced by factors such as population growth, urbanization, rising disposable income, and evolving lifestyle preferences. Developers in this space increasingly focus on sustainable building designs, smart-home integration, and community-centric layouts to attract modern buyers. Additionally, flexible financing options and government housing initiatives further stimulate growth, positioning the residential segment as both a stable investment avenue and a reflection of shifting socio-economic and demographic trends within the global real estate landscape.
By Ownership Insights
How are Ownership Driving the Real Estate Industry in 2025?
On the basis of ownership, the market is segmented into owner occupied properties, rental properties and co ownership.
The owner-occupied properties segment represents real estate owned and primarily used by individuals or families as their primary residence. This segment reflects long-term stability in the market, driven by the emotional and financial value attached to homeownership. Demand for owner-occupied properties rises in regions with favorable mortgage rates, strong employment opportunities, and supportive housing policies. Buyers in this category prioritize factors such as location, safety, connectivity, and future appreciation potential. Moreover, ownership provides a hedge against inflation and offers wealth-building advantages through property appreciation over time. Developers and policymakers view this segment as a critical indicator of market health, as high levels of owner occupancy generally signify consumer confidence, economic stability, and sustained demand in the broader real estate landscape.
By End User Insights
Which End User is Driving the Real Estate Industry in 2025?
On the basis of end user, the market is segmented into individual buyers, business entities and others.
The Individual Buyers segment forms the foundation of the real estate market, encompassing diverse buyer profiles such as first-time homeowners, repeat buyers, luxury purchasers, and retirees. This group is primarily driven by personal lifestyle needs, financial capacity, and long-term investment goals rather than short-term returns. Individual buyers significantly influence residential property demand, shaping trends in urban expansion, housing design, and location preferences. Their choices are affected by factors like interest rates, employment stability, and government incentives for homeownership. As digital platforms and virtual property tours enhance accessibility and transparency, individual buyers are becoming more informed and selective. This segment’s sustained participation supports steady transaction volumes and fosters resilience in the market, particularly within the residential and mixed-use development categories.
Regional Outlook
The real estate market share is geographically studied across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America and each region is further studied across countries.
Real Estate Market in North America
North America’s market is evolving under the influence of changing demographics, investment flows, and shifting occupier expectations. Migration toward warmer regions and growing interest in mid-sized cities are driving development toward mixed-use, infill, and logistics projects. Investors are increasingly targeting industrial and rental assets for their stability and returns, while fluctuating financing costs and tighter lending conditions are encouraging developers to prioritize projects with reliable cash flows and quicker occupancy. The direction of the market will also hinge on government initiatives around zoning, infrastructure, and housing affordability, all of which will shape how new supply meets emerging urban demand across the region.
Real Estate Market in the United States
The U.S. real estate market is undergoing a structural transformation, driven by shifting economic fundamentals, changing work patterns, and evolving investor priorities. Multifamily housing and industrial assets remain the backbone of growth, supported by resilient rental demand and e-commerce logistics expansion. In contrast, traditional downtown office spaces and certain retail segments are still recalibrating in the post-pandemic era as hybrid work reshapes occupancy needs. According to Federal Reserve Economic Data, fluctuations in mortgage rates and constrained housing inventory continue to impact affordability and transaction activity across major metros. Geographically, capital is migrating from expensive coastal gateways toward Sunbelt and secondary cities markets like Austin, Nashville, and Phoenix where affordability, infrastructure expansion, and employment growth support stronger yields. Developers are increasingly focusing on transit-connected, mixed-use, and adaptive reuse projects, especially conversions of under-utilized office properties into residential and community spaces, which aligns long-term asset resilience with evolving urban living patterns.
Real Estate Market in Canada
Canada’s market is being shaped by strong population growth, limited developable land, and rising demand for rental housing. These forces are driving greater focus on multi-unit and purpose-built rental developments, as investors seek steady, long-term returns from resilient housing assets. Major cities and expanding mid-sized urban centres continue to attract most real estate investment, reflecting their economic stability and infrastructure strength. However, the pace of future growth will depend on government policies that promote higher-density development, rental housing incentives, and faster project approvals. Developers who embrace innovative construction methods and collaborative models with public partners are best positioned to capture opportunities in this sustained, housing-driven market environment.
