Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market By Condition Profile (Severity, Causes, Demographics, Laterality), By Technology (Conventional, Minimally Invasive, and, Digital or Telehealth Enabled), By Solution Type (Diagnostic Services, Non-Surgical Treatment, Surgical Treatment, and Post-Treatment Rehabilitation), and By End-User (Primary Care Clinics, Specialty Outpatient Clinics, Hospitals, Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Homecare Settings, and Workplace Programs) – Global Analysis & Forecast, 2025–2030
Industry Outlook
The global Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market size was valued at USD 153.19 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 163.67 billion by 2025. Looking ahead, the industry is projected to expand significantly, reaching USD 227.84 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 6.84% from 2025 to 2030.
The market represents a growing segment within the broader neurological and orthopaedic healthcare landscape, focusing on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of ulnar nerve compression disorders. As awareness of repetitive strain injuries and nerve entrapment syndromes rises, healthcare providers and medical device manufacturers are increasingly emphasizing early detection and minimally invasive management solutions.
The sector encompasses diagnostic tools, splinting and bracing systems, physiotherapy aids, and advanced surgical instruments designed to restore nerve function and reduce patient discomfort. Looking ahead, the market is poised for advancement through technological innovation and digital health integration.
Emerging treatment modalities, including image-guided and robotic-assisted surgeries, are enhancing procedural accuracy and recovery outcomes. Tele-rehabilitation and wearable monitoring devices are also gaining traction, offering continuous post-surgical support and improving treatment compliance. The industry’s future will likely be driven by the convergence of diagnostics, therapeutic solutions, and remote care models, enabling faster intervention and personalized treatment strategies. As healthcare systems prioritize minimally invasive and cost-efficient solutions, the market is expected to evolve into a more holistic and technology-enabled domain.
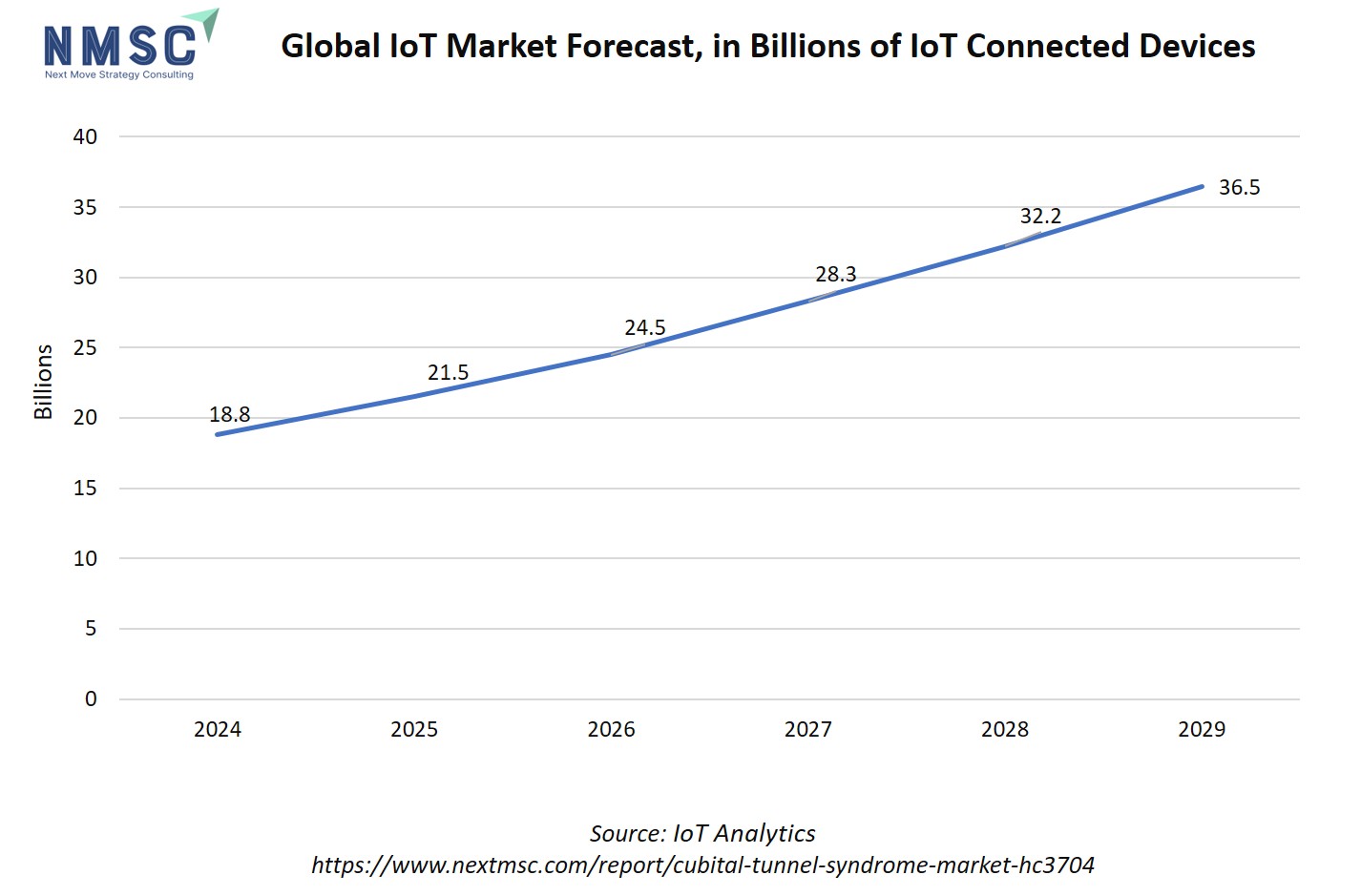
Additionally, IoT-connected devices are poised to significantly impact the cubital tunnel syndrome market growth by transforming how the condition is diagnosed, monitored, and managed. These devices enable continuous tracking of nerve function, muscle activity, and movement patterns, helping clinicians detect early signs of ulnar nerve compression before symptoms worsen.
Wearable IoT sensors monitor patient posture, arm positioning, and rehabilitation progress in real time, allowing for personalized treatment adjustments and better adherence to recovery plans. Integration of IoT data with tele-rehabilitation platforms also supports remote monitoring and outcome tracking, reducing the need for in-person visits.
What are the Key Trends in the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Industry?
How is the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market Transforming Care Through Tele-Rehabilitation and Wearable Monitoring?
Tele-rehabilitation and wearable sensors are moving from niche experiments into practical care pathways for cubital tunnel patients, with recent systematic reviews showing tele-rehab deliver similar functional gains and pain relief to in-person therapy for upper-limb conditions. Remote exercise programs, guided by consumer wearables or clinical sensors, let therapists monitor adherence and range of motion remotely, which shortens follow-up cycles and helps spot patients who need escalation.
That shift matters because it reduces travel burden, improves continuity after decompression surgery, and supports conservative management in earlier stages. Companies therefore, invest in interoperable sensor platforms and clinician dashboards that integrate with standard outcome scales; pairing a low-cost wearable with a subscription tele-rehab program creates recurring revenue while lowering per-patient costs.
How is Wider Adoption of Diagnostic Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Reshaping Early Detection and Treatment Pathways?
Point-of-care musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSK-US) is increasingly used to evaluate the ulnar nerve at the elbow, enabling clinicians to visualise focal enlargement, subluxation, and dynamic compression. Recent clinical reviews document rising clinician uptake and utility in triage. Because ultrasound gives anatomical detail at the bedside, it shortens the diagnostic timeline, identifies candidates for conservative care versus surgery earlier, and supports ultrasound-guided injection procedures when needed.
For device and service companies, the opportunity is that they offer compact, nerve-specific imaging bundles and short competency courses for physiatrists and hand surgeons. Health systems also adopt ultrasound-first diagnostic algorithms to reduce unnecessary electrodiagnostic testing; vendors who demonstrate reproducible cross-sectional area thresholds and streamline reporting into EMRs win early contracts.
How are Minimally Invasive and Robot-Assisted Techniques Changing Surgical Outcomes and Market Expectations?
Minimally invasive cubital tunnel releases and early reports of robot-assisted peripheral nerve procedures are raising expectations for less postoperative pain, smaller scars, and faster return to work. These technologies shift purchasing decisions, where hospitals expect shorter LOS and higher throughput per OR block, while payers ask for evidence of faster functional recovery. For medtech firms, the pragmatic move is that they focus on modular instrument sets that enable both open and endoscopic/robotic workflows, accompanied by surgeon training and real-world outcome registries.
How are Changing Work Patterns and Population Dynamics Driving Demand and Shaping Future Product Strategies?
Shifts in occupational exposures, more prolonged desk work, variable ergonomics in home setups, and ageing workforces are contributing to persistent demand for diagnostic and treatment services for ulnar neuropathy, with multiple reports noting higher positive screening among groups with longer years of repetitive elbow loading. Research reports also projected rising market value for cubital tunnel care products and services over the next decade.
That combination means companies expand beyond acute surgical solutions into prevention and early-stage management: think ergonomic digital tools, clinician-led screening programs for high-risk employee cohorts, and direct-to-consumer educational bundles that steer early cases to conservative care. Health systems and occupational health vendors pilot employer programs that combine risk screening, remote exercise modules, and quick-access diagnostic ultrasound, a model that reduces lost workdays and creates predictable service volumes.
What are the Key Market Drivers, Breakthroughs, and Investment Opportunities that will Shape the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Industry in the Next Decade?
The cubital tunnel syndrome market sits at the intersection of neurology, orthopaedics, and occupational health. Today the industry centres on earlier diagnosis, conservative management, and a range of surgical options from open decompression to endoscopic releases.
Clinical literature and clinical guidelines emphasise a stepped approach, conservative care first for mild-to-moderate cases and surgery for persistent or progressive motor deficit, so the market spans devices, diagnostic imaging, rehabilitation services, and hospital/ASC procedural volumes.
