Responsible AI Market By Power Components (Software (Governance platform, Explainability tools and Others), and Services), By Commercial model (Software subscription, Consumption based pricing, and Others), By Deployment Mode (On‑Premises, Hybrid, and Others), By Enterprise Size (Large Enterprises, and SMEs), By Buyer type (Cloud platform providers, System integrators, and Others), By End-User (Government & Defence, Media & Entertainment, and Others)– Global Analysis & Forecast, 2025–2030
Responsible AI Industry Outlook
The Responsible AI Market size was valued at USD 1.09 billion in 2024, and is expected to be valued at USD 1.58 billion by the end of 2025. The industry is projected to grow, hitting USD 10.26 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 45.3% between 2025 and 2030.
The responsible AI market is emerging as a critical focus area as organizations increasingly deploy artificial intelligence across core business functions. With AI adoption expanding in sectors such as finance, healthcare, government, and retail, the need for systems that are transparent, fair, explainable, and aligned with ethical standards has become central. responsible AI encompasses governance frameworks, bias detection and mitigation tools, explainability solutions, privacy protection mechanisms, and auditing practices, all designed to ensure trust and accountability in AI-driven decisions. The push is further reinforced by evolving regulatory requirements and growing expectations from customers, employees, and investors for ethical AI practices.
At the same time, companies face challenges in embedding responsible AI into their operations. Barriers include limited availability of specialized skills, complexity in integrating governance into fast-moving AI pipelines, and the lack of universal standards for compliance. Despite these hurdles, enterprises and technology providers are investing in responsible AI solutions and services, with consulting, certification, and training emerging alongside technical tools as important enablers. This shift reflects a broader recognition that AI ethics is not only about compliance but also about building trust, safeguarding brand reputation, and enabling sustainable AI-driven innovation.
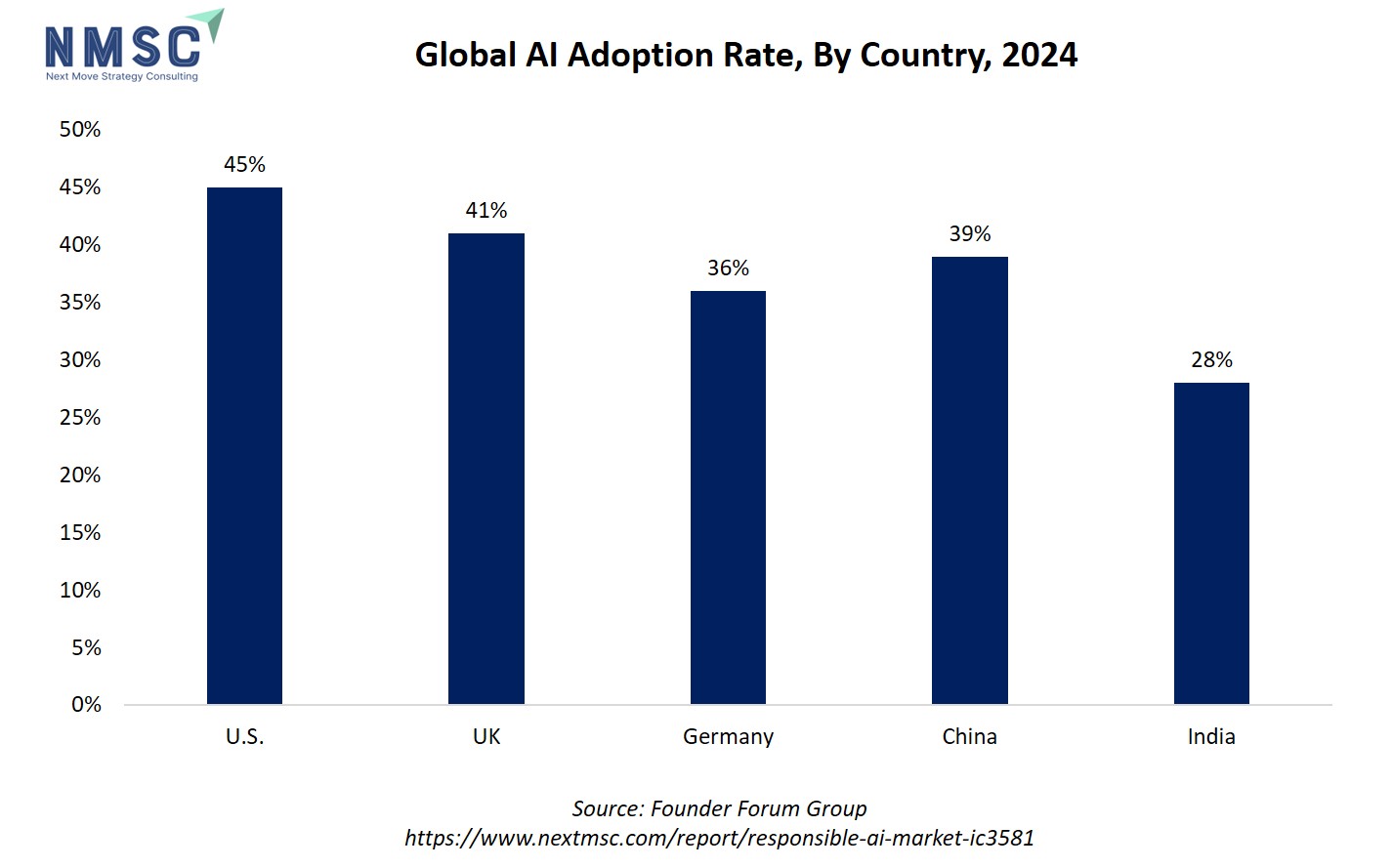
The chart illustrates the global AI adoption rate by country for 2024, revealing significant disparities: the U.S. leads at 45%, followed by the UK at 41%, China at 39%, Germany at 36%, and India at 28%. Higher adoption rates in countries like the U.S., UK, and China signal robust investment and rapid deployment of AI technologies, which creates an urgent momentum for the growth of the market to address ethical, transparency, and governance challenges tied to widespread AI use. Conversely, nations with lower adoption, such as India, highlight the opportunity for responsible AI providers to enable safe scaling and compliance as digital transformation accelerates, making responsible AI a pivotal component of sustainable innovation and risk management worldwide.
What are the Key Responsible AI Industry Trends?
How is Responsible AI Market Changing the Regulatory and Standards Landscape?
Regulation and formal standards are moving from guidance to operational requirements and that is reshaping buyer priorities in the responsible AI market. Governments and regional bodies have been publishing binding rules and clarifications, and international standards for AI management systems are already available for adoption. This shift is visible in milestone moves such as the EU AI Act entering into force and setting a risk-based compliance regime, the wider uptake of the NIST AI Risk Management Framework as a practical lifecycle playbook, and the ISO AI management systems standard providing an auditable management system approach. These developments mean procurement and compliance questions now sit at the centre of responsible AI buying decisions and product roadmaps, so teams must map their models to regulatory risk categories and demonstrate lifecycle controls.
How is Responsible AI Market Driving Integration of Governance into Mlops and Observability?