Real Estate Market in Europe
Europe’s market reflects a diverse regional landscape shaped by differing economic priorities and sectoral strengths. In northern Europe, the focus is on sustainable redevelopment and retrofitting older assets to meet environmental goals. Central European markets are experiencing rising demand for logistics and industrial spaces driven by expanding trade and e-commerce activity. Meanwhile, southern Europe is seeing renewed momentum in tourism and residential segments as economies recover and lifestyle-driven investments increase. Western Europe’s mature urban centres remain attractive for their stability but face tight supply and stringent sustainability regulations, steering investors toward green and adaptive reuse projects. Across the continent, capital is increasingly flowing into resilient sectors such as logistics, life sciences, and sustainable redevelopment, underscoring a broader shift toward long-term value creation through environmental and regulatory alignment.
Real Estate Market in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom’s real estate market is navigating a period of adjustment marked by affordability challenges, evolving workplace dynamics, and shifting regulatory priorities. While London continues to attract global investment for its prime assets and financial importance, regional cities are gaining traction as hubs for logistics and build-to-rent developments, appealing to investors seeking stronger returns. Changing planning frameworks, new rental regulations, and rising environmental standards are influencing where and how new projects emerge, as developers balance compliance with profitability. The trend toward converting underused office spaces into residential or mixed-use developments is reshaping urban centres, reflecting the market’s adaptation to changing occupier needs and long-term housing demand.
Real Estate Market in Germany
Germany’s market is characterized by a balance between strong institutional demand and a tightly regulated development environment shaped by planning controls and sustainability standards. Residential and logistics properties remain key drivers of market activity, supported by stable economic fundamentals and growing occupier needs. Major cities such as Berlin, Munich, and Frankfurt continue to draw investment due to their role as economic and innovation hubs, while high energy-efficiency requirements and tenant protections influence development strategies and capital allocation. The country’s ongoing energy transition and focus on sustainable construction favour investors with a long-term outlook who support retrofitting and climate-resilient projects. Overall, well-connected urban and industrial regions offer stronger liquidity and value stability, reinforcing Germany’s position as one of Europe’s most resilient markets.
Real Estate Market in France
A major driver of France’s market is the country’s strong commitment to sustainability and urban regeneration. National and regional authorities are promoting energy-efficient construction, green retrofitting, and adaptive reuse of older properties in line with France’s long-term climate objectives and the EU’s green transition agenda. This focus is reshaping investment strategies as developers prioritize low-carbon materials, high energy performance standards, and mixed-use neighbourhoods that blend housing, commerce, and public spaces. Urban regeneration initiatives particularly in metropolitan areas such as Paris, Lyon, and Marseille are revitalizing existing districts while aligning with environmental and social goals. As a result, sustainability and innovation are becoming central to market growth, attracting institutional investors and developers seeking long-term, resilient value creation.
Real Estate Market in Italy
A key driver of Italy’s market is the resurgence in property transactions supported by a sharp rise in mortgage financing. According to Istat data reported by ANSA, new mortgage agreements in 2024 increased by 7.2% compared to the previous year, reflecting renewed buyer confidence and improved lending conditions. This uptick in financing activity is fueling demand in both urban and regional housing markets, as easier access to credit encourages more first-time buyers and investors to re-enter the market. The combination of stronger transaction volumes and favourable borrowing terms is driving residential property values upward, signalling a period of recovery and renewed momentum for Italy’s real estate sector.
Real Estate Market in Spain
Spain’s real estate market is gaining momentum, driven by a strong rebound in tourism and rising demand for logistics and industrial spaces. Major cities like Madrid and Barcelona continue to serve as central hubs for investment, attracting both domestic and international interest. Coastal and island regions remain highly sought after for residential and hospitality developments, supported by lifestyle-driven demand, while inland areas and logistics corridors near ports are drawing institutional capital aimed at expanding warehouse and distribution capacity. Evolving regulations on short-term rentals and government investment in infrastructure are shaping where new opportunities emerge. Developers who embrace sustainable tourism, mixed-use coastal projects, and strategically located logistics assets are well positioned to benefit from Spain’s diversified and resilient market growth.