Applications today include point-of-care diagnostics, bracing/splinting products, clinic and home-based rehabilitation programs, and surgical instruments and implants used in decompression or transposition. As population ageing, prolonged desk work, and ergonomic risk exposures persist, demand for early detection and low-cost conservative pathways grows.
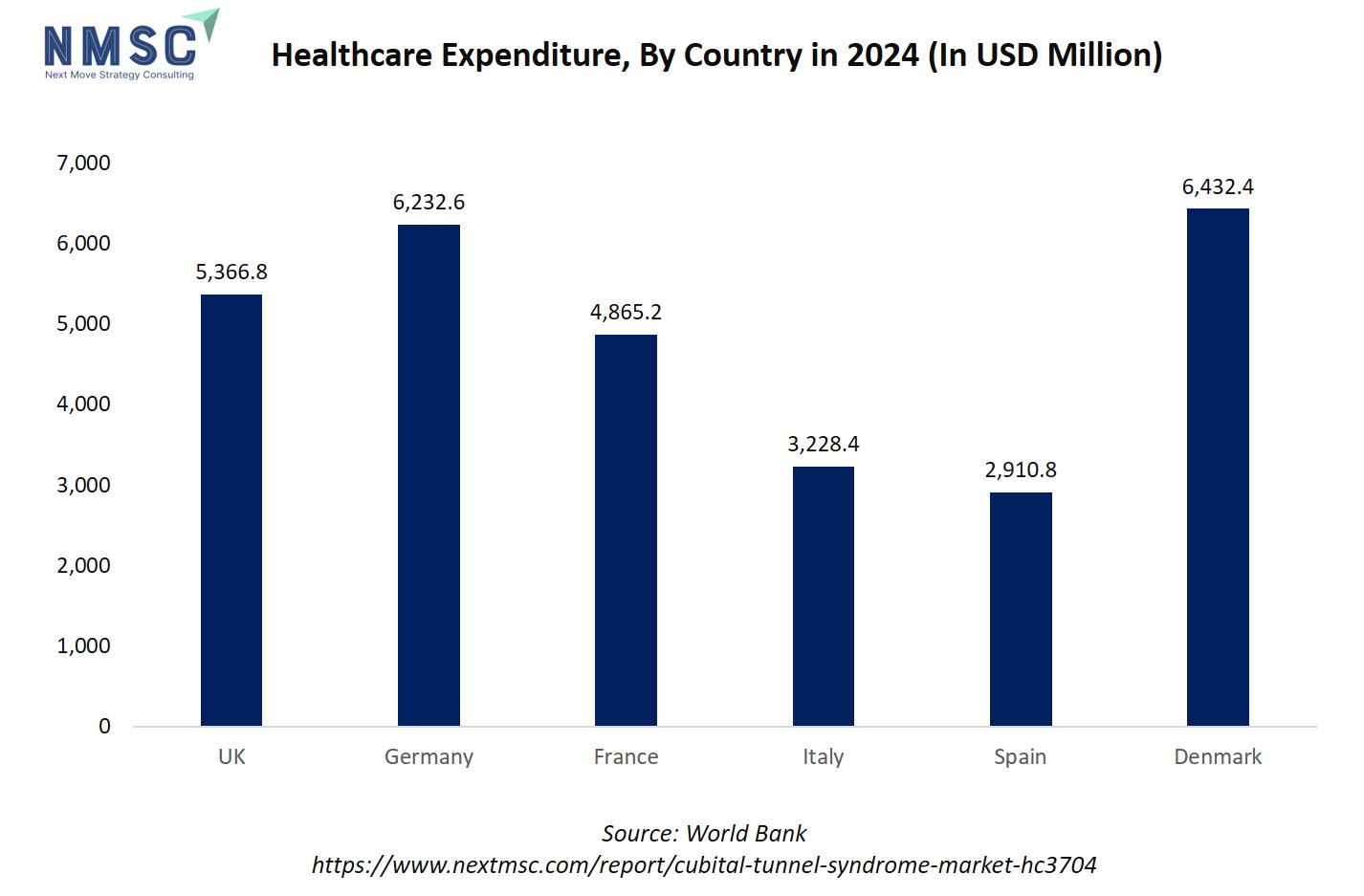
The rising healthcare expenditure positively influences the cubital tunnel syndrome market trends by improving access to advanced diagnostics, minimally invasive procedures, and rehabilitation services. As countries allocate more funds toward outpatient care and musculoskeletal health, patients benefit from earlier diagnosis and better treatment outcomes.
Increased spending also supports the adoption of tele-rehabilitation platforms and ergonomic interventions, helping reduce long-term costs associated with nerve compression injuries. In regions with limited healthcare investment, treatment delays and underdiagnosis remain common, slowing market growth. Overall, higher healthcare spending drives innovation, accessibility, and adoption across the entire nerve compression care continuum.
Growth Drivers:
How will Rising Prevalence of Ulnar Neuropathy and Changing Work Patterns Drive Market Demand?
Studies show Cubital Tunnel Syndrome (CuTS), also known as ulnar neuropathy, is the second most common nerve compression disorder in the arm. Its prevalence ranges from about 1.8% in U.S.-based studies to nearly 6% in some community surveys, figures that reflect a significant number of clinical cases seen across general practice, rehabilitation, and hand surgery.
With more people working long hours at computers and an ageing workforce, the number of cases continues to rise steadily. This trend creates consistent demand for diagnostic tools, supportive devices, and treatment services. For companies, it means an opportunity to develop affordable, easy-to-scale products and care packages that employers and healthcare systems use to reduce sick leave. Businesses are therefore focusing on ergonomic prevention programs and quick screening solutions that fit seamlessly into workplace health setups.
How Can Better Conservative-Care Evidence and Outpatient Pathways Accelerate Adoption of Non-Surgical Solutions?