The market is pushing governance out of slide decks and into the MLOps pipeline so that explainability monitoring and bias controls run alongside CI CD and model telemetry. As AI use has scaled rapidly, surveys report roughly three quarters of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, where the need for operational controls after deployment has become urgent. That means organizations are buying or building model monitoring observability and incident response capabilities that mirror application observability best practices so teams can detect drift bias or safety incidents in production. The practical consequence is that responsible AI tooling must interoperate with feature stores data lineage pipelines and telemetry collectors rather than remain isolated.
How is Responsible AI Market Demand Expanding for Assurance Certification Training and Verification?
As standards and regulation harden the responsible AI market is creating a growing assurance and skills economy where certification third party audits and tailored training are purchased alongside software. Organizations want demonstrable evidence that controls work and that internal teams can operate them; this has amplified demand for certification readiness services ISO aligned process implementation and staff training in AI governance and auditing. With international standards available and regulators expecting lifecycle evidence the market is moving toward packaged assurance offerings that bundle tooling governance playbooks and certification support. For companies that deliver technology, the opportunity is to add lightweight compliance modules audit trails and certification pipelines into products and to partner with accredited auditors to shorten customer certification timelines.
How is Responsible AI Market Reshaping Vendor Risk Management and Procurement?
Responsible AI expectations are changing how organizations select vendors and contract for AI capabilities. With regulators requiring traceability human oversight and incident disclosure enterprises now view model provenance data lineage and vendor transparency as procurement must haves. The NIST framework and the EU Act both emphasize provenance pre deployment testing and disclosure which increases demand for supplier attestations secure model supply chains and contractual SLAs that cover safety and explainability obligations. At the same time rising AI enabled cyber threats make verification of model integrity a security question as much as an ethics one.
What are the Key Market Drivers, Breakthroughs, and Investment Opportunities that will Shape the Responsible AI Industry in the Next Decade?
In recent years, responsible AI has moved from optional ethics statements to core risk, trust, and regulatory programs in many organizations. As AI systems proliferate in mission-critical domains like healthcare, financial services, and public sector, stakeholders demand transparency, fairness, and accountability. Standards like ISO/IEC 42001 and regulations such as the EU AI Act have raised the bar for what compliance and assurance mean, driving demand for tooling, oversight, monitoring, and auditability. At the same time, advances in large language models, generative AI, and scale of deployment are pushing issues like model drift, bias, hallucination and data privacy into sharper focus making responsible AI dimensions not just moral or regulatory but also operational.
However, firms continue to face obstacles in embedding responsible AI deeply into their workflows. Many organizations are still at early maturity in trust and risk practices. In a recent survey, the average responsible AI (or AI trust) maturity score among respondents is around 2.0 on a 0-4 scale. Gaps in governance, lack of skills, unclear regulatory directions across regions, and high costs of compliance tools present real inhibitors. That said, there is an emerging investment opportunity in assurance, certification, audit, vendor risk management, and instrumentation for monitoring bias or risk in production, areas which are poised to grow as regulation and adoption deepen.
Growth Drivers:
How are Regulations and Standards Accelerating Responsible AI Adoption?
Regulatory mandates are no longer distant possibilities but becoming enforceable realities which propel investment in responsible AI. For example, the EU AI Act was adopted and risk categories established for AI systems. Also, the ISO/IEC 42001 standard provides organizations with an audit-friendly framework for AI management systems. These regulatory and standards developments force companies to change procurement, deployment, and validation processes so that ethical oversight is built in. For businesses, that means aligning model risk classification, establishing impact assessments, maintaining documentation, and planning for audits from early design through deployment. Complying with these requirements is becoming a must-have rather than a nice-to-have.
Why is Large-Scale AI Deployment Driving Demand for Operational Responsible AI Controls?
As more AI systems go into production, organizations are confronting operational risks such as bias drift, security vulnerabilities, and unintended behaviors. In McKinsey’s Global AI Trust Maturity Survey, many companies reported they are still building foundational governance, data quality, explainability, and incident response capabilities. As systems advance, especially generative AI and large language models, concerns over hallucination, fairness, transparency, and data privacy have amplified. This has led to demand for monitoring, observability, validation tools, and continuous compliance in production. Companies should instrument AI systems with telemetry, test for bias over time, and build mechanisms for rollback or human oversight. Those who embed such capabilities early in their AI pipelines will reduce risk and gain trust.
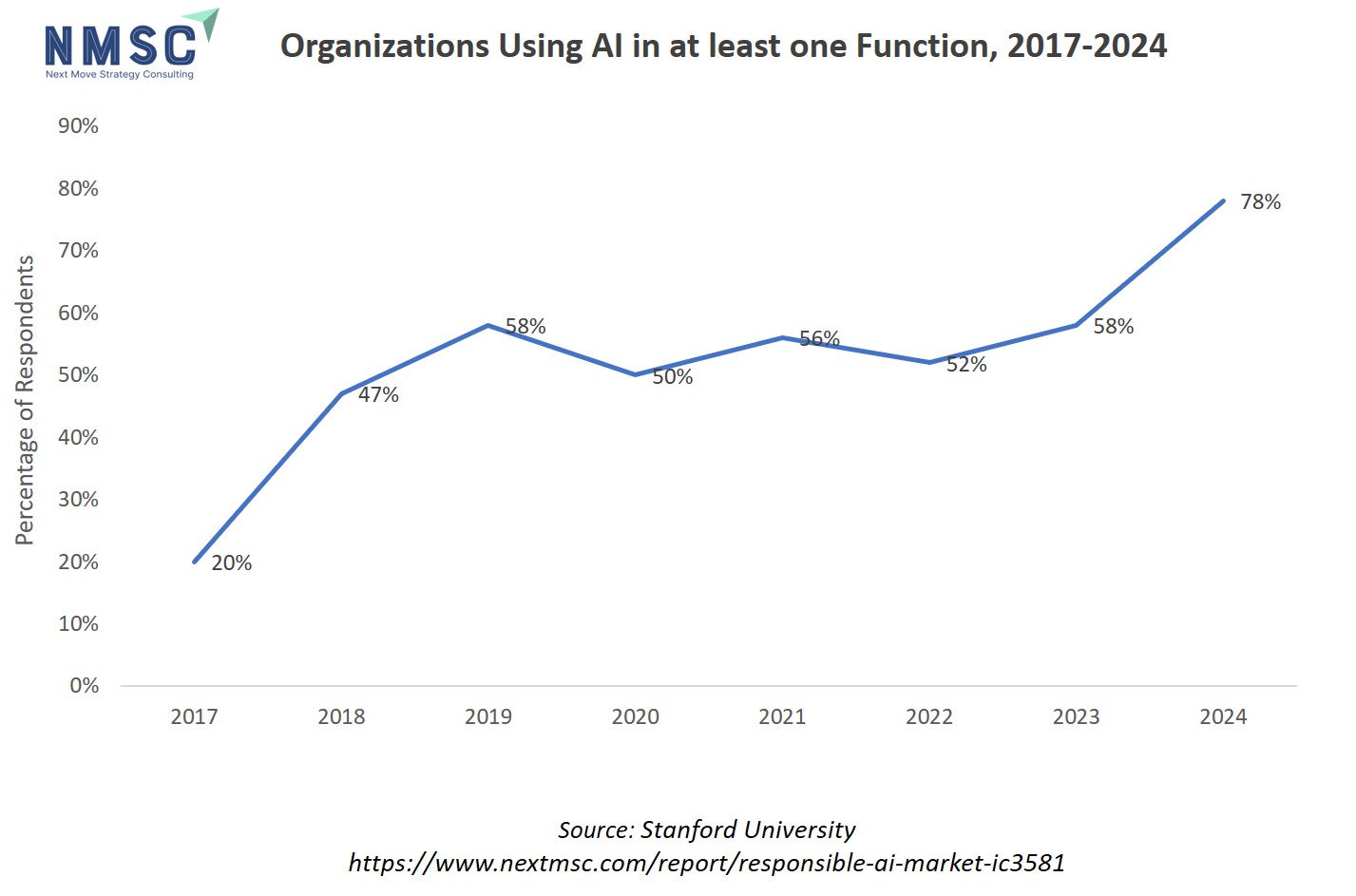
The sharp rise in the percentage of organizations using AI in at least one business function, jumping from 20% in 2017 to 78% in 2024, signals a rapid and widespread adoption of artificial intelligence across industries. This broad deployment heightens the urgency and demand for responsible AI solutions, as more firms must navigate complex challenges around ethics, transparency, fairness, and regulatory compliance that accompany large-scale AI usage. As a result, the responsible AI market is growing quickly, required to provide robust frameworks, tools, and practices that help businesses ensure their AI systems are trustworthy, secure, and aligned with stakeholder expectations.