Real Estate Market in the Nordics
The Nordic market is defined by its strong focus on sustainability, social infrastructure, and stable institutional frameworks that foster long-term growth and reduce volatility. The region’s commitment to green building practices, energy efficiency, and climate adaptation continues to shape investment strategies, with capital increasingly directed toward environmentally responsible and future-ready assets. Major cities such as Stockholm, Copenhagen, and Oslo maintain high demand for housing as well as for ESG-aligned office and logistics spaces that meet modern standards. Compact urban layouts and well-developed public transport networks encourage dense, mixed-use development and sustainable urban living. Investors who prioritize energy-efficient construction, long-term partnerships with public entities, and high-quality design standards are well positioned to achieve stable, risk-adjusted returns in this environmentally conscious and resilient market.
Real Estate Market in the Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific market is shaped by a dynamic mix of mature urban centres and rapidly developing secondary cities, underpinned by urban migration, digital transformation, and extensive infrastructure investment. Major economies such as China, India, Southeast Asian nations, and Australia each follow distinct growth paths, yet all share a focus on aligning real estate development with broader economic modernization. Infrastructure upgrades in transport, energy, and technology are unlocking new investment corridors and enhancing the appeal of logistics, residential, and mixed-use projects. Coastal cities, port hubs, and technology clusters continue to attract strong institutional and private investment due to their connectivity and growth potential, while inland areas face slower progress where infrastructure expansion lags. Overall, the region’s market momentum reflects the interplay between urbanisation, innovation, and strategic infrastructure development, which together shape the geography of opportunity across Asia-Pacific.
Real Estate Market in China
A key driver of China’s market is the government’s large-scale urban renewal initiative aimed at revitalising ageing residential communities. Through these programmes, authorities are upgrading hundreds of thousands of housing units, improving thousands of kilometres of essential utilities, and expanding green and social infrastructure. This transformation is enhancing the quality and livability of urban environments, stimulating demand for modern housing, and attracting both domestic and institutional investment into redeveloped districts. By integrating sustainability, connectivity, and community amenities, these projects are not only improving existing housing stock but also creating new opportunities for mixed-use and commercial developments. As a result, China’s real estate growth is increasingly driven by regeneration and quality enhancement rather than new speculative expansion, positioning the market for more sustainable, long-term value creation.
Real Estate Market in Japan
Japan’s real estate market offers stable and predictable investment opportunities, primarily concentrated in major urban centres such as Tokyo, Osaka, and a few growing regional hubs. The country’s ageing population and continued urban concentration are shaping demand patterns, driving interest in sectors like logistics, data centres, and senior housing, while rural property markets face gradual decline. Urban redevelopment projects, improvements in seismic resilience, and adaptive reuse of existing structures are emerging as key value drivers, reflecting the market’s focus on safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Investors with a long-term perspective are increasingly drawn to core assets in logistics, data infrastructure, and retirement housing, which align with Japan’s demographic trends and its emphasis on resilient, well-connected urban environments.
Real Estate Market in India
India’s market is expanding rapidly, fuelled by urbanisation, rising household formation, and large-scale infrastructure development. Massive investments in transport, housing, and utilities are reshaping cityscapes and unlocking long-term opportunities across residential, logistics, and organised retail sectors. While major metropolitan regions continue to anchor growth, Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities are emerging as vibrant investment destinations as affordability pressures drive decentralisation from megacities. Government policies promoting affordable housing and urban reform are guiding capital flows toward priority regions, though challenges in land acquisition and project approvals persist. Developers capable of building strong local partnerships and efficiently managing regulatory processes are best positioned to capture the country’s sustained real estate growth and evolving urban demand.
Real Estate Market in South Korea
A key driver of South Korea’s market is the nation’s growing focus on smart-city development and digital infrastructure integration. The government’s push toward technologically advanced urban environments is transforming how real estate projects are planned and executed, with emphasis on connectivity, sustainability, and energy efficiency. Smart-city initiatives in regions such as Seoul, Busan, and Incheon are blending real estate with digital innovation using data-driven systems to manage transport, energy, and housing more efficiently. This trend is boosting demand for high-tech commercial spaces, smart residential buildings, and integrated mixed-use developments. As South Korea continues to lead in digital transformation, real estate aligned with smart infrastructure and sustainable design is becoming a preferred investment avenue for both domestic and international investor.