Non-surgical treatments, such as splinting, targeted physical therapy, and guided injections, provide effective symptom relief for many patients with early-stage Cubital Tunnel Syndrome (CuTS). These methods help delay or avoid surgery and allow healthcare systems to manage patient loads more efficiently and at lower cost. This opens new opportunities for companies that produce certified splints, digital rehabilitation platforms, and remote monitoring tools that help patients stay consistent with their therapy.
From a business standpoint, firms work with healthcare providers to test these solutions through well-structured clinical trials that prove faster recovery or fewer surgeries. Bundling devices with tele-rehabilitation services also generate steady income. However, success relies on publishing reliable clinical results and cost-saving data that are trusted by insurers, hospitals, and employers.
Growth Inhibitors:
How will Reimbursement, Coding Complexity, and Fragmented Payer Rules Inhibit Broader Adoption of Advanced Diagnostics and Integrated Care?
Challenges at the system level, such as uneven reimbursement for advanced diagnostic tools, inconsistent insurance coverage for tele-rehabilitation, and unclear coding rules, are slowing the wider adoption of new Cubital Tunnel Syndrome (CuTS) solutions. While OSHA and BLS data show that musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) create a significant economic burden, there are still no standard payment or coverage pathways for these services.
As a result, healthcare providers and companies deal with a complex and uncertain payment landscape. For device and service providers, this means that even proven clinical benefits do not lead to quick market adoption without clear engagement from insurers. To overcome this, companies work closely with reimbursement specialists, build strong economic evidence showing savings from reduced work-loss, and launch pilot programs funded by employers. These steps reduce financial risks while generating real-world proof to support broader coverage.
Where is the Most Attractive Emerging Investment Opportunity for Integrated Employer/Occupational-Health Prevention Programs?
As workplace strain and poor home-office ergonomics continue to fuel, cases of ulnar nerve entrapment, employer-led prevention programs are emerging as a promising investment area. National occupational data show that musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) remain a leading cause of lost productivity, making early screening and intervention a cost-effective strategy.
Companies implement programs that include employee screening, quick access to diagnostic ultrasound, and short tele-rehabilitation sessions to minimize recovery time and prevent surgeries. Investors and service providers are already testing integrated screen–triage–treat packages aimed at large employers or occupational health firms.
Success is measured through fewer lost workdays, lower surgical referrals, and clear financial returns within a year. Businesses that combine wearable-based screening, clinician-guided diagnosis, and ongoing digital rehabilitation, supported by measurable outcomes, build steady revenue streams and expand quickly across corporate wellness networks.
How is the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market Report Segmented, and What are the Key Insights from the Segmentation Analysis?
By Condition Profile Insights
Is Patient Heterogeneity Driving Segmentation Strategies in the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market In 2025?
Based on condition profile, the cubital tunnel syndrome market share is segmented into severity, causes, demographics, and laterality.
Clinical literature consistently describes a wide spectrum of CuTS presentations, from intermittent numbness (mild) to motor weakness and muscle atrophy (severe). Incidence and treatment choice correlate with severity, population analyses report rising surgical intervention rates with increasing age and severity, meaning severe cases consume disproportionate procedural and rehab resources.
Anatomical constriction, chronic elbow flexion or repetitive pressure, prior trauma, and systemic contributors are all implicated. Case–control and review studies highlight occupational exposure and elbow mechanics as frequent contributors, while some patient groups show idiopathic presentations. This diversity argues for both diagnostic precision and prevention products.
By Technology Insights
Is Technology Redefining Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches in the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market In 2025?
On the basis of technology, the market is segmented into conventional, minimally invasive, and digital or telehealth-enabled.
Traditional diagnostic and surgical methods, such as physical examination, nerve conduction studies, and open decompression, remain the most widely practiced approaches for Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. These techniques are well-established, supported by clinical guidelines like, which recognize open decompression as the standard for severe nerve compression cases.
Endoscopic and limited-incision decompression procedures have grown steadily due to shorter recovery times and reduced scarring. Clinical findings indicate that minimally invasive approaches achieve equivalent or improved functional outcomes compared to open surgery, with reduced postoperative pain and faster return to work. This trend is particularly evident in North America and Europe, where hospital systems prioritize cost-effectiveness and patient throughput.
Tele-rehabilitation and digital diagnostic solutions are reshaping post-operative and conservative care. A 2024 review found that telerehabilitation for upper-limb neuropathies achieved similar outcomes to in-person therapy, while improving adherence and accessibility. Wearable nerve monitoring devices and app-based rehab platforms now allow clinicians to track progress remotely, making care continuous and personalized. This technology segment is gaining rapid traction in advanced healthcare markets where digital health integration and remote patient management are priorities.
By Solution Type Insights
Is Diversification of Clinical Solutions Shaping the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market Future in 2025?
On the basis of solution type, the market is segmented into diagnostic services, non-surgical treatment, surgical treatment, and post-treatment rehabilitation.
Diagnostic precision has become central to Cubital Tunnel Syndrome management. Standard approaches such as physical examination, nerve conduction studies, and electromyography (EMG) are increasingly supported by imaging modalities like musculoskeletal ultrasound, which visualize nerve swelling and dynamic compression.
Conservative management remains the first-line approach for most CuTS cases. This includes splinting, physiotherapy, ergonomic adjustments, and corticosteroid injections. Demand for this segment is growing due to cost containment priorities and patient preference for less invasive options. For companies, there’s a clear opportunity to innovate ergonomic support devices, develop home-based therapy apps, and provide guided tele-rehab programs that improve adherence and symptom monitoring, helping health systems manage caseloads more efficiently.
Postoperative and long-term rehabilitation are gaining attention as key determinants of functional recovery. Physiotherapy, home-based exercises, and tele-rehabilitation platforms enable faster return to work and prevent recurrence. The growing shift toward remote monitoring and patient engagement tools presents new commercial opportunities for digital health providers.
By End-User Insights
Are Shifting Care Settings Redefining End-User Dynamics in the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in 2025?
On the basis of end-user, the market is segmented into primary care clinics, specialty outpatient clinics, hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, homecare settings, and workplace programs.
Online retail is emerging as the dominant distribution channel for Cubital Tunnel Syndrome products, offering convenience, broad product variety, and easy comparison of features and prices. E-commerce platforms allow consumers to access rare and specialty Cubital Tunnel Syndromes that are not available locally. Brands leverage online channels to provide detailed product descriptions, usage guidance, and subscription models, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
Supermarkets and hypermarkets remain important channels, particularly for everyday herbal teas, powders, and dried Cubital Tunnel Syndromes. These channels provide wide accessibility and bulk purchasing options, appealing to mainstream consumers. While less dominant than online retail in niche or high-value segments, they are critical for mass-market penetration and brand visibility.
Hospitals remain the central hub for complex CuTS cases requiring advanced imaging, multidisciplinary evaluation, or surgical intervention. Research published indicates hospitals perform the majority of decompression and transposition surgeries for severe nerve compression.
Given their infrastructure and reimbursement access, hospitals drive demand for advanced surgical tools, nerve repair systems, and inpatient rehabilitation programs. Manufacturers focus on providing high-precision, cost-efficient devices and surgical kits while partnering with hospitals for post-market clinical validation to strengthen credibility and market reach.
Regional Outlook
The cubital tunnel syndrome market share is geographically studied across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America and each region is further studied across countries.
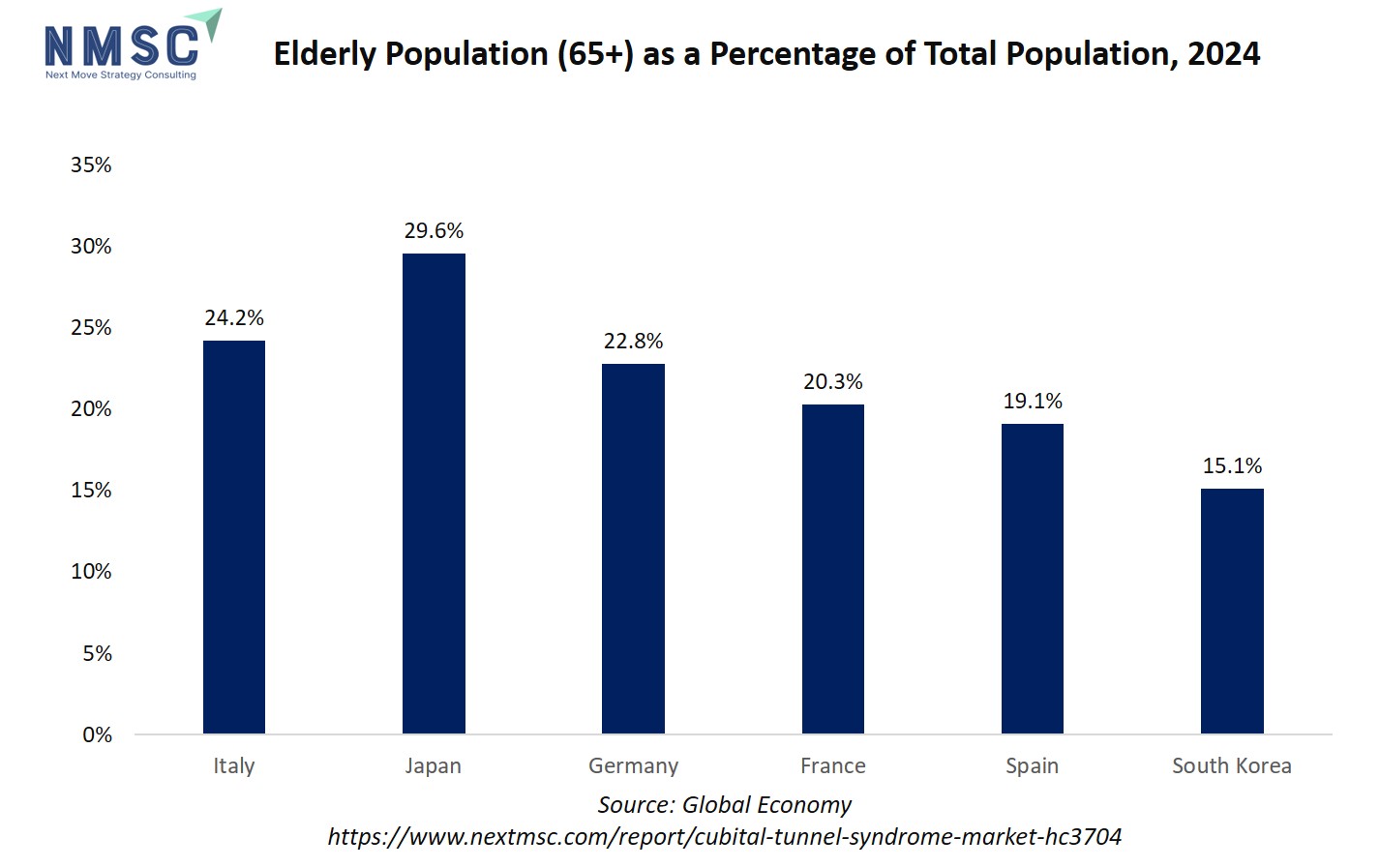
The regional outlook is impacted by the growing elderly population in the sector. Age-related physiological changes, such as reduced nerve elasticity, slower tissue healing, and degenerative joint conditions, make older adults more susceptible to ulnar nerve compression. Additionally, many elderly individuals experience comorbidities like diabetes or arthritis, which further increase the risk of peripheral neuropathies, including CuTS. This results in a steady rise in demand for tailored for geriatric patients.