Growth Inhibitors:
Why is Lack of Skilled Talent and Governance Maturity Slowing Responsible AI Adoption?
One major inhibitor is the skills gap and organizational maturity in governance and ethics disciplines. Many organizations lack sufficient internal capability to perform bias detection, impact assessment, explainability engineering, or regulatory compliance across jurisdictions. Surveys show concerns about data bias, accuracy, and fairness are common. IBM found about 45% of respondents identify data bias or accuracy concerns as a top AI adoption challenge. Also, unclear or fragmented regulation across regions adds complexity and cost. Without clear and consistent laws, organizations struggle to know how to comply and invest appropriately. Building these capabilities requires investment in people, tools, and process change, which some firms find difficult to justify without immediate ROI.
How is Assurance and Vendor Risk Management Emerging as an Investment Opportunity in Responsible AI?
As responsible AI requirements become more formalized, assurance, third-party certification, audits, and vendor risk management are becoming powerful levers for investment. Companies increasingly need to validate that their models and suppliers meet standards, manage provenance of training data, and enforce contractually that external models or tools incorporate required ethical guardrails. Assurance offerings that bundle certification readiness, audit trails, bias testing in production, and vendor transparency are likely to see rising demand. Enterprises can differentiate by investing in scalable audit-tooling, internal assurance frameworks, or partner with accredited auditors. Vendors who build such capabilities into their product offerings or services early will likely win contracts that require high trust and compliance.
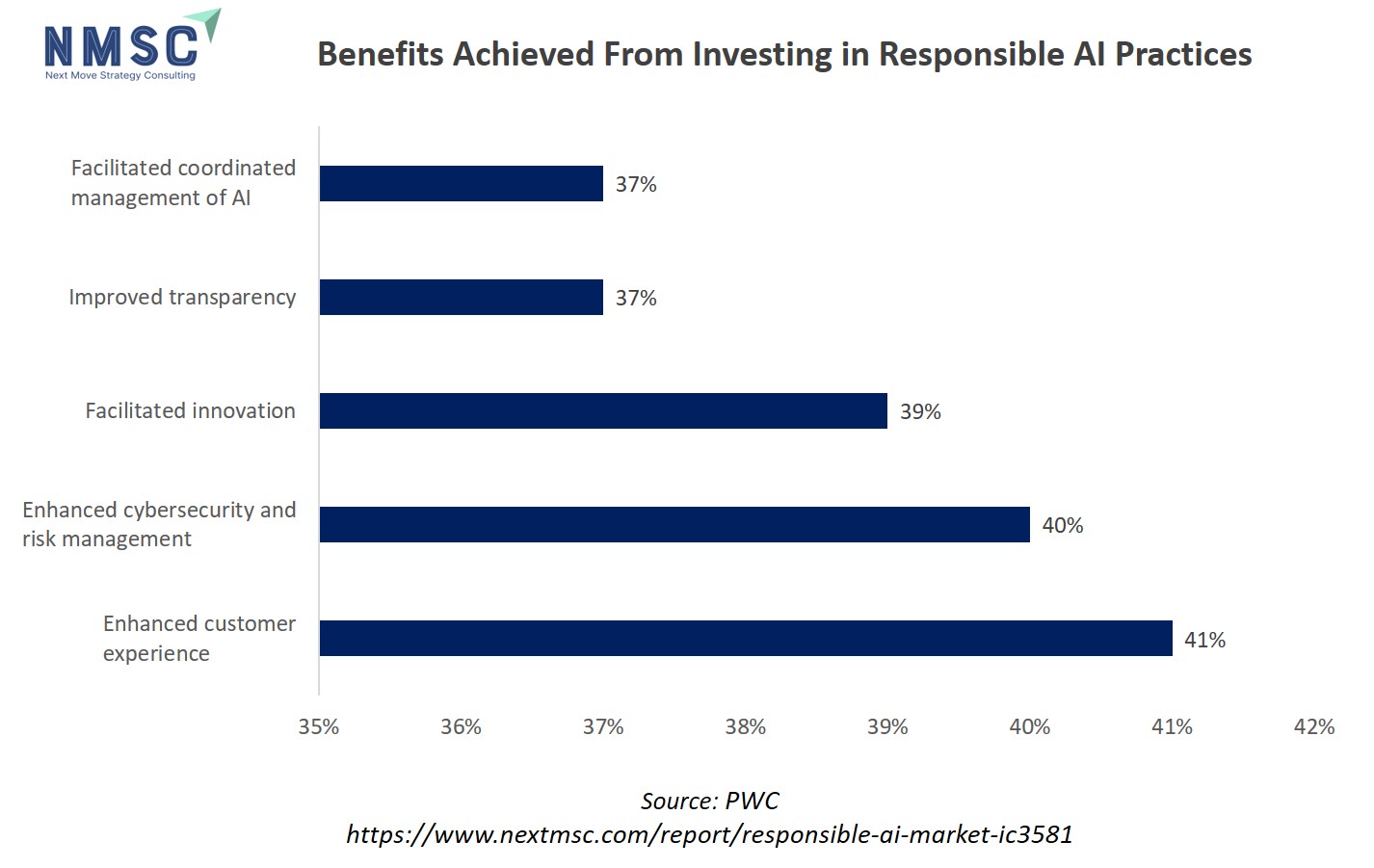
The chart highlights that organizations investing in responsible AI practices gain major benefits such as enhanced customer experience (41%), better cybersecurity and risk management (40%), increased innovation (39%), improved transparency (37%), and facilitated management of AI systems (37%). These tangible outcomes make responsible AI an attractive and essential investment, prompting wider adoption across sectors as companies seek to maximize value and minimize risks from their AI initiatives. As more firms recognize and realize these advantages, the responsible AI market is expected to expand rapidly, supplying the frameworks and solutions needed for safe, ethical, and effective AI deployment.
How Responsible AI Market is Segmented in this Report, and What are the Key Insights from the Segmentation Analysis?
By Components Insights
Which Component Drives Growth in the Responsible AI Market?
On the basis of components, the market is segmented into software and services.
Software solutions encompass tools and platforms designed to implement AI governance, fairness, explainability, and compliance. These tools are often integrated into existing AI systems to ensure they operate responsibly. The software segment is currently leading the market. This dominance is driven by the increasing demand for scalable, automated solutions that can be integrated into AI systems across various industries. For instance, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) emphasizes the need for AI systems to be safe, secure, responsible, trustworthy, and human-centered, highlighting the importance of built-in governance and compliance features.
Services, on the other hand, involve consulting, audits, training, and implementation support to help organizations adopt and maintain responsible AI practices. While services remain essential for tailored implementation and compliance, the scalability and automation offered by software solutions make them the preferred choice for many organizations aiming to implement responsible AI practices efficiently.
By Commercial Model Insights
How are Commercial Models Shaping the Responsible AI Market?
Based on commercial model, the market is segmented into software subscription, consumption-based pricing, project-based services, retainer-based services and certification fee.
Software subscription remains the most widely adopted model, allowing organizations to access AI governance and monitoring platforms on a recurring basis while minimizing upfront costs. Consumption-based pricing is gaining traction among companies that require scalable solutions for fluctuating workloads, particularly for cloud-native AI applications. While, Project-based and retainer-based services cater to consulting, implementation, and managed governance, providing tailored support for enterprises with complex AI deployments. Certification fees apply to independent audits and compliance verification. The adoption of diverse commercial models enables vendors to address different organizational needs, increase flexibility, and accelerate responsible AI adoption across industries, aligning with guidance from NIST and DHS on scalable and accountable AI practices.
By Deployment Mode Insights
Which Deployment Mode Leads the Responsible AI Market?
Based on deployment mode, the market is divided into on‑premises/private cloud, cloud‑based/SaaS and hybrid.
Cloud-based or SaaS deployments currently dominate the responsible AI market. Their popularity is driven by scalability, lower upfront costs, and ease of integration with existing enterprise AI systems. The U.S. Department of Homeland Security and NIST highlight cloud platforms as critical enablers of trustworthy and responsible AI practices, reinforcing the preference for cloud-native solutions in large enterprises and fast-growing AI deployments.
On-premises or private cloud deployments are preferred by organizations with highly sensitive data or strict regulatory requirements. These setups provide enhanced control, data security, and compliance, making them critical for industries like BFSI, healthcare, and government. While adoption is slower than cloud, on-premises deployments remain indispensable for organizations that cannot rely on public cloud environments due to data sovereignty or internal policies.
Hybrid deployment combines the benefits of cloud and on-premises infrastructures, allowing enterprises to scale workloads while maintaining control over sensitive operations. This model is increasingly adopted by large enterprises with complex AI ecosystems that require flexibility and compliance simultaneously. Hybrid solutions support gradual migration to cloud while ensuring mission-critical AI systems remain secure on-premises.
By Enterprise Size Insights
Are Large Enterprises Driving the Growth of the Responsible AI Market?
Based on enterprise size, the market is divided into large enterprises and SMEs.
Large enterprises currently dominate the responsible AI market. Their complex AI portfolios, regulatory scrutiny, and higher risk exposure drive significant investment in governance platforms, monitoring tools, and compliance services. Large organizations often adopt both software and service solutions to ensure AI fairness, transparency, and accountability across multiple business units. Similarly, SMEs are gradually adopting responsible AI solutions, primarily through cloud-based software and subscription services due to lower upfront costs and ease of deployment. Their AI portfolios are smaller, and regulatory pressures are less intense, resulting in slower adoption rates compared to large enterprises. However, as awareness of AI risks and compliance requirements grows, SMEs are expected to contribute increasingly to market growth, especially in cloud-focused and hybrid deployment models.
By Buyer Type Insights
Which Buyer Types are Driving Adoption in the Responsible AI Market?
Based on buyer type, the market is segmented into cloud platform providers, independent software vendors, consulting firms and integrators, system integrators and others.
Cloud platform providers are key adopters of responsible AI solutions, integrating governance, explainability, and compliance tools directly into their AI and cloud services. Their large customer base and advanced AI capabilities make them early adopters, driving product innovation and market awareness. The U.S. DHS and NIST highlight the importance of embedding responsible AI practices in cloud services to ensure safe and trustworthy deployment.
ISVs, on the other hand, adopt responsible AI tools to enhance their AI products, ensuring fairness, transparency, and compliance for end customers. These buyers focus on embedding governance and monitoring features into proprietary software, helping differentiate their solutions in a competitive market.
System integrators combine AI platforms and services for enterprise deployment, ensuring seamless operation and compliance across complex IT environments. Other buyers include research institutions, regulators, and specialized agencies that adopt responsible AI solutions for experimentation, compliance, or evaluation purposes.
By End-User Insights
How are End-User Segments Driving Growth in the Responsible AI Market?
Based on end-user, the market is bifurcated into BFSI, government & defence, healthcare & life sciences, media & entertainment, retail, it & telecommunications, automotive, and others.
BFSI is the leading end-user segment in the responsible AI market. Financial institutions face strict regulatory compliance requirements, high-stakes risk management, and the need for transparent AI decision-making in credit scoring, fraud detection, and investment management. The adoption of AI governance, monitoring, and fairness tools ensures accountability and mitigates reputational and financial risks. Government and defence organizations adopt responsible AI to ensure ethical use, transparency, and accountability in public services and defense systems. The segment prioritizes compliance with national AI policies and ethical frameworks, often requiring on-premises or hybrid deployments for sensitive operations.
Media and entertainment organizations, on the other hand, deploy responsible AI to prevent biased content, automate moderation, and enhance personalization responsibly. Adoption is growing but remains smaller compared to BFSI or healthcare. Retailers leverage responsible AI for recommendation engines, supply chain optimization, and customer insights while ensuring data privacy and fairness. Cloud-based solutions dominate this segment. Whereas, Automotive industry adoption focuses on AI in autonomous driving, safety systems, and predictive maintenance. Compliance and explainability are critical due to safety and liability concerns.
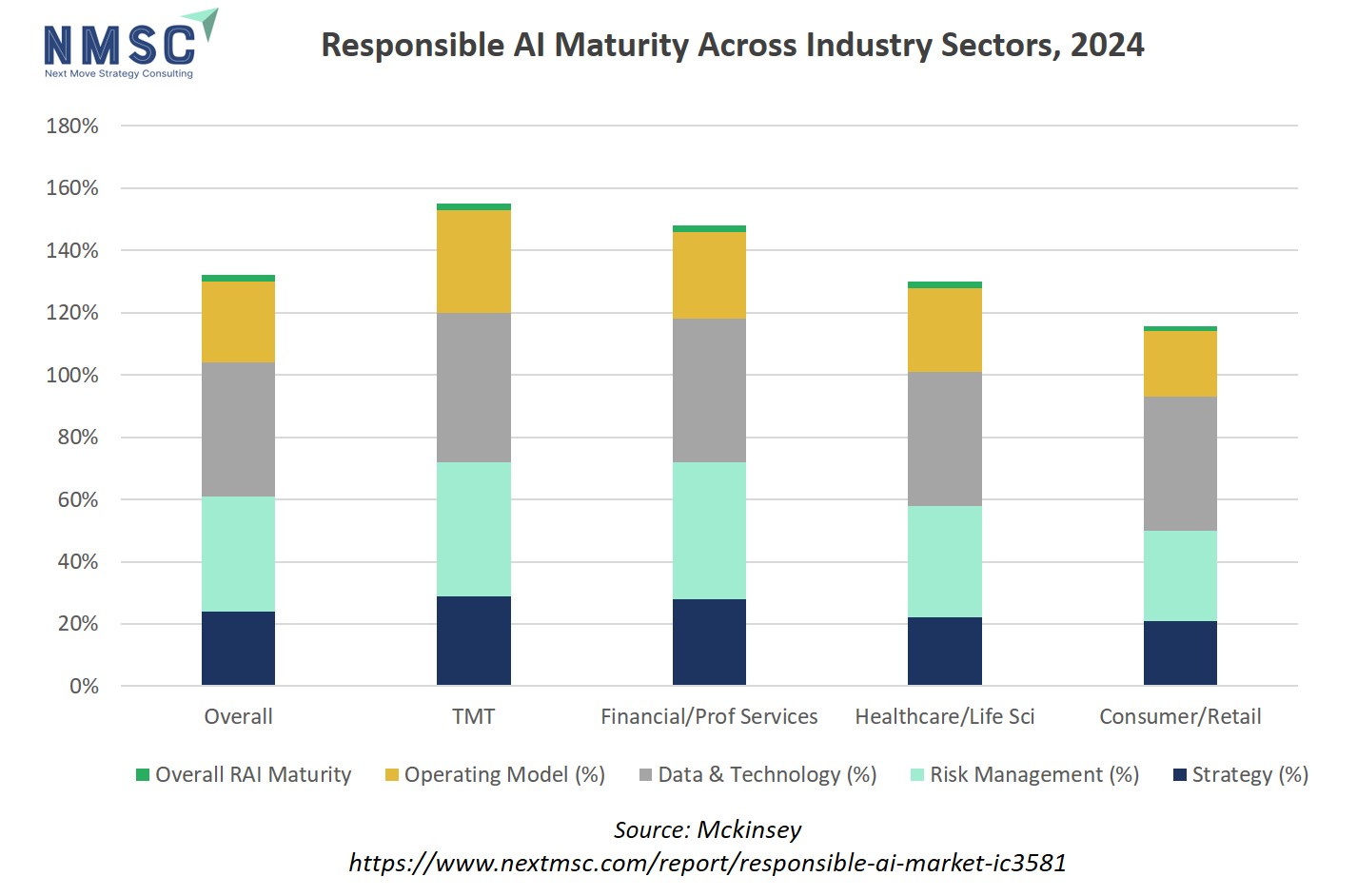
The chart above compares how different sectors, including Overall, TMT (Technology, Media, & Telecommunications), Financial/Professional Services, Healthcare/Life Sciences, and Consumer/Retail, perform across key dimensions of responsible AI. Strategy, risk management, data & technology, and operating model. It shows that TMT and Financial/Professional Services lead in overall responsible AI (RAI) maturity, while Consumer/Retail lags, with each category stacking up the percentage of organizations at higher maturity levels in these areas. The visual demonstrates both the strengths and challenges by sector, highlighting where investments in responsible AI practices are most advanced and where there is still significant room for growth.
Regional Outlook
The market is geographically studied across North America, Europe, the Middle East & Africa, and Asia Pacific, and each region is further studied across countries.
Responsible AI Market in North America
North America remains a dominant force in the responsible AI market, driven by robust technological infrastructure, significant AI investments, and a proactive regulatory environment. The United States leads with a substantial share of the global market, bolstered by federal agencies introducing numerous AI-related regulations to ensure ethical AI deployment. Canada mirrors this trend, emphasizing transparency and accountability in AI systems. The convergence of innovation, regulation, and public awareness fosters a conducive environment for responsible AI adoption, positioning North America as a global leader in ethical AI practices
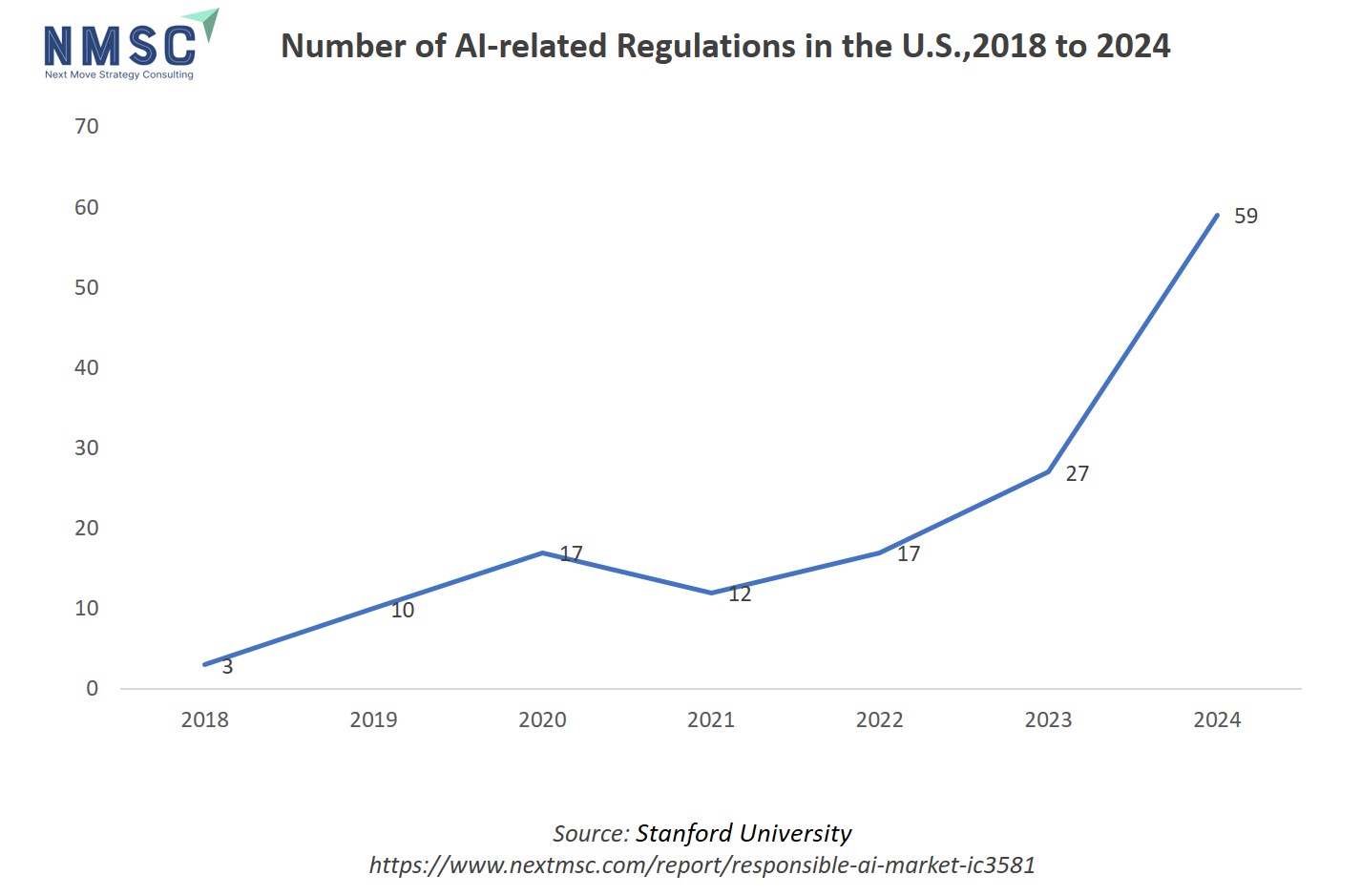
Responsible AI Market in the United States
The United States stands at the forefront of responsible AI adoption, propelled by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory initiatives, and a growing emphasis on ethical considerations in AI development. Federal agencies have introduced a significant number of AI-related regulations, reflecting a commitment to ensuring that AI technologies are developed and deployed responsibly. This regulatory framework, coupled with substantial investments in AI research and development, has cultivated a thriving ecosystem for responsible AI solutions. The U.S. market's maturity and proactive stance on AI ethics contribute to its leadership in the global responsible AI landscape.