Real Estate Market in Taiwan
Taiwan’s real estate market is centred around Taipei and major industrial hubs, where demand is driven by the strength of the technology and export sectors alongside limited land availability. The country’s position as a global technology leader sustains steady need for modern office, logistics, and industrial spaces located near key manufacturing and innovation zones. Geographic advantages, such as proximity to ports, industrial parks, and advanced digital infrastructure continue to enhance property values in these areas. Developers and investors prioritising high-quality assets with strong locations and ESG or seismic resilience are well positioned to capture stable returns, supported by Taiwan’s robust tech-driven economy and enduring industrial demand.
Real Estate Market in Indonesia
Indonesia’s real estate market is being shaped by large-scale urban regeneration in Jakarta and the rapid rise of secondary cities fueled by expanding manufacturing and service industries. Ongoing infrastructure development, including new roads, ports, and transit systems is opening up peri-urban areas and logistics corridors, driving demand for residential, retail, and industrial spaces near these emerging hubs. The most dynamic growth is occurring across Java and the developing eastern regions, where connectivity improvements are unlocking new investment opportunities. However, challenges such as complex land ownership structures and varying local permitting processes continue to test developers’ execution capabilities. Investors who cultivate strong local partnerships and take a long-term approach are best positioned to capitalize on Indonesia’s evolving urban and regional real estate landscape.
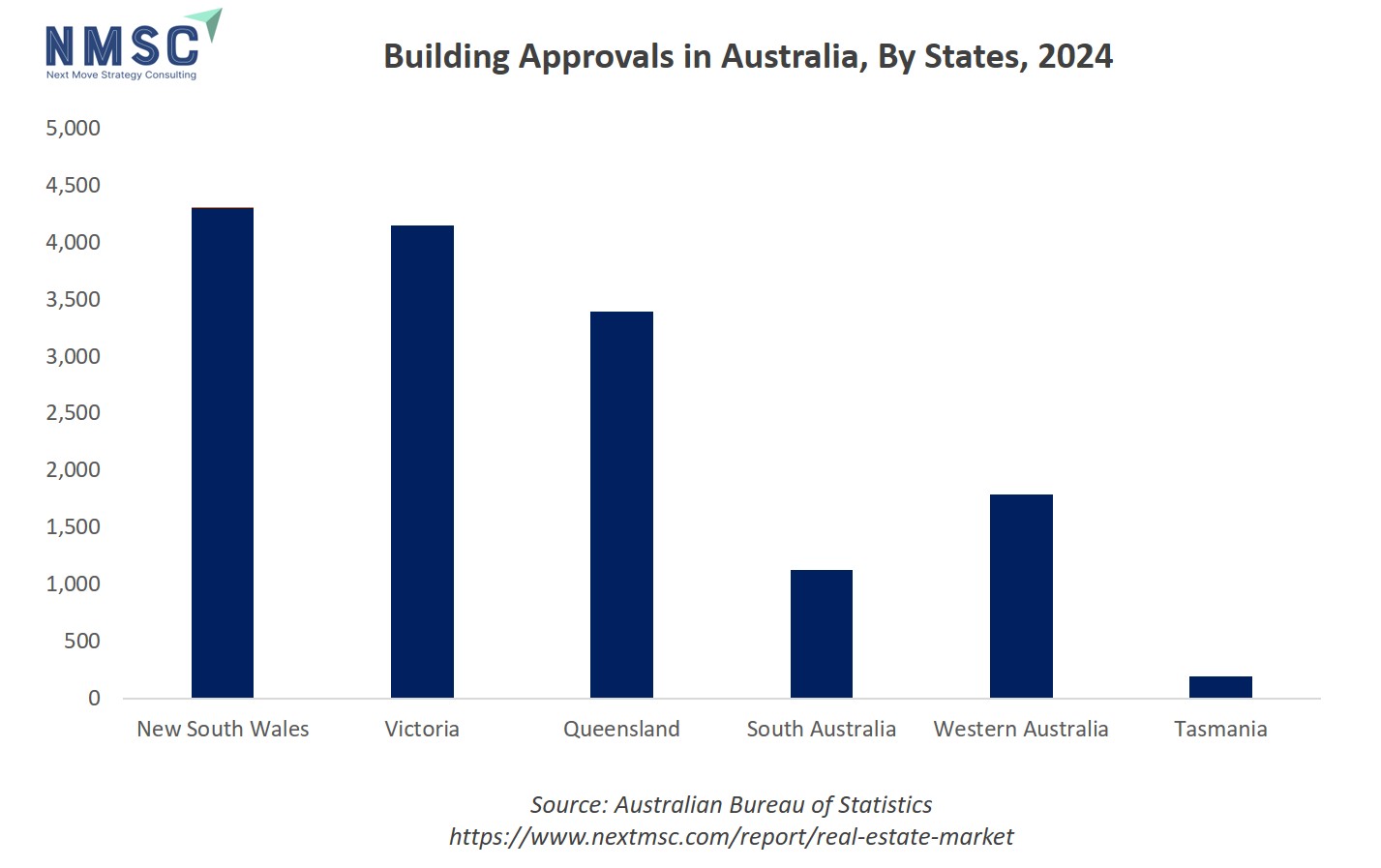
Real Estate Market in Australia
A major driver of Australia’s real estate market is the persistent housing shortage amid a rapidly growing population. As strong migration inflows and natural population growth continue to increase housing demand, the pace of new home construction has struggled to keep up. This imbalance between supply and demand is pushing both property prices and rental rates higher, particularly in major metropolitan areas such as Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane. The shortage is also accelerating investor and developer interest in build-to-rent projects, higher-density housing, and urban infill developments that efficiently meet growing demand. At the same time, government initiatives aimed at boosting housing supply and improving affordability are shaping where new development occurs. Overall, the sustained population growth combined with limited housing availability is reinforcing Australia’s market as a competitive environment focused on addressing long-term structural demand.
Real Estate Market in Latin America
Latin America’s market presents a mix of opportunities and challenges shaped by varying economic and political conditions across the region. Major capital and coastal cities continue to experience strong demand for residential and logistics assets, driven by urban growth, trade expansion, and rising consumer markets. However, broader macroeconomic fluctuations and regulatory uncertainty create execution risks that require careful management. The region’s significant housing and infrastructure needs offer long-term potential, particularly where supportive policies and stable financing environments are in place. Investors are increasingly drawn to sectors such as affordable housing, industrial parks, and logistics hubs, which align with demographic trends and supply-chain growth. Success in the market depends on strategic deal structuring and a deep understanding of local dynamics to mitigate currency, policy, and political risks while capturing sustainable returns.
Real Estate Market in the Middle East & Africa
The real estate market across the Middle East and Africa reflects a highly diverse landscape shaped by differing levels of development and investment maturity. In the Gulf region, well-capitalized economies are driving large-scale projects in tourism, housing, and logistics as part of broader economic diversification efforts. These initiatives are creating vibrant real estate hubs supported by strong government backing and long-term infrastructure planning. In contrast, many African markets are in earlier stages of urbanization, where rapid population growth and expanding cities are generating substantial demand