High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market By Equipment Type (Batch HPP Machines and Continuous HPP Systems), By Vessel Volume (Less than 100 Liters,100-300 Liters and More than 300 Liters), By Pressure Range (Less than 600 MPa, 600 to 800 MPa and More than 800 MPa), By Vessel Orientation (Horizontal and Vertical), By Application (Fruits & Vegetables, Meat & Poultry, and Others), By End-User (Food Processors, Retail & Food service, and Others) – Global Analysis & Forecast, 2025–2030
Industry Outlook
The global High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market size was valued at USD 885.5 million in 2024, and is expected to be valued at USD 1002.3 million by the end of 2025. The industry is projected to grow, hitting USD 1863.1 million by 2030, with a CAGR of 13.2% between 2025 and 2030.
High-pressure processing (HPP) equipment enables non-thermal preservation by applying very high hydrostatic pressure to sealed, packaged foods and beverages, inactivating pathogens and spoilage organisms while preserving fresh-like taste, texture, and nutrients. That capability places HPP squarely at the intersection of food-safety regulation, consumer demand for clean-label/minimally processed products, and manufacturers’ need to extend shelf life without chemical preservatives. As retailers and foodservice operators prioritize fresh-format products (ready-to-eat meals, cold-pressed juices, deli meats, guacamole and dips, etc.), adoption of HPP equipment has broadened from niche processors to larger co-packers and brand owners seeking differentiation and faster market entry.
The equipment market is shaped by a mix of drivers and constraints, capital intensity, floor space and batch throughput limits remain barriers for smaller producers, while scale efficiencies, continuous HPP developments, and rising outsourcing (toll-processing) create growth pathways. Geographically, growth has been strongest where regulatory frameworks reward validated non-thermal interventions and where consumers pay a premium for freshness, but emerging markets are beginning to adopt HPP as cold-chain and retail infrastructure improve. Looking ahead, incremental technology improvements (automation, integration with packaging lines, energy efficiency) plus expanding application categories should sustain steady market expansion, albeit unevenly, while competitive dynamics favor suppliers that can lower total cost of ownership and offer scalable service/support models.
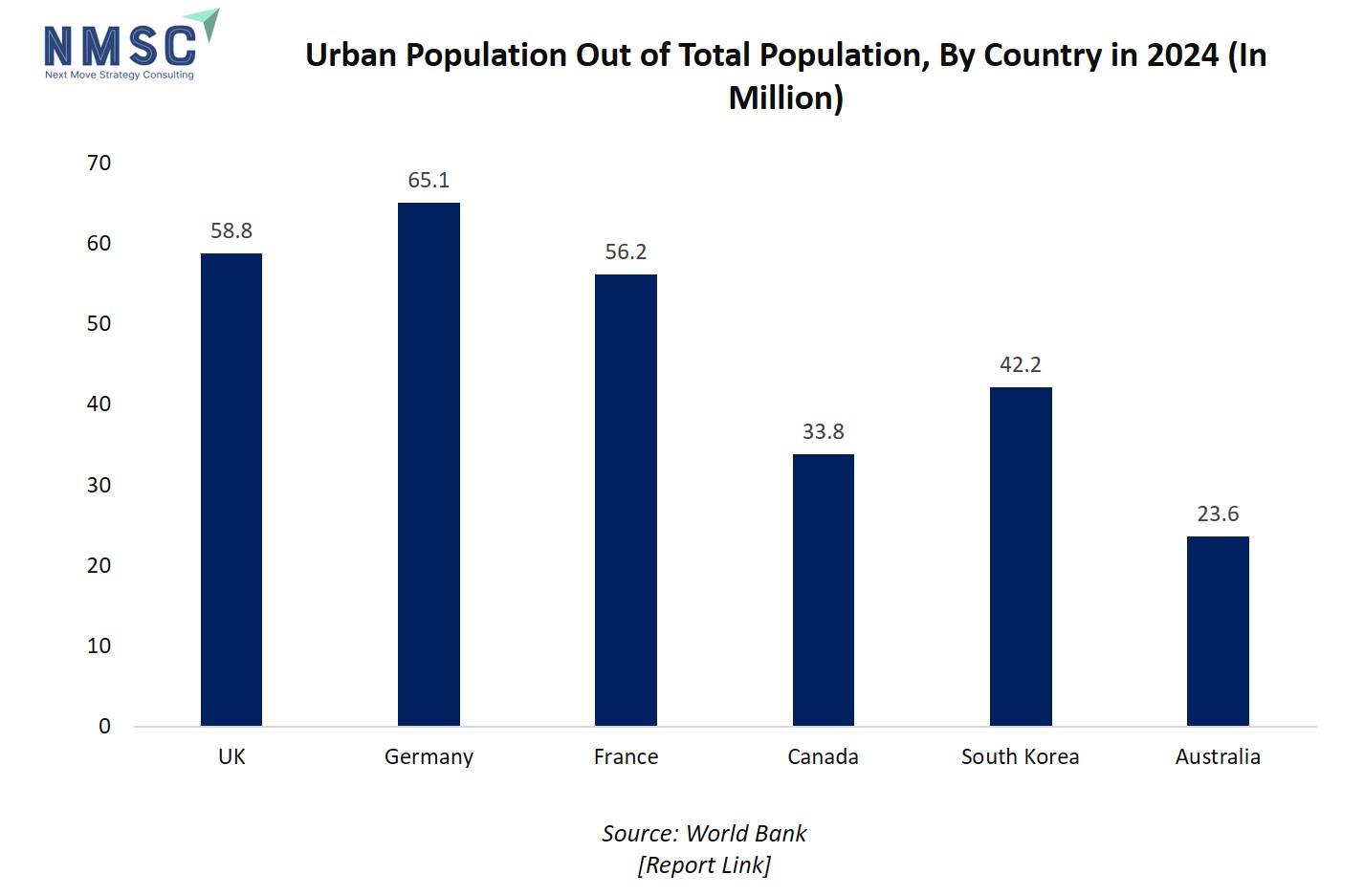
Urban population growth acts as a significant driver for the high-pressure processing (HPP) equipment market by increasing demand for convenient, safe, and longer-lasting food products commonly consumed in urban lifestyles. As more people migrate to cities, their fast-paced living requires ready-to-eat, minimally processed foods with extended shelf life, which HPP technology enables by preserving freshness without preservatives.