The rapid increase in the number of AI-related regulations in the U.S. from 2018 to 2024, as shown in the chart, reflects growing governmental attention to the risks and societal impact of artificial intelligence systems. This surge in regulation directly accelerates the growth of the responsible AI market, as companies must adapt to new compliance requirements, transparency standards, and ethical guidelines imposed by lawmakers. As a result, both organizations and technology providers are increasingly investing in responsible AI solutions, governance frameworks, and risk management tools to ensure their AI systems align with emerging regulatory expectations and maintain trust with stakeholders.
Responsible AI Market in Canada
Canada's approach to responsible AI emphasizes transparency, fairness, and accountability, aligning with global best practices. The Canadian government has implemented policies that encourage the development and deployment of AI technologies in a manner that respects privacy and promotes public trust. These initiatives have spurred growth in the responsible AI sector, with Canadian companies and research institutions leading efforts in AI ethics and governance. Canada's commitment to responsible AI practices positions it as a key player in the North American market.
Responsible AI Market in Europe
Europe is rapidly emerging as a hub for responsible AI, driven by stringent regulations, a focus on human-centric AI, and a commitment to ethical standards. The European Union's AI Act, along with national initiatives like Italy's comprehensive AI law, underscores the region's dedication to ensuring AI technologies are developed and used responsibly.
Responsible AI Market in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom has established itself as a leader in AI regulation and governance, with initiatives aimed at promoting ethical AI development. The UK's approach focuses on ensuring that AI technologies are aligned with societal values and legal standards. This regulatory environment has spurred the growth of responsible AI solutions, particularly in sectors such as healthcare, finance, and public services. The UK's commitment to responsible AI practices enhances its position in the global market.
Responsible AI Market in Germany
Germany's strong industrial base and commitment to ethical standards have driven the adoption of responsible AI, particularly in manufacturing and automotive sectors. The country's focus on data protection, transparency, and accountability aligns with European Union regulations, fostering trust in AI technologies. Germany's proactive stance on AI ethics has facilitated the integration of responsible AI solutions into its industrial processes, promoting sustainable and ethical AI development.
Responsible AI Market in France
France is actively promoting responsible AI through national strategies that emphasize transparency, fairness, and accountability. The French government's initiatives support the development of AI technologies that respect privacy and human rights. These efforts have led to the adoption of responsible AI solutions in various sectors, including public administration, healthcare, and education. France's commitment to ethical AI practices contributes to the broader European movement towards responsible AI.
Responsible AI Market in Spain
Spain is advancing responsible AI adoption through national policies that promote ethical AI development and deployment. The Spanish government's initiatives focus on ensuring AI technologies are developed in a manner that respects privacy and promotes public trust. These efforts have led to the integration of responsible AI solutions in various sectors, including public administration and healthcare, aligning with broader European objectives.
Responsible AI Market in Italy
Italy has taken a significant step by enacting comprehensive legislation regulating AI use, becoming the first EU country to align its regulations with the EU's AI Act. The law focuses on human-centric, transparent, and secure AI use, balancing innovation with citizens' rights, privacy, and cybersecurity. This regulatory framework has accelerated the adoption of responsible AI solutions in Italy, setting a precedent for other European nations.
Responsible AI Market in Asia Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth in AI adoption, with countries like China, Japan, India, South Korea, Taiwan, and Indonesia leading the charge. Government initiatives, such as China's AI development plans and Japan's focus on AI innovation, have spurred investments in AI technologies. However, the pace of responsible AI adoption varies across the region, with some countries prioritizing innovation over regulation. The need for balanced approaches to AI governance is becoming increasingly evident as the region strives to ensure ethical AI development.
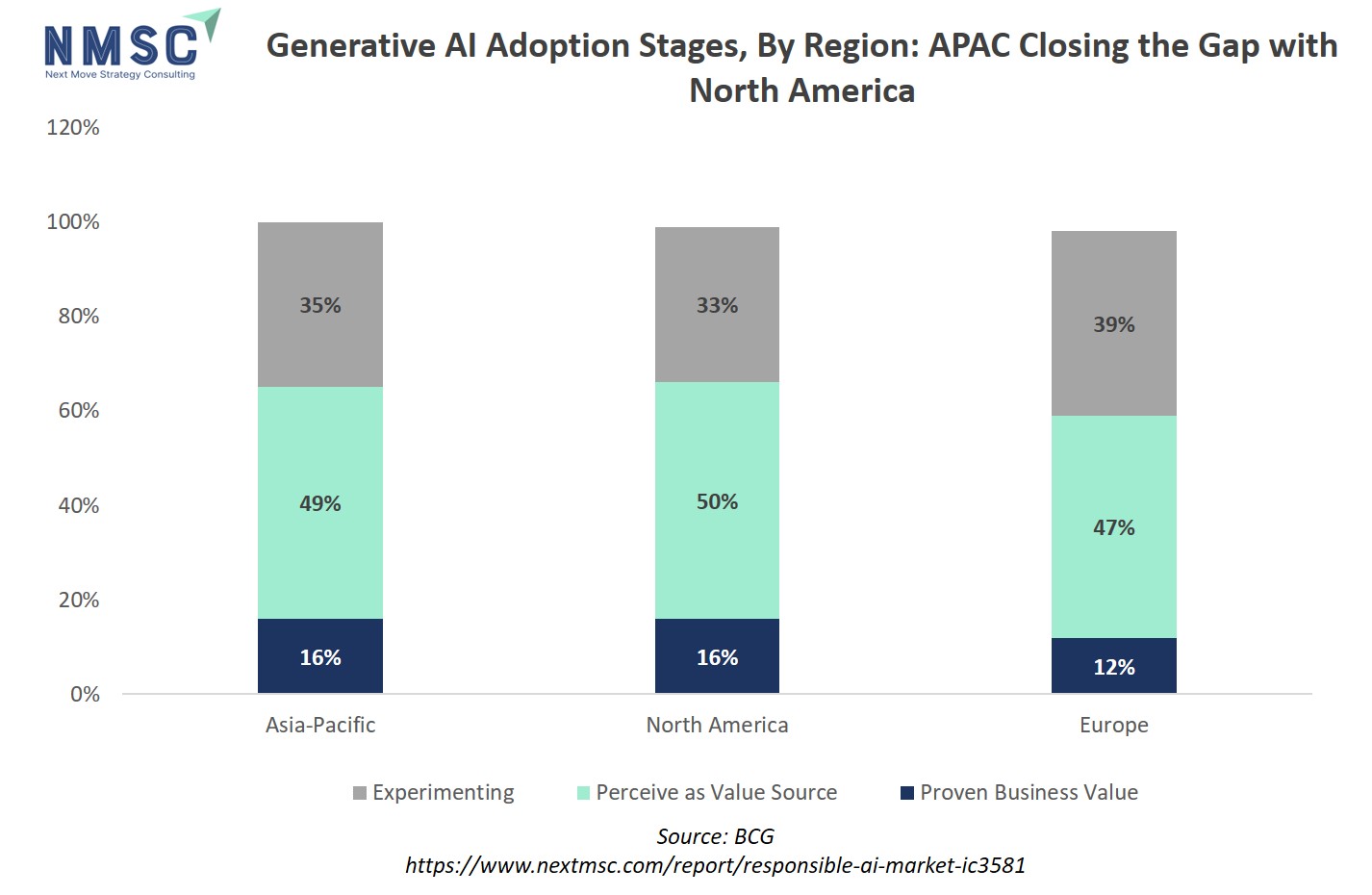
Also, Asia Pacific (APAC) is catching up with North America and surpassing Europe in adopting generative AI (GenAI), by investing more money and involving more workers in digital and AI-related activities. North America has long been the world’s leader in technology adoption, but in terms of GenAI, Asia-Pacific is narrowing the distance. Across the region, the perceived value of generative technologies is higher than in Europe and just a percentage point behind North America. In both North America and Asia-Pacific, 16% of organizations are finding proven value with AI, but APAC is investing more heavily overall.
Asia-Pacific (APAC) is quickly closing the generative AI gap with North America, with both regions having 16% of organizations realizing proven AI value. However, APAC is investing more aggressively in AI overall and perceives higher value from these technologies compared to Europe and nearly at par with North America. This rapid investment and adoption accelerate the shift from experimentation to generating real business outcomes, driving strong demand for responsible AI practices. As AI use scales, organizations need ethical governance, transparency, and safeguards to manage risks and comply with regulations, fueling growth in the responsible AI market globally.
Responsible AI Market in China
China's aggressive push towards AI development is complemented by initiatives aimed at establishing AI governance frameworks. The government's focus on AI innovation has led to significant investments in AI research and development. While the emphasis has traditionally been on technological advancement, there is a growing recognition of the need for responsible AI practices to address ethical concerns and ensure public trust in AI technologies.
Responsible AI Market in Japan
Japan is integrating responsible AI principles into its technological advancements, focusing on transparency, accountability, and human-centric AI. The country's approach includes developing AI systems that align with societal values and legal standards. Japan's commitment to responsible AI is evident in its policies and initiatives that promote ethical AI development, particularly in sectors like robotics, healthcare, and automotive industries.
Responsible AI Market in India
India is rapidly adopting AI technologies across various sectors, including healthcare, agriculture, and education. The government's initiatives, such as the National AI Strategy, aim to promote AI development while addressing ethical considerations. India's focus on inclusive and transparent AI practices is driving the adoption of responsible AI solutions, fostering public trust and ensuring that AI technologies benefit all segments of society.
Responsible AI Market in South Korea
South Korea is advancing responsible AI adoption through national strategies that emphasize ethical AI development and deployment. The government's initiatives focus on ensuring AI technologies are developed in a manner that respects privacy and promotes public trust. South Korea's commitment to responsible AI practices is evident in its policies and efforts to integrate ethical considerations into AI research and development.
Responsible AI Market in Taiwan
Taiwan is leveraging AI technologies to enhance various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation. The government's focus on AI innovation is accompanied by efforts to establish governance frameworks that ensure ethical AI development. Taiwan's approach to responsible AI includes promoting transparency, accountability, and public trust in AI systems.
Responsible AI Market in Australia
Australia is actively promoting responsible AI through national strategies that emphasize ethical AI development and deployment. The government's initiatives focus on ensuring AI technologies are developed in a manner that respects privacy and promotes public trust. Australia's commitment to responsible AI practices is reflected in its policies and efforts to integrate ethical considerations into AI research and development.
Responsible AI Market in Latin America
Latin America is witnessing a surge in AI investments, projected to reach USD 17.3 billion by 2025. Countries in the region are developing AI governance frameworks to regulate the design, deployment, and use of AI according to their specific ethical and legal standards. These efforts aim to balance innovation with the protection of individual rights and freedoms, fostering the growth of responsible AI solutions across various sectors.
Responsible AI Market in the Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa are experiencing rapid growth in AI adoption, driven by national strategies and investments in AI technologies. Countries like the UAE are leading the way with initiatives such as the launch of the Middle East's first AI and robotics research lab in collaboration with Nvidia. These developments underscore the region's commitment to advancing responsible AI practices and fostering innovation
Competitive Landscape
Which Companies Dominate the Responsible AI Market and How do they Compete?
The responsible AI market is led by a mix of tech giants and specialized firms, each leveraging unique capabilities to capture market share. IBM, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon Web Services dominate through broad AI platforms integrating fairness, explainability, privacy, and compliance tools. Specialized companies like Credo AI and Arthur AI focus on governance, risk management, and regulatory compliance, providing tailored solutions for enterprises. Competition is shaped by innovation, speed of deployment, and adherence to emerging regulations and standards. Firms differentiate through advanced AI oversight platforms, consulting services, and strategic partnerships, creating a dynamic market where both scale and niche specialization drive success.
Market dominated by Responsible AI Giants and Specialists
The responsible AI market is characterized by a dynamic mix of established tech giants and specialized firms, each contributing uniquely to the landscape. Companies like IBM, Google, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) lead the charge, integrating responsible AI practices such as transparency, fairness, and privacy into their operations. These tech giants are setting the tone for ethical AI that balances innovation with regulatory compliance. Alongside them, specialized firms like Credo AI focus on providing governance platforms that help enterprises streamline AI adoption by implementing and automating AI oversight, risk management, and compliance. This combination of broad industry leaders and niche specialists is shaping a competitive environment where both scale and specialization are crucial for success.
Innovation and Adaptability Drive Market Success
Innovation is a key driver for companies in the responsible AI market. For instance, Credo AI offers an enterprise AI governance platform that enables organizations to manage AI risks and compliance across the AI lifecycle. Their platform provides centralized oversight, policy configuration, and automated compliance, catering to the needs of generative AI, AI agents, and third-party AI vendors. Similarly, Boston Consulting Group (BCG) assists organizations in implementing responsible AI strategies through tailored programs based on five pillars, aiming to minimize the time to responsible AI maturity while maximizing value creation. These innovations demonstrate how adaptability to emerging AI challenges and regulatory requirements can position companies for success in the evolving market.
Market Players to OPT for Merger & Acquisition Strategies to Expand their Presence
To strengthen their positions in the responsible AI market, companies are increasingly turning to mergers and acquisitions. For example, PwC's 2024 US responsible AI Survey indicates that organizations are targeting responsible AI practices not only for risk management but also for competitive differentiation. This strategic focus has led firms to acquire specialized capabilities in AI governance and compliance. Additionally, collaborations and partnerships are on the rise, with companies like AWS and IBM joining initiatives that promote responsible AI usage. These strategic moves highlight the industry's trend toward consolidating expertise and expanding offerings to meet the growing demand for responsible AI solutions.
List of Key Responsible AI Companies
-
Microsoft Corporation
-
Google Cloud
-
Amazon Web Services
-
DataRobot, Inc.
-
Credo AI
-
SAS Institute
-
Monitaur
-
Datatron
-
Boston Consulting Group
-
H2O.ai
-
Arthur AI
-
Holistic AI
-
Fiddler AI
What are the Latest Key Industry Developments?
-
February 2025- IBM signed the AI Seoul Summit's commitments for AI Frontier Safety, reinforcing its dedication to safe and trustworthy AI development. IBM's AI Safety and Governance Framework support the responsible development and use of AI, aligning with the Seoul commitments' core objectives.
-
February 2025- Google Cloud introduced new responsible AI tools, including Explainable AI, Model Cards, and the TensorFlow open-source toolkit. These resources aim to provide model transparency in a structured, accessible way, supporting the responsible development and use of AI.
-
December 2024- AWS announced new responsible AI tools, capabilities, and resources at its re:Invent conference. These enhancements aim to improve the safety, security, and transparency of AWS's AI services and models, supporting customers' responsible AI journeys.
-
September 2024- SAP released an updated version of its AI Ethics Handbook, providing comprehensive guidelines for creating ethical generative and traditional AI solutions. The handbook supports SAP's commitment to delivering relevant, reliable, and responsible AI by applying the SAP Global AI Ethics policy.
-
September 2024- Microsoft, in partnership with G42 and the Abu Dhabi Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Technology Council, established two centers in Abu Dhabi. These centers aim to advance responsible AI practices by developing best practices and industry standards for the responsible use of AI, particularly in the Middle East and the Global South.
What are the Key Factors Influencing Investment Analysis & Opportunities in the Responsible AI Market?
Investment in the responsible AI market has experienced significant growth, driven by increasing demand for ethical AI solutions and regulatory compliance. In 2024, venture capital funding for AI companies reached a record USD 100 billion, with nearly a third allocated to AI-related ventures, highlighting the sector's prominence in global investment portfolios. Notably, the U.S. led this surge, attracting UD S109.1 billion in private AI investments, nearly 12 times higher than China's USD 9.3 billion.
Strategic investment hotspots include the U.S., particularly Silicon Valley, which secured USD 15.2 billion across 476 deals in Q2 2024 alone. Corporate investors are also actively participating, with sovereign wealth funds from regions like Saudi Arabia, Abu Dhabi, and Singapore backing AI and semiconductor firms globally, viewing AI as both a strategic and high-return asset. These investments underscore the growing recognition of responsible AI as a critical component for sustainable and ethical technological advancement.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
Next Move Strategy Consulting (NMSC) presents a comprehensive analysis of the responsible AI Market, covering historical trends from 2020 through 2024 and offering detailed forecasts through 2030. Our study examines the market at global, regional, and country levels, providing quantitative projections and insights into key growth drivers, challenges, and investment opportunities across all major responsible AI segments.
The responsible AI market creates significant value for a range of stakeholders. Investors benefit from high-growth opportunities, as companies developing ethical AI tools, governance platforms, and compliance solutions attract substantial funding and deliver strong potential returns. Policymakers gain from the market’s focus on transparency, fairness, and accountability, which helps shape regulatory frameworks and ensures AI adoption aligns with societal and ethical standards. Customers, including enterprises deploying AI solutions, enjoy enhanced trust, reduced operational and reputational risks, and improved decision-making through explainable and bias-mitigated AI systems. Together, these benefits create a virtuous cycle, driving adoption, innovation, and investment while promoting safer and more responsible AI practices.
Report Scope:
|
Parameters |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 1.58 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 10.26 Billion |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 45.3% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Analysis Period |
2024–2030 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2030 |
|
Market Size Estimation |
Billion (USD) |
|
Growth Factors |
|
|
Countries Covered |
28 |
|
Companies Profiled |
15 |
|
Market Share |
Available for 10 companies |
|
Customization Scope |
Free customization (equivalent to up to 80 analyst-working hours) after purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Approach |
In-depth primary and secondary research; proprietary databases; rigorous quality control and validation measures. |
|
Analytical Tools |
Porter's Five Forces, SWOT, value chain, and Harvey ball analysis to assess competitive intensity, stakeholder roles, and relative impact of key factors. |
Key Market Segments
By Components
-
Software
-
Governance platform
-
Explainability tools
-
Fairness and bias tools
-
Privacy and data protection tools
-
Testing and validation tools
-
Monitoring and observability tools
-
Security and robustness tools
-
Certification and compliance automation
-
-
Services
-
Strategy and governance consulting
-
Risk assessment and auditing
-
Implementation and integration
-
Managed services and monitoring
-
Training and capability building
-
Certification readiness and verification
-
By Commercial model
-
Software subscription
-
Consumption based pricing
-
Project based services
-
Retainer based services
-
Certification fee
By Deployment Mode
-
On‑Premises/Private Cloud
-
Cloud‑based / SaaS
-
Hybrid
By Enterprise Size
-
Large Enterprises
-
SMEs
By Buyer Type
-
Cloud platform providers
-
Independent software vendors
-
Consulting firms and integrators
-
System integrators
-
Others
By End-User Vertical
-
BFSI
-
Government & Defense
-
Healthcare & Life Sciences
-
Media & Entertainment
-
Retail
-
IT & Telecommunications
-
Automotive
-
Others
Conclusion & Recommendations
Our report equips stakeholders, industry participants, investors, policy-makers, and consultants with actionable intelligence to capitalize on responsible AI transformative potential. By combining robust data-driven analysis with strategic frameworks, NMSC’s responsible AI market report serves as an indispensable resource for navigating the evolving landscape.
The responsible AI market is poised for sustained growth as regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and stakeholder demand converge. Companies that integrate robust governance, transparency, and compliance practices early will gain a competitive edge, while investors can capitalize on high-value opportunities in AI oversight tools and ethical platforms. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions will continue to shape the landscape, enabling rapid scaling of capabilities. Looking ahead, the market is expected to expand globally, driven by increasing AI adoption across industries, evolving regulations, and heightened awareness of ethical AI. Organizations that prioritize responsible AI strategies will not only mitigate risks but also unlock long-term value and trust in an increasingly AI-driven world.

















 Speak to Our Analyst
Speak to Our Analyst

