for housing, commercial space, and modern infrastructure. However, these opportunities come with higher execution and political risks. Investors who form partnerships with local developers, government entities, or multilateral institutions and who adopt patient, long-term capital strategies are best positioned to balance risk and reward while capturing the region’s vast development potential.
Competitive Landscape
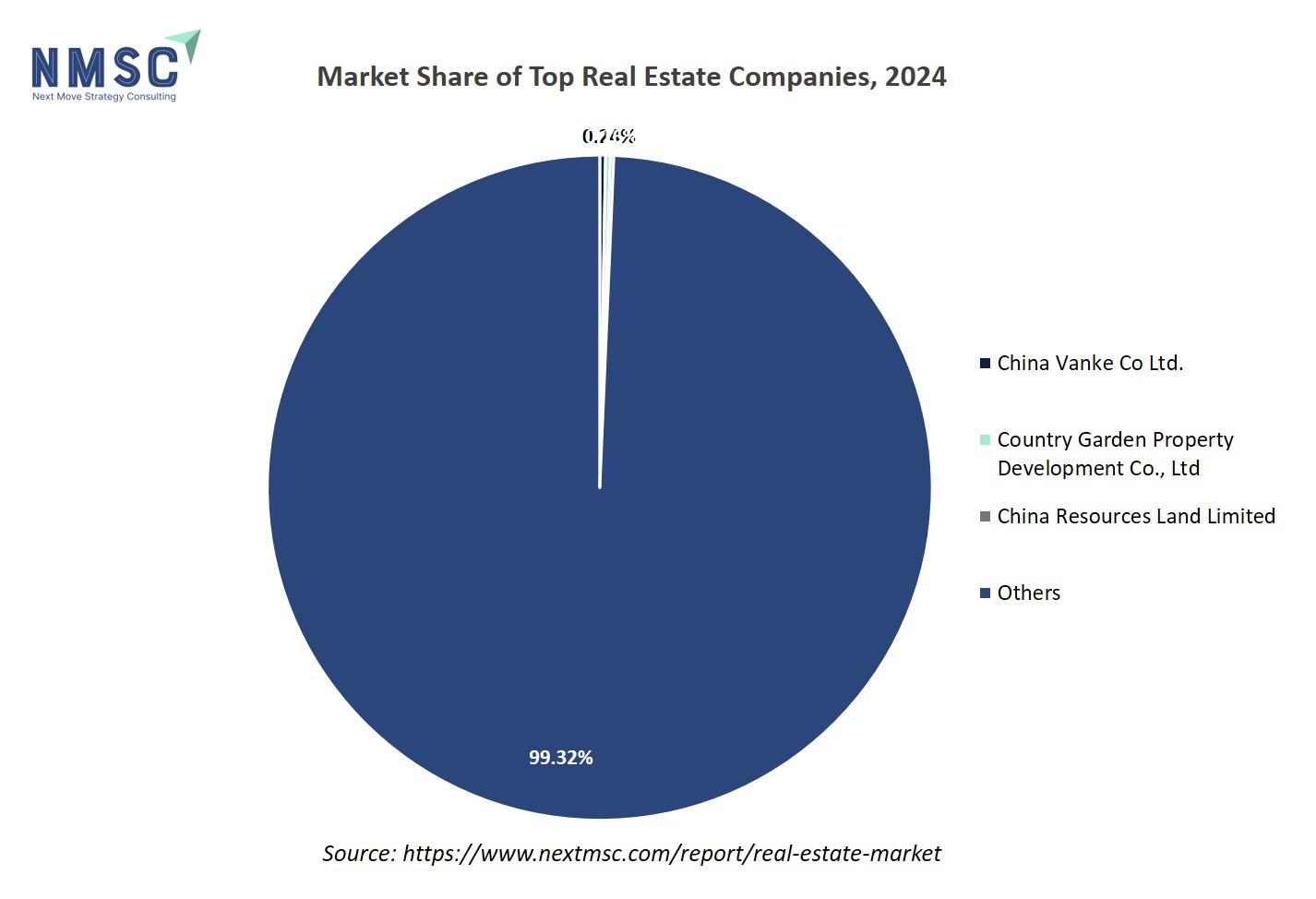
Which Companies Dominate the Real Estate Industry and How do They Compete?
Leading companies in the real estate market, such as China Vanke Co. Ltd., Country Garden Property Development Co., Ltd., and China Resources Land Limited, have established strong positions through large-scale urban development projects and diversified property portfolios. These firms focus on mixed-use developments, sustainable urban planning, and residential communities that cater to growing urban populations. In Asia, particularly China, real estate giants are expanding their footprints beyond traditional housing by integrating commercial, retail, and smart infrastructure components into their developments. Their strategies emphasize digital transformation, green construction practices, and strategic land acquisitions in emerging metropolitan regions, positioning them as key contributors to modern urban growth and sustainable city planning.
Global players such as CBRE Group, Inc., Jones Lang LaSalle IP, Inc. (JLL), Prologis, Inc., and American Tower Corporation are driving the international real estate landscape through investment management, logistics, and digital infrastructure. Companies like Digital Realty Trust and Crown Castle International are at the forefront of data center and communication infrastructure development, aligning real estate growth with the digital economy. Meanwhile, Simon Property Group Inc., Realty Income Corporation, Public Storage, and Vici Properties focus on commercial, retail, and specialized asset classes, leveraging REIT structures to ensure stable returns and portfolio diversification. Collectively, these industry leaders are shaping the global market through innovation, sustainability, and the strategic alignment of physical and digital assets.
Market Dominated by Real Estate Giants and Specialists
The real estate industry is defined by a diverse mix of global leaders and specialized firms, each commanding influence across distinct segments and regions. Prominent developers such as China Vanke Co. Ltd., Country Garden Property Development Co., Ltd., and China Resources Land Limited dominate large-scale urban and residential projects, shaping modern skylines through integrated and sustainable developments. Meanwhile, international firms like CBRE Group, Inc. and Jones Lang LaSalle IP, Inc. (JLL) lead in real estate advisory, asset management, and commercial property services. Infrastructure-focused players such as American Tower Corporation, Prologis, Inc., Crown Castle International, and Digital Realty Trust are transforming the logistics and digital real estate segments through investments in data centers, industrial parks, and communication networks. On the investment side, companies like Simon Property Group Inc., Realty Income Corporation, Public Storage, Vici Properties, and Boston Properties strengthen the market through their diversified REIT portfolios. This blend of developers, service providers, and investment firms fosters competitive innovation, balancing regional expertise with global scalability across the evolving real estate landscape.
Market Players to Opt for Merger & Acquisition Strategies to Expand Their Presence
Merger and acquisition (M&A) strategies have become pivotal for companies aiming to strengthen their position in the real estate market. In 2024 and 2025, key transactions exemplify this trend. For instance, China Vanke Co. Ltd. announced that its subsidiary, Onewo Business Enterprise Space Technology Co., Ltd., would acquire the remaining 55% stake in Shanghai Xiangda Real Estate Development Co., Ltd. for approximately USD 119.99. This move enables Onewo to achieve full ownership of Xiangda and reflects Vanke’s broader strategy to consolidate its operations and streamline business performance. Such strategic acquisitions are becoming increasingly common as real estate developers seek to expand market presence, improve operational efficiency, and diversify their property portfolios to maintain competitiveness in a dynamic global real estate landscape.
List of Key Real Estate Companies
-
China Vanke Co Ltd.
-
Country Garden Property Development Co., Ltd
-
China Resources Land Limited
-
CBRE Group, Inc.
-
Jones Lang LaSalle IP, Inc.
-
Crown Castle International
-
Realty Income Corporation
-
Digital Realty Trust
-
Simon Property Group Inc
-
Public Storage
-
Guangzhou R&F Properties Co., Ltd.
-
Vici Properties
-
Boston Properties
What are the Latest Key Industry Developments?
In June 2024, CBRE Group, Inc. announced plans to merge its project management business with its majority-owned subsidiary, Turner & Townsend, to establish a unified global project management platform. This strategic integration aims to enhance CBRE’s end-to-end service capabilities, combining its deep real estate expertise with Turner & Townsend’s strong infrastructure and construction management proficiency. The move reflects a broader trend in the real estate market, where leading firms are consolidating operations to deliver more comprehensive solutions across property development, construction, and asset management. By leveraging this combined strength, CBRE is positioned to improve efficiency, scale, and value delivery for clients worldwide, further solidifying its leadership in the global real estate and infrastructure landscape.
What are the Key Factors Influencing Investment Analysis & Opportunities in the Real Estate Market?
Investment in the real estate industry is increasingly shaped by evolving urban dynamics, demographic transitions, and sustainability imperatives. Investors are focusing on assets that align with long-term structural trends such as urban regeneration, digital infrastructure, and resilient housing demand. There is a growing preference for portfolios that emphasize environmental performance, adaptive reuse, and smart design integration, as these features enhance long-term value and tenant retention. Institutional and private equity investors are showing strong interest in projects that combine sustainable construction, technology-enabled operations, and flexible mixed-use models, as these offer stable income and adaptability in changing economic environments.
Valuations in the real estate sector are now influenced less by location alone and more by the asset’s ability to generate consistent cash flows, meet ESG standards, and respond to digital transformation. Investment hotspots are emerging in regions undergoing rapid infrastructure expansion, population growth, and regulatory modernization. Developers that incorporate energy-efficient materials, smart-building technologies, and data-driven property management systems are gaining investor confidence. Strategic partnerships between investors, developers, and urban planners are further shaping the next wave of sustainable, high-value developments that balance profitability with long-term social and environmental impact.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
Next Move Strategy Consulting (NMSC) presents a comprehensive analysis of the real estate market, covering historical trends from 2020 through 2024 and offering detailed forecasts through 2030. Our study examines the market at regional and country levels, providing quantitative projections and insights into key growth drivers, challenges, and investment opportunities across all major real estate segments.
The real estate industry offers wide-ranging benefits to stakeholders by aligning economic value with evolving social, environmental, and lifestyle needs. Investors gain from stable, long-term income streams and asset diversification, while developers and builders benefit from expanding opportunities in sustainable urban development and adaptive reuse projects. For businesses and residents, real estate provides access to well-designed, functional, and connected spaces that enhance productivity, comfort, and community well-being. Urban planners and governments also benefit through job creation, infrastructure growth, and improved city resilience. This interconnected ecosystem fosters shared value—where sustainability, innovation, and strategic planning not only drive profitability but also contribute to inclusive urban growth and environmental stewardship across communities.
Report Scope:
|
Parameters |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 25.26 Trillion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 33.61 Trillion |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 5.87% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Analysis Period |
2024–2030 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2030 |
|
Market Size Estimation |
Billion (USD) |
|
Growth Factors |
|
|
Companies Profiled |
15 |
|
Countries Covered |
33 |
|
Market Share |
Available for 10 companies |
|
Customization Scope |
Free customization (equivalent to up to 80 analyst-working hours) after purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Approach |
In-depth primary and secondary research; proprietary databases; rigorous quality control and validation measures. |
|
Analytical Tools |
Porter's Five Forces, SWOT, value chain, and Harvey ball analysis to assess competitive intensity, stakeholder roles, and relative impact of key factors. |
Key Market Segments
By Property Size
-
Small (<500 sq. ft.)
-
Medium (500–2000 sq. ft.)
-
Large (2000+ sq. ft.)
By Property Type
-
Residential
-
Apartments/Flats
-
Single-Family Homes
-
Multi-Family Homes
-
Condominiums
-
Townhouses
-
Vacation Homes
-
-
Commercial
-
Office Spaces
-
Retail Spaces
-
Co-working Spaces
-
Warehouses
-
-
Land
-
Urban Plots
-
Suburban/Rural Plots
-
-
Industrial
-
Manufacturing Plants
-
Distribution Centers
-
Data Centers
-
By Business Type
-
Buying
-
Selling
-
Leasing
-
Renting
-
Real Estate Investment
-
Direct Property Investment
-
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
-
By Ownership
-
Owner-Occupied Properties
-
Rental Properties
-
Co-ownership
By Property Value
-
Affordable Housing
-
Luxury Housing
-
Ultra-Luxury Housing
By End User
- Individual Buyers
-
First-time Homebuyers
-
Repeat Buyers
-
Luxury Buyers
-
Seniors/Retirees
-
-
Business Entities
-
Startups
-
SMEs
-
Large Corporations
-
-
Government
-
Civic Projects
-
Affordable Housing Initiatives
-
-
Institutional Investors
Geographical Breakdown
-
North America: U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
-
Europe: U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Netherlands, and rest of Europe.
-
Asia Pacific: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Indonesia, Vietnam, Australia, Philippines, Malaysia and rest of APAC.
-
Middle East & Africa (MEA): Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Israel, Turkey, Nigeria, South Africa, and rest of MEA.
-
Latin America: Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, and rest of LATAM
Conclusion & Recommendations
Our report equips stakeholders, investors, developers, and consultants with strategic insights to navigate and capitalize on the evolving real estate industry. By combining in-depth analytical frameworks with market intelligence, the NMSC’s real estate market report serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding shifting demand patterns, policy reforms, and sustainability-driven transformation. The market is positioned for long-term growth, supported by trends such as urbanization, digital infrastructure development, and the growing importance of ESG principles. Strategic takeaways emphasize the significance of sustainable construction, adaptive reuse, and smart technologies, as these not only enhance asset performance but also strengthen investor confidence and long-term market resilience. Companies that adopt data-driven design, integrate green certifications, and align with evolving urban needs are better positioned to capture enduring value.
For executives and investors, the path to maximizing opportunities in real estate lies in identifying high-growth corridors, investing in energy-efficient developments, and forming strategic alliances that accelerate project delivery. Emphasizing design innovation, community integration, and long-term maintenance planning enhances both financial performance and social impact. Furthermore, fostering transparency, stakeholder collaboration, and sustainability commitments helps real estate players differentiate themselves in a competitive environment, attract institutional capital, and build trust with end users. This balanced approach positions industry participants to thrive in a market where innovation, adaptability, and responsible growth define success.

















 Speak to Our Analyst
Speak to Our Analyst
