The above chart showing urban populations out of total populations by country in 2024 is highly justifiable, as high urbanization correlates strongly with increased demand for processed, convenience, and ready-to-eat foods segments where HPP technology is most commonly applied. Countries like Germany, UK, and France with large urban populations are ideal markets for HPP equipment manufacturers, as food industry players in these regions pursue innovative processing technologies to meet the safety, shelf-life, and quality expectations of urban consumers.
What are the Key High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Industry Trends?
How is High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market Transforming the Industry’s Sustainability and Business-Diversification Story?
Manufacturers of HPP equipment are increasingly positioning the technology not just as a food-safety tool but as a sustainability and industrial-diversification play. A striking example is of Hiperbaric, the long-time leader in food HPP, reported expansion investments and publicly signalled new business lines (notably hydrogen compression and green-tech applications) while still claiming very large share in food HPP installations; that mix of moves shows vendors looking beyond packaged-food to amortize high fixed costs and to lean on HPP engineering strengths. This trend matters because buyers and investors now evaluate equipment suppliers on their energy roadmap, circular-economy thinking and ability to cross-sell services across adjacent industrial uses which shortens payback when capex is high
How is HPP Equipment Market Unlocking New Product Categories and What Does that Mean for Equipment Adoption?
Recent technical and field studies, including producer R&D published in 2024–25 show HPP’s applicability expanding into categories that previously hesitated. Craft and non-alcoholic beers, ready-to-eat meats, plant-based prepared meals and even pet foods. Hiperbaric and JBT/Avure lab programs published product-level results showing extended shelf life and retained sensory/nutritional quality for beverages and many protein formats, which reduces reformulation risk for brands. Practically, that creates a second-order effect on equipment buyers: processors who once used HPP for juice now justify larger or multi-line systems because the same asset can process deli meats on weekday runs and beverages on weekends, improving utilization and ROI.
How is the Rise of Tolling, Co-Packing and Pay-Per-Use Models Changing the HPP Equipment Market Economics?
Because HPP equipment is capital-intensive and requires specific packaging and logistics, the industry has seen rapid growth in tolling (contract HPP) and co-packing networks that let smaller brands access HPP benefits without buying machines. Industry guidance and operator networks describe tolling as the pragmatic first step for many SMEs; toll centers also provide regional scale and smooth demand peaks for system makers. The upshot for equipment manufacturers and investors: build service ecosystems (site selection, packaging validation, shared-use scheduling software and outcome-based contracts) rather than just selling boxes.
How are Throughput, Automation and Modular-Design Improvements in the HPP Equipment Market Lowering TCO and Changing Buyer Requirements?
Vendors and integrators are pushing faster cycles, smarter automation and modular layouts to reduce per-unit cost of HPP and make it compatible with modern fill/pack lines. Large OEMs such as, JBT/Avure now emphasise higher-output models, better CIP/maintenance packages and lab-to-factory services to shorten commissioning time; independent market studies also flag improving CAGR and larger installed base, which creates aftermarket and service revenue that buyers must account for when comparing TCO. For equipment suppliers, the concrete play is to bundle uptime guarantees, predictive maintenance and modular upgrades, so a buyer can start with a smaller machine and scale capacity without a full replacement.
What are the Key Market Drivers, Breakthroughs, and Investment Opportunities that will Shape the High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Industry in Next Decade?
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment is riding a wave of shifting consumer expectations and regulatory changes. People increasingly want fresh, natural, preservative-free foods, and HPP stands out because it can inactivate pathogens without the heat that degrades taste or nutrients. Regulatory authorities are reinforcing food safety standards, giving HPP a clearer path into mainstream supply chains. At the same time, environmental concerns and food waste reduction goals make shelf-life extension more than just a selling point, it has become a sustainability imperative. Recent breakthroughs in equipment efficiency, automation, packaging compatibility, and novel hybrid processes are helping reduce costs and improve adoption, positioning HPP as both a food safety solution and a sustainability enabler for the next decade of global food innovation.
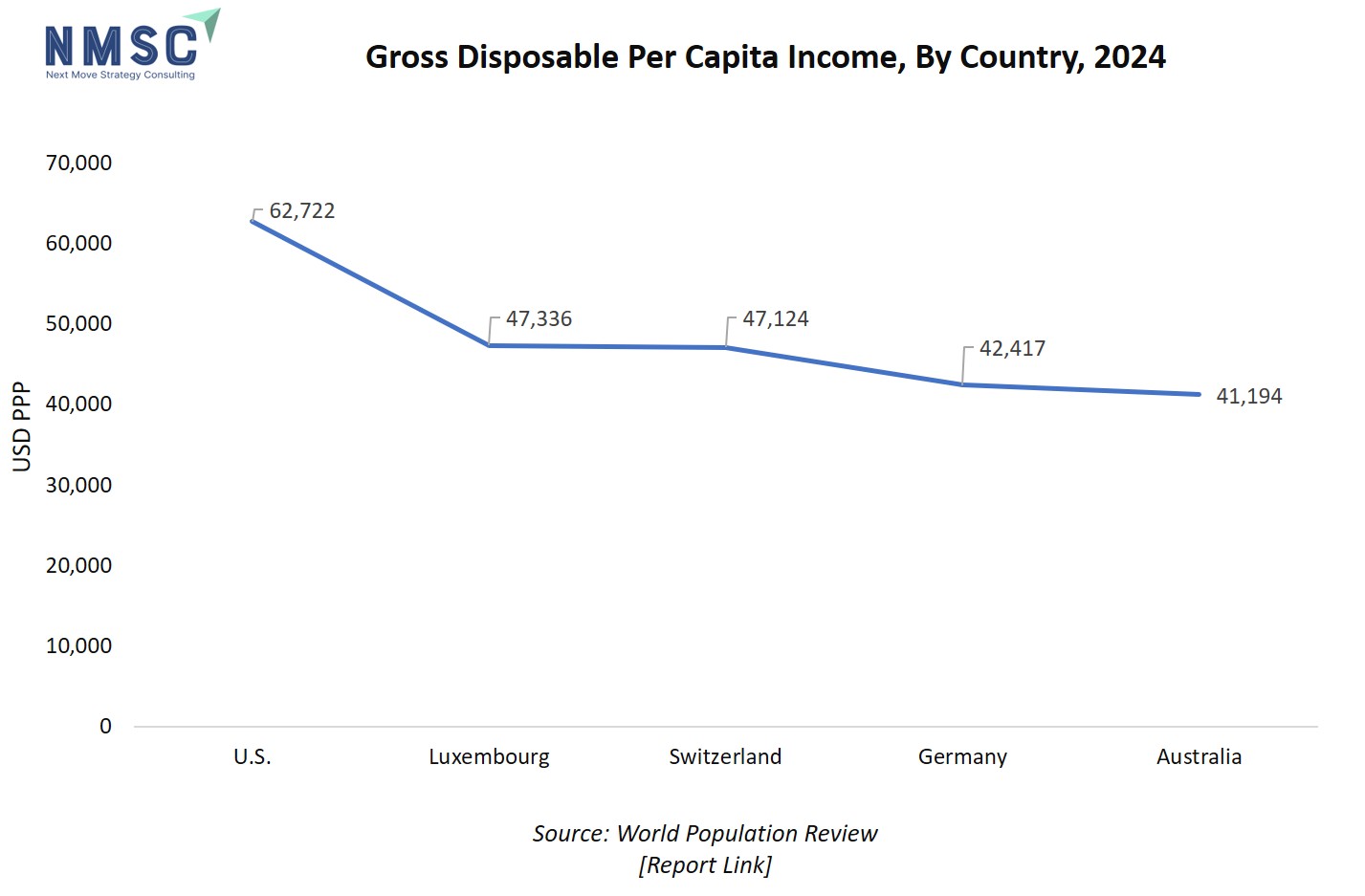
Additionally, the gross disposable income also acts as a key driver for the HPP equipment market by influencing consumers' ability to spend on premium, safe, and convenient food products that leverage HPP technology. Higher disposable incomes enable greater demand for minimally processed, preservative-free, and fresh-tasting foods, which HPP effectively provides by extending shelf life and maintaining nutritional quality. As populations in affluent countries prioritize health and food safety, this spurs food manufacturers to invest in advanced HPP equipment to meet consumer expectations, thereby driving market growth and technological advancements.
The above chart depicting gross disposable per capita income by country in 2024 is highly relevant for the HPP equipment market, as higher disposable incomes directly influence consumer purchasing power and the demand for premium, convenience-oriented, and health-focused food products processed using HPP technology. Markets like the U.S., Luxembourg, and Switzerland with higher per capita income, tend to prioritize food safety, quality, and innovation, encouraging food companies to invest in advanced processing technologies such as HPP. Therefore, regions represented at the higher end of this income spectrum drive both consumer demand for HPP-treated foods and HPP equipment market growth.
Growth Drivers:
How is Consumer Preference for Clean-Label, Minimally Processed Foods Driving HPP Equipment Adoption?
Retail and food service shoppers increasingly prefer preservative-free, fresh-format products. Studies and industry tests show HPP can extend refrigerated shelf life by weeks without heat damage, enabling wider retail distribution and fewer recalls. For example, dairy and juice reviews from 2023–24 highlight consistent microbial reductions and quality retention after HPP treatments. That demand pattern means processors can justify higher COGS for premium positioning if SKU velocity and price premium offset amortized equipment costs
How are Evolving Regulations and Food-Safety Programs Accelerating Investment in HPP Equipment?
Regulatory shifts and USDA/FSIS pilot initiatives to tighten pathogen controls (and proposals targeting reduced Salmonella in poultry) increase the value of validated non-thermal controls like HPP for processors seeking compliance and market access. The USDA’s recent policy activity around pathogen standards and inspection pilots reinforces investment rationale for validated interventions. From a practical perspective, food companies should map upcoming regulatory proposals by product line, then prioritize HPP validation where policy risk (or retailer requirements) could restrict distribution. Working with accredited labs and tollers for compliance data shortens time-to-market and spreads the cost of regulatory validation across SKUs.
Growth Inhibitors:
What Cost, Capacity and Integration Barriers Remain the Biggest Inhibitors to HPP Equipment Adoption?
HPP remains capital- and space-intensive. Buyers face large upfront cost, specific packaging constraints and throughput limits versus continuous thermal lines. OEM literature also flags that while modern designs cut energy per cycle, initial capex, floor-space and changeover complexity are practical inhibitors for SMEs. JBT-Avure documentation highlights modular/expandable designs to lower per-unit cost, but the break-even still depends on utilization. Actionably, processors should treat HPP as a staged decision, run 3–6 month toll-trials to measure real throughput, packaging yield and distribution lifts; only pursue ownership when projected utilization and service agreements (spare parts, training) drive payback within an agreed horizon.
Where are the Most Attractive Emerging Investment Opportunities in the HPP Equipment Ecosystem?
Beyond selling machines, OEMs and investors are finding higher-margin opportunities in services such as, regional tolling hubs, outcome-based contracts, modular upgrades and cross-industry applications, like, Hiperbaric’s hydrogen-compression line generated ~10% of 2024 turnover as the company diversified. Building service ecosystems (pack validation, scheduling platforms, predictive maintenance) increases recurring revenue and reduces seasonality. A practical entry play is to develop a regional tolling site or partner with an existing toller, bundle packaging validation and short-term contracts, and pilot a pay-per-use model, this converts large capex into service revenue and opens clear KPIs (utilization, yield, churn) that investors can value.
How is the High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market is Segmented in this Report, and What are the Key Insights from Segmentation Analysis?
By Equipment Type Insights
How is the HPP Equipment Market Shaped by Batch and Continuous Systems?
Based on equipment type, the HPP equipment market is segmented into batch HPP machines, and continuous HPP systems.
Batch HPP systems continue to dominate the global landscape in 2025, accounting for the majority of installed capacity worldwide. Their success lies in operational flexibility, allowing processors to handle a wide range of SKUs, packaging types, and product categories such as ready-to-eat meals, dips, seafood, and pet food. These machines require lower upfront investment compared to continuous systems, making them more accessible for small and mid-sized processors as well as tolling service providers.
Continuous HPP systems, while still emerging, are gaining attention in high-volume applications such as juices, smoothies, and dairy alternatives where standardized liquid processing enables rapid throughput. These systems are particularly appealing to large beverage companies and global co-packers seeking to minimize per-unit cycle time and labor costs. Although their capital intensity remains a barrier, technological advancements are narrowing the cost gap, with manufacturers investing in automation and energy recovery systems to improve ROI.
By Vessel Volume Insights
Which Vessel Volume is Emerging as the Most Flexible in the HPP Market?
Based on vessel volume, the HPP equipment market is segmented into less than 100 liters, 100 to 300 liters and more than 300 liters.
Vessel volumes below 100 liters and between 100–300 liters dominate adoption among tolling centers, small-scale processors, and startups testing new SKUs. These vessels provide flexibility to process multiple product types without committing to large-scale capital expenditure. Small and medium vessels are particularly popular for specialty RTE foods, plant-based products, and premium juices, where batch diversity and package size variation are critical. Their moderate cost and compact footprint allow processors to enter the HPP market with lower risk while achieving regulatory compliance for pathogen reduction and shelf-life extension.
Vessels exceeding 300 liters are preferred by high-throughput processors and exporters, particularly in beverages, juices, and bulk liquid foods. Large vessels allow for higher per-cycle throughput, reducing labor and per-unit energy costs, which is critical for industrial-scale operations. These systems are often combined with automation, such as robotic loading, palletizers, and clean-in-place (CIP) solutions, to maximize efficiency. Adoption is strongest in mature markets such as the U.S., Europe, and Japan, where regulatory compliance, product consistency, and export requirements justify the investment.
By Pressure Range Insights
How is the High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market Shaped by Pressure Range Segmentation?
Based on pressure range, the HPP equipment market is segmented into less than 600 MPa, 600 to 800 MPa, and more than 800 MPa.
HPP systems operating below 600 MPa dominate the market due to their ability to inactivate vegetative bacteria, yeasts, and molds in most food products without affecting taste, texture, or nutrients. This pressure range is sufficient for applications like juices, RTE meals, deli meats, seafood, and plant-based products, which form the bulk of HPP adoption globally. These systems are favored by tolling centers, small-to-medium processors, and brands entering the HPP market due to lower capital and operational costs.
Pressures in the 600–800 MPa and above 800 MPa range are typically deployed for more demanding applications, including extended shelf-life beverages, high-risk protein products, or sterilization of certain low-acid foods. While adoption is less widespread due to higher equipment costs and engineering complexity, these high-pressure systems are gaining traction among industrial-scale beverage producers, seafood processors, and exporters targeting international markets with strict safety and shelf-life requirements. Continuous innovation, such as reinforced vessel designs and energy-efficient pumping, is expanding the feasibility of ultra-high-pressure HPP. This segment represents a growth opportunity for OEMs supplying premium, high-throughput installations, particularly in mature markets like the U.S., Japan, and Western Europe.
By Vessel Orientation Insights
How are Horizontal and Vertical Vessel Orientation Driving the High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market?
Based on vessel orientation, the HPP equipment market is segmented into horizontal and vertical.
Horizontal HPP vessels dominate the global market due to their operational flexibility and ease of handling packaged foods. They are ideal for batch processing of diverse SKUs, including RTE meals, deli meats, seafood, and plant-based products, as baskets can be loaded and unloaded efficiently. Horizontal orientation also simplifies integration with existing production lines and supports modular automation, such as palletizing and robotic handling.
Vertical vessels, while less common, are valued in facilities with constrained floor space or for high-throughput industrial applications. They allow processors to optimize facility layout, particularly in multi-story plants or compact production environments. Vertical orientation is often paired with continuous or semi-continuous systems for liquids, such as juices or sauces, where consistent loading and pressure distribution are critical. This configuration is gaining traction in beverage-centric markets and export-oriented plants, especially in Europe and Asia-Pacific, where space efficiency and throughput justify the higher engineering complexity.
By Application Insights
How are Fruits & Vegetables, Meat & Poultry, Pharmaceuticals, and Other Sectors Fueling Growth in the HPP Equipment Market Demand?
Based on application, the HPP equipment market is segmented into fruits & vegetables, meat & poultry, seafood, dairy & alternatives, juices & beverages, ready-to-eat meals/sauces, pharmaceuticals/biotech, cosmetics and other.
The majority of HPP adoption is concentrated in food and beverage applications, including fruits & vegetables, meat & poultry, seafood, dairy & alternatives, juices & beverages, and ready-to-eat meals or sauces. HPP preserves sensory qualities and extends shelf life while ensuring microbial safety, making it highly attractive for these perishable categories. Fruits, vegetables, and plant-based products benefit from minimal nutrient loss, while seafood and meat see improved safety and export potential. Juices and beverages increasingly adopt HPP to meet consumer demand for preservative-free, fresh-tasting drinks.
Beyond food, HPP finds applications in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, cosmetics, and other specialty sectors. In pharmaceuticals and biotech, HPP is used for the sterilization of temperature-sensitive formulations without chemical preservatives. Cosmetics and personal care products leverage HPP to maintain natural ingredients while preventing microbial growth. Although currently a smaller share of the overall market, these segments represent high-margin growth opportunities, particularly in regions like North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific where regulatory and consumer standards encourage minimally processed, contaminant-free solutions.
By Sales Channel Insights
How are Direct Sales, Distributors/Dealers, Online Sales, and Aftermarket Services Driving the High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market Growth?
Based on sales channel, the HPP equipment market is segmented into direct sales, distributors/dealers, online sales, and aftermarket services.
Direct sales and distributor/dealer networks remain the backbone of HPP equipment adoption. OEMs such as Hiperbaric, JBT, and MULTIVAC leverage direct sales to maintain strong customer relationships, provide technical support, and tailor equipment to client-specific needs. Distributors and dealers help extend reach into regions where OEMs lack local presence, enabling small and mid-sized processors to access HPP technology.
Convenience stores provide critical visibility for single-serve HPP beverages, snacks, and small meal kits, catering to on-the-go consumption. Their limited shelf space emphasizes high-turnover items, making HPP juices, smoothies, and dips attractive offerings.
Online sales channels and aftermarket services are becoming increasingly influential in shaping adoption patterns. Online platforms simplify initial inquiry, provide detailed product specifications, and allow buyers to compare models efficiently, which is particularly valuable for SMEs exploring HPP. Aftermarket services, including preventive maintenance, retrofitting, spare parts, and training, enhance equipment uptime and extend operational life, making HPP adoption more cost-effective.
By End-User Insights
How are Key End Users Driving Adoption and Growth in the High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market?
The end-user segmentation includes Food Processors, Retail & Foodservice, CPG & contract packagers, pharma & biotech manufacturers, cosmetics & personal‑care manufacturers and R&D / testing labs.
Food processors, retailers, and CPG/contract packagers represent the primary engine of HPP adoption. Food processors leverage HPP to extend shelf life, ensure microbial safety, and maintain flavor and nutritional integrity in categories like juices, seafood, ready-to-eat meals, and plant-based products. Retailers and foodservice operators drive demand by seeking safe, fresh-tasting products with longer shelf life, encouraging processors to invest in both in-house systems and tolling services.
Pharmaceutical and biotech manufacturers, cosmetics and personal-care producers, and R&D/testing labs are emerging end-users for HPP systems. In pharmaceuticals and biotech, HPP sterilizes temperature-sensitive formulations without chemical preservatives, while cosmetics maintain natural ingredient integrity and safety. R&D labs adopt HPP for experimental validation, pilot testing, and process optimization. Although smaller in volume than food applications, these sectors offer high-margin growth opportunities and encourage OEMs to develop specialized vessels, automation, and process validation protocols to meet strict regulatory standards and consumer expectations.
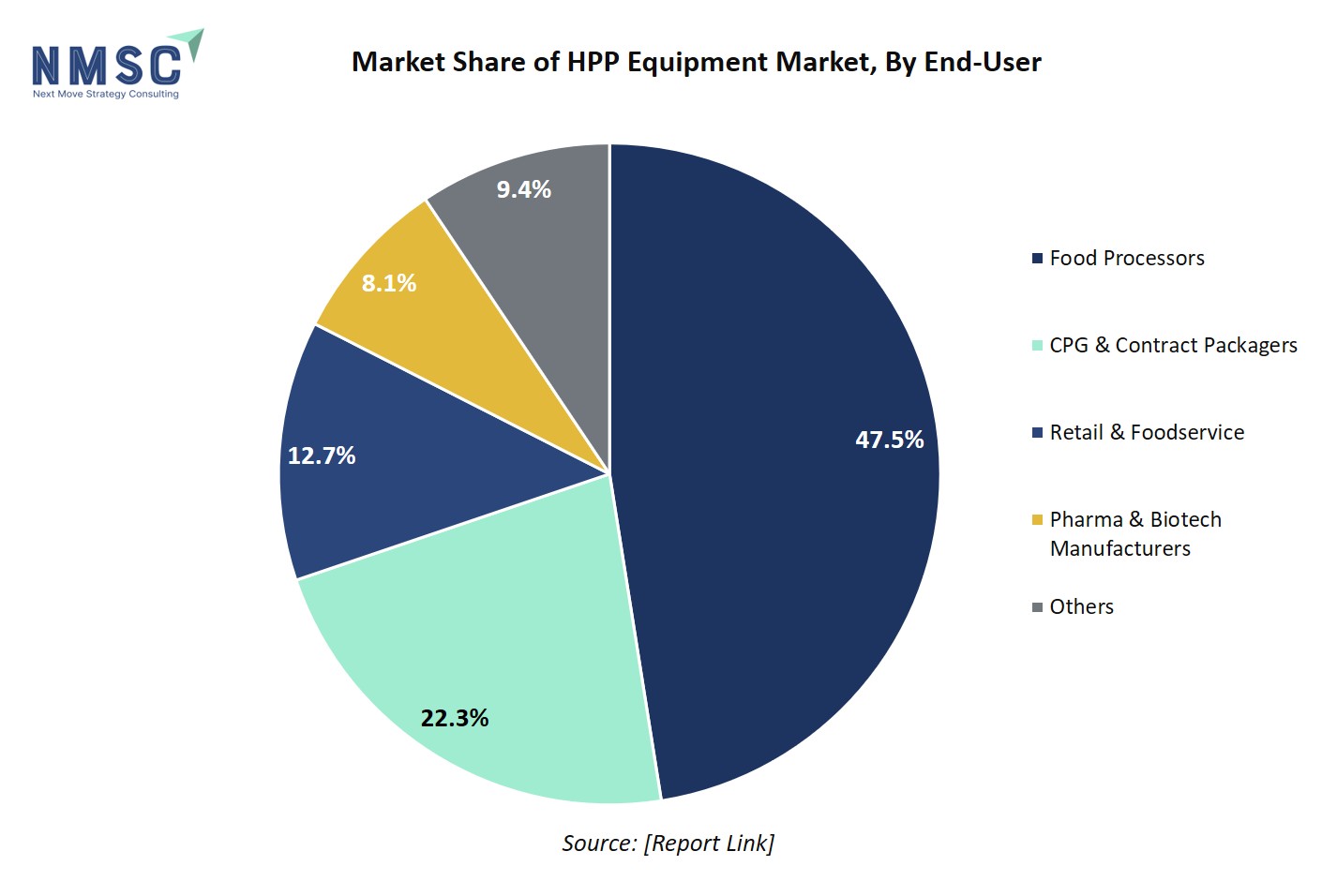
The chart shows the market share of the high-pressure processing (HPP) equipment market by end-user, with Food Processors leading at 47.5%, followed by CPG & Contract Packagers at 22.3%, Retail & Foodservice at 12.7%, Pharma & Biotech Manufacturers at 8.1%, and Others at 9.4%. This distribution highlights that the largest HPP equipment demand comes from food processors who require advanced technology to extend shelf life and ensure food safety without compromising quality, which drives significant investments in HPP machinery. The substantial share held by CPG & Contract Packagers indicates strong growth potential driven by packaged food markets, while the presence of retail, foodservice, and pharmaceutical sectors points to diversified applications supporting the broad adoption of HPP technology. Consequently, this varied end-user base fuels sustained growth in the HPP equipment market, underpinned by increasing consumer demand for fresh, preservative-free foods and stringent food safety regulations globally.
Regional Outlook
The market is geographically studied across North America, Europe, the Middle East & Africa, and Asia Pacific, and each region is further studied across countries.
Government Initiatives Supporting HPP Equipment Market Growth, By Region:
|
Region/Country |
Initiative / Policy |
Focus Area |
|
USA |
USDA HPP Pilot Program |
Advance research and extension activities in food safety |
|
India |
Atmanirbhar Bharat |
Promotes self-reliance in the food processing sector |
|
European Union |
FutureFoodS Partnership |
Focused on transforming food production towards sustainable and resilient systems |
Source: USDA REEIS, Ministry of Food Processing Industries, FutureFoodS
Next Move Strategy Consulting
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in North America
North America leads HPP adoption because of tight food-safety expectations, mature retail channels that value fresh/clean-label products, and a dense tolling/co-packing network that makes HPP accessible to SMEs. In the U.S., regulatory activity, for example, USDA proposals on Salmonella limits in raw poultry in 2024 and long-standing FDA recognition of HPP for shellfish create both compliance and commercial incentives for meat, juice and seafood processors. Canada reflects the same dynamic but with quicker tolling adoption.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in the United States
The U.S. HPP equipment market combines regulatory pressure, retailer demand, and established OEM service networks, which together accelerate HPP investment for high-value categories (RTE meats, juices, seafood, pet food). JBT/Avure and other suppliers emphasize integrated service and predictive maintenance to shorten commissioning and uptime; JBT resources describe HPP’s role in meat/poultry safety and shelf-life. The USDA’s public policy work on pathogen control (see the Salmonella framework) increases urgency for validated non-thermal controls and makes tolling a pragmatic route for many brands to meet retailer and regulatory specs. That regulatory-commercial nexus drives equipment uptake where scale economics make sense.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Canada
Canada’s HPP story is shaped by early adopters in seafood and plant-based sectors and a strong tolling culture. Hiperbaric documents early installations dating to the 2000s and notes that its machines account for a large share of Canadian HPP capacity; Health Canada’s regulatory stance has allowed established HPP-processed foods to move without prior-notification in some cases, lowering friction for commercialization. The country’s geography and export orientation (seafood, prepared foods) make regional tolling hubs attractive; Canadian processors often use tolling to test export-ready SKUs before investing in their own presses.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Europe
Europe features advanced adoption across food categories, strong OEM presence, and growing vertical integration between packaging and HPP. Hiperbaric’s USD 4.2 million facility expansion and ongoing R&D underline Europe’s innovation base. Also, MULTIVAC’s majority stake in Italianpack in Aug 2024 highlights packaging–HPP convergence that eases line integration for processors. Overall, Europe’s regulatory frameworks, premium consumer segments and established service networks make it a leader in both equipment sophistication and tolling scale.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in the United Kingdom
The UK combines rigorous food-safety science and active FSA research into non-thermal technologies, which encourages cautious but steady HPP adoption in chilled meats, juices and RTE segments.Tolling centers and packaging integrators are enabling new entrants in beverages and premium chilled goods; processors often use UK tolling to validate labeling, shelf life and retailer acceptance before committing to capital investment.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Germany
German demand is driven by engineering-led OEMs and integration with large food and packaging systems. Thyssenkrupp’s Uhde High Pressure Technologies promotes industrial-scale HPP solutions and positions the country as a hub for heavy-duty, customized presses suitable for large processors. The result is that German processors who prioritize throughput and integration buy larger, service-backed systems, while regional specialists supply lower-cost or niche configurations.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in France
France shows strong tolling network maturity and specialty-category growth. HPP Atlantique is an example of a high-capacity toller that scaled to become France’s largest HPP treatment centre. French artisan and premium-food producers favor HPP for pâtés, RTE meats and cold-pressed beverages; tollers accelerate startups and exporters without large upfront capital.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Spain
Spain is both a technology exporter and a local adoption market. Spanish OEM leadership translates into an outsized installed base regionally and growing export of HPP expertise and tolling models to Europe and Latin America. Hiperbaric continues to invest in capacity and R&D, reinforcing Spain’s role as an HPP engineering center.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Italy
Italy’s food-processing and packaging ecosystem supports HPP adoption in premium ready meals, deli meats and seafood value chains. MULTIVAC’s acquisition of Italianpack signals tighter packaging–HPP coupling, simplifying commissioning for processors that want validated end-to-end lines. Regional M&A and partnerships are smoothing integration and shortening time-to-market for HPP-treated SKUs.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Asia Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing HPP region because of rising middle-class demand for fresh, exportable foods and rapid retailer modernization. Hiperbaric opened a Shanghai office and an HPP incubator there in 2024 to accelerate local sales, tolling partnerships and pilot validation. China’s scale plus increased urban consumption patterns mean significant growth for tolling hubs and for OEMs that localize service. The practical impact is clear, Asia-based tollers and pilot plants reduce market entry friction and accelerate SKU validation for regional brands and exporters.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in China
China’s retail and export orientation makes HPP attractive for juices, RTE seafood and premium ready meals. Local OEMs and tollers are emerging to meet domestic demand, often at lower price points, but global OEMs are establishing service footprints to support multinational food companies.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Japan
Japan’s HPP use is long-standing in seafood and ready-to-eat applications; HPP shucking and seafood processing are notable use-cases. Industrial partnerships, such as, Kobe Steel’s acquisition of Quintus tie domestic engineering strength to HPP capabilities, reinforcing Japan’s position for high-quality, process-intensive HPP systems. The result is robust OEM competence and conservative but steady adoption among processors focused on export quality and shelf-life.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in India
India’s HPP adoption is nascent but emerging where exporters, premium beverage makers and pet-food brands seek shelf-life extension for urban and export markets. Companies have signalled intent for Indian market engagement and cold-isostatic technology expansion, indicating OEMs see India as strategic but practical barriers remain, such as, capex, cold chain and packaging specs, but tolling or partnership models are likely early-stage routes for Indian brands to adopt HPP affordably.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in South Korea
South Korea shows growing interest in HPP for convenience foods and premium pet food; manufacturers and tollers are investing in pilot capacity while Korean OEMs and importers support local processors. Industry reports and regional market analyses point to increased demand driven by food safety norms and consumer preference for minimally processed products. The practical effect is a mixed landscape where tollers and a few in-house adopters will lead initial growth.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Taiwan
Taiwan’s HPP activity centers on seafood, beverage and niche RTE segments; OEMs supply pilot equipment to research institutions and exporters. HPP is used to meet export standards for fresh seafood and to extend local product shelf life for urban retail channels. Company incubators and HPP events help raise technical familiarity and supplier networks in Taiwan.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Australia
Australia’s adoption is led by premium meat, RTE meals and seafood exporters who need validated safety and shelf-life for distant markets. HPP tolling and OEM service support are available, and industry conversations increasingly link HPP to sustainability and waste-reduction goals. Company’s global events and case studies often reference Australia in broader Asia-Pacific outreach.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in Latin America
Latin America is an expansion frontier for HPP thanks to abundant raw materials (fruit, seafood), export potential, and growing premium domestic demand; Hiperbaric documents adoption across Chile, Peru, Brazil and Colombia and traces the region’s first HPP installs back to the mid-2000s. Tolling networks and partnerships with European OEMs are the most common early-stage adoption route, helping exporters meet shelf-life and safety standards required by overseas buyers.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market in the Middle East & Africa
Adoption in the Middle East & Africa is uneven but growing where cold-chain improvements, tourism and retail modernization push demand for fresh, high-quality convenience foods. Industry coverage and HPP vendor outreach show early tolling and project activity in Gulf states, often focused on juices, RTE chilled foods, and prepared seafood. The main constraints remain cold-chain reliability and upfront investment capacity, so tolling and shared-use models are the most practical near-term routes to adoption.
Competitive Landscape
Who are the Leading Companies in the High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market and How are they Competing?
The global HPP equipment market is shaped by a handful of dominant players and a long tail of regional specialists. Hiperbaric S.A. remains widely recognized as a pioneer and global leader, with more than 350 units installed worldwide and a strong emphasis on R&D and tolling support. JBT Corporation, through its Avure Technologies unit, combines its established food processing footprint with HPP innovation, while also leveraging acquisitions like Urtasun to broaden its offering.
Quintus Technologies AB and Thyssenkrupp’s Uhde High Pressure Technologies bring deep engineering know-how and robust system design to the HPP equipment market, competing on reliability and industrial scalability. Meanwhile, companies such as MULTIVAC, Kobe Steel, and Resato International are strengthening their portfolios by integrating HPP with packaging, automation, and industrial process systems. Competition is driven less by price and more by proof of safety, performance validation, service reach, and global technical support.
Competition is fueled by strategic collaborations with retailers, scaling regional tolling centers, and adopting advanced packaging solutions to maintain product quality and shelf-life. Investments in automated HPP systems, cold-chain optimization, and process validation further strengthen market positions. Additionally, companies are emphasizing ESG compliance, sustainable sourcing, and consumer education, reinforcing brand trust and long-term market leadership.
Market Dominated by HPP Equipment Giants and Specialists
Competition in the HPP equipment space is unevenly distributed, with global giants commanding most of the high-value contracts and regional specialists filling cost-sensitive niches. In North America and Europe, food companies generally gravitate toward Hiperbaric, Avure (JBT), and Quintus because of their validated safety data, global service infrastructure, and regulatory expertise. These firms dominate high-throughput applications such as ready-to-eat meats, juices, and dips. In contrast, Asian markets, particularly China, have seen the rise of local suppliers like Bao Tou KeFa, Guangzhou Jingye, and Pengneng Machinery, who compete primarily on affordability and accessibility. Packaging integration players like MULTIVAC compete in specialized niches where food safety and line efficiency are equally important. This dynamic creates a tiered market where large-scale processors rely on proven global OEMs, while regional brands and SMEs often adopt smaller-scale, cost-efficient systems from domestic suppliers.
Innovation and Adaptability Drive Market Success
Innovation is a critical differentiator in the HPP equipment market, as customers demand higher throughput, lower costs, and greater packaging flexibility. Hiperbaric has focused heavily on R&D, launching improved vessel designs, automation systems, and new R&D centers while simultaneously diversifying into hydrogen compression technology to spread risk and expand into sustainable energy markets. Similarly, Quintus has rolled out modular press systems designed for scalability, allowing companies to invest incrementally rather than commit to oversized systems at the start, while MULTIVAC’s innovation strategy centers on integrating HPP units into packaging and automation solutions, streamlining food safety with end-of-line efficiency. JBT, through Avure, is emphasizing global service support, predictive maintenance, and integration with its wider food processing equipment portfolio. In all cases, adaptability, whether through hybrid processes, service models, or equipment scalability, is proving to be the most effective strategy to maintain leadership in a competitive, capital-intensive market.
Market Players to Opt for Merger & Acquisition Strategies to Expand their Presence
Mergers and acquisitions are playing a key role in shaping competition across the HPP equipment landscape. JBT Corporation’s acquisition of Avure Technologies provided it immediate leadership in HPP and complemented its existing processing lines, while its later acquisition of Urtasun expanded its fresh produce equipment footprint. Kobe Steel’s acquisition of Quintus Technologies strengthened its position in isostatic pressing and high-pressure systems, diversifying its engineering portfolio beyond steel. Similarly, MULTIVAC has also pursued inorganic growth, acquiring a majority stake in Italianpack S.p.A. to expand its packaging and integrated processing solutions. These moves highlight a consistent strategy: expand capabilities, gain access to new customer bases, and strengthen service networks. Looking ahead, mid-tier players may also pursue consolidation to remain competitive against dominant suppliers, while global OEMs continue to look for synergies in packaging, automation, and industrial high-pressure applications.
List of Key High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Companies
-
JBT Corporation (Avure Technologies & Urtasun)
-
Thyssenkrupp AG (Uhde High Pressure Technologies)
-
MULTIVAC Sepp Haggenmuller SE & Co KG
-
Kobe Steel, Ltd.
-
Quintus Technologies AB
-
Bao Tou KeFa High Pressure Technology Co., Ltd.
-
CHIC FresherTech
-
Stansted Fluid Power Ltd.
-
HP TECH
-
Klockner Hansel Processing GmbH
-
HTSM
-
Chuntian Machinery Technology Co., Ltd. (HiLock)
-
Idus HPP Systems S.L.U.
-
Hydrolock (Steribar HPP)
-
Resato International B.V.
-
Pengneng Machinery
-
Guangzhou Jingye Machinery Co Ltd
-
Xiamen Ollital Machinery Equipment Co Ltd
-
Zhengzhou Zhuozhihao Mechanical Equipment Co., Ltd.
What are the Latest Key Industry Developments?
-
October 2024 - Quintus Technologies launches the QIF 600L, the industry’s largest-capacity HPP press (600 L), targeting processors needing higher vessel capacity and improved loading efficiency; this product widens buyer choice for larger-scale operations and pressures rivals to offer bigger, modular solutions.
-
October 2024 – Hiperbaric announces a USD 4.2 million facility expansion as it marks 25 years, citing a dominant installed base and investments to scale production and R&D; that capital push aims to shorten lead times and support global demand for higher-efficiency HPP systems.
-
August 2024 - MULTIVAC Group acquires an 80% majority stake in Italianpack S.p.A., extending its packaging and integrated processing offering; this M&A deepens line-integration capabilities for HPP customers seeking combined packaging–HPP solutions and improved end-of-line efficiency.
-
June 2024 – Hiperbaric opens a new Shanghai office (Free Trade Zone) to accelerate sales, service and tolling partnerships across China’s growing HPP food market; the move strengthens local support, speeds commissioning and signals intensified competition for regional suppliers.
-
January 2024 – JBT (Avure) debuts a larger HPP basket to boost per-cycle loading and throughput, helping processors increase volume without wholesale line replacement; this pragmatic throughput upgrade reduces per-unit processing costs and shortens payback for mid-size co-packers expanding HPP capacity.
What are the Key Factors Influencing Investment Analysis & Opportunities in High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment Market?
Investment activity in the high-pressure processing (HPP) equipment market is increasingly shaped by food safety regulations, sustainability goals, and consumer demand for minimally processed foods. Funding is flowing toward companies that can scale cost-effective systems, improve energy efficiency, and expand capacity for co-packing services. Venture and private equity investors are targeting HPP tolling centers in North America and Europe, which are viewed as low-barrier entry points for smaller food brands without the capital for in-house machines.
Valuations remain attractive in high-growth niches like plant-based proteins, premium beverages, and pet food, where HPP extends shelf life and preserves nutritional value. Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, is emerging as a hotspot, with recent expansions, for example, Hiperbaric’s Shanghai office signaling strong regional potential. For investors, this combination of technology scalability, regulatory tailwinds, and emerging market adoption positions HPP as a compelling mid-to-long-term play in food-tech infrastructure.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
Next Move Strategy Consulting (NMSC) presents a comprehensive analysis of the global high-pressure processing (HPP) equipment market, covering historical trends from 2020 through 2024 and offering detailed forecasts through 2030. Our study examines the market at global, regional, and country levels, providing quantitative projections and insights into key growth drivers, challenges, and investment opportunities across all major High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Equipment segments.
The high-pressure processing (HPP) equipment industry creates distinct benefits across stakeholders. Investors gain exposure to a technology-driven market with resilient demand, supported by growth in premium foods, beverages, and pet nutrition, where HPP adds tangible value through safety and shelf-life extension. Policymakers benefit as HPP aligns with public health priorities, reducing foodborne illness risk and supporting national sustainability targets by cutting food waste and reliance on chemical preservatives. Customers, from food manufacturers to end consumers, enjoy fresher, cleaner-label products that retain nutrients and flavor while meeting modern safety standards. This convergence of financial returns, regulatory alignment, and consumer trust makes HPP an industry where multiple stakeholders advance their goals simultaneously.
Report Scope:
|
Parameters |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 1002.3 Million |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 1863.1 Million |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 13.2% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Analysis Period |
2024–2030 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2030 |
|
Market Size Estimation |
Million (USD) |
|
Growth Factors |
|
|
Countries Covered |
28 |
|
Companies Profiled |
15 |
|
Market Share |
Available for 10 companies |
|
Customization Scope |
Free customization (equivalent up to 80 analyst-working hours) after purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Approach |
In-depth primary and secondary research; proprietary databases; rigorous quality control and validation measures. |
|
Analytical Tools |
Porter's Five Forces, SWOT, value chain, and Harvey ball analysis to assess competitive intensity, stakeholder roles, and relative impact of key factors. |
Key Market Segments
By Equipment Type
-
Batch HPP Machines
-
Standalone HPP Systems
-
Integrated HPP Lines
-
-
Continuous HPP System
-
Standalone HPP Systems
-
Integrated HPP Lines
-
By Vessel Volume
-
Less than 100 Liters
-
100 to 300 Liters
-
More than 300 Liters
By Pressure Range
-
Less than 600 MPa
-
600 to 800 MPa
-
More than 800 MPa
By Vessel Orientation
-
Horizontal
-
Vertical
By Application
-
Fruits & Vegetables
-
Meat & Poultry
-
Seafood
-
Dairy & Alternatives
-
Juices & Beverages
-
Ready-to-Eat Meals/Sauces
-
Pharmaceuticals/Biotech
-
Cosmetics
-
Other
By Sales Channel
-
Direct Sales
-
Distributors/Dealers
-
Online Sales
-
Aftermarket Services
By End-User
-
Food Processors
-
Retail & Food Service
-
CPG & Contract Packagers
-
Pharma & Biotech Manufactures
-
Cosmetics & Personal‑Care Manufactures
-
R&D / Testing Labs
Geographical Breakdown
-
North America: U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
-
Europe: U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Netherlands, and rest of Europe.
-
Asia Pacific: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Indonesia, Vietnam, Australia, Philippines, and rest of APAC.
-
Middle East & Africa (MENA): Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Israel, Turkey, Nigeria, South Africa, and rest of MENA.
-
Latin America: Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, and rest of LATAM.
Conclusion & Recommendations
The future of the high-pressure processing (HPP) equipment market rests on its ability to balance innovation with cost-efficiency, while addressing rising global demand for safe, natural, and sustainable food solutions. Strategic moves such as scaling production, integrating HPP with packaging automation, and expanding into emerging regions will determine who leads in the next growth phase. For investors, this sector offers mid- to long-term resilience, while policymakers can leverage HPP as a tool to advance public health and waste-reduction mandates. Executives, meanwhile, must pursue partnerships and efficiency upgrades to stay competitive in a maturing but still expanding landscape.

















 Speak to Our Analyst
Speak to Our Analyst
