As the global population aged 60 and above continues to expand, especially in countries like Japan, Germany, and the U.S., healthcare systems are prioritizing early diagnosis and conservative management of nerve compression disorders. This demographic shift directly fuels the need for minimally invasive procedures, digital monitoring, and home-based rehab programs, reinforcing long-term market growth.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in North America
In North America, the market is shaped by a mix of clinical capacity, high diagnostic access, and a large working-age population exposed to computer/desk ergonomics. Musculoskeletal disorders are a major source of lost work time in the U.S., with MSDs accounting for a substantial share of cases and days-away-from-work in BLS reporting; that occupational burden feeds demand for screening, conservative devices, point-of-care ultrasound, and outpatient procedures. Higher per-capita healthcare spending and broad telehealth uptake accelerate adoption of remote rehabilitation and wearable monitoring, while fragmented payer rules still require strong health-economic evidence to scale new bundled-care models.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in the United States
The U.S. combines a high prevalence of musculoskeletal complaints with mature outpatient surgical and rehabilitation infrastructure. National data show large absolute numbers of MSD-related lost-work cases and meaningful median days-away-from-work, which creates employer and payer interest in prevention and rapid conservative care to limit absenteeism. Clinically, the U.S. leads adoption of point-of-care ultrasound, minimally invasive techniques, and tele-rehab pilots, factors that support device sales, digital subscriptions, and employer programs, provided vendors demonstrate cost offsets and measurable reductions in work loss.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Canada
Canada’s single-payer provincial systems and strong primary-care networks encourage standardized care pathways; early screening and non-surgical management are emphasized to limit specialist referrals and surgical backlog. Public funding dynamics mean device and digital-health vendors need provincial-level evidence and pilot results before scaling. Occupational health programs in major employers and provincial workers’ compensation boards that fund early intervention create an opportunity for bundled screening and tele-rehab offerings aligned to evidence of reduced recovery time.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Europe
Europe shows a clear pattern, where high awareness of work-related MSDs, active occupational health policies, and variable national adoption of new diagnostics and outpatient surgery. EU-level studies and reviews demonstrate MSDs are among the most reported work-health problems, pressuring employers and health systems to invest in prevention and early treatment. Countries with robust outpatient surgical networks and reimbursement for telehealth see faster uptake of minimally invasive procedures and tele-rehab; in contrast, nations with tighter hospital-centric budgets prioritize a low-cost conservative pathway.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in the United Kingdom
The UK NHS’s emphasis on wait-list management and community care pushes CuTS management toward primary-care screening, physiotherapy pathways, and prioritization of surgical slots for severe cases. NHS commissioning and occupational health programs in larger employers support early intervention pilots; vendors that show NHS-relevant health-economic benefits and integration into community physiotherapy services are best positioned to expand. National guidelines and resource constraints favour cost-effective splints, tele-rehab, and point-of-care triage models over high-cost novel devices without clear ROI.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Germany
Germany’s strong ambulatory specialist network, high surgical volumes, and willingness to reimburse advanced diagnostics create fertile ground for point-of-care ultrasound, advanced endoscopic tools, and outpatient surgical implants. Employer occupational health is active, and statutory accident insurance fund prevention programs. For vendors, proving clinical superiority and integrating with specialist workflows opens adoption, while hospital-level purchasing remains competitive and evidence-driven.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in France
France combines centralized health planning with considerable outpatient care delivered via private clinics. There’s interest in ergonomic prevention and early conservative care driven by public health authorities and employer programs. Reimbursement pathways favor interventions with clear clinical guidelines and published outcomes, so vendors prioritize clinical validation and collaborations with public rehabilitation services for faster market entry.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Italy
Italy’s regionalized health services show variation: some regions rapidly adopt outpatient and minimally invasive pathways while others remain more hospital-focused. Occupational health regulation and EU guidance on workplace MSDs stimulate employer-driven prevention pilots, which is an effective entry points for tele-rehab, screening, and compact diagnostic bundles. Evidence generation at a regional level also precedes national rollout.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Spain
Spain’s public health services and growing private ambulatory sector favor scalable conservative-care programs and community physiotherapy. As with other EU countries, workplace ergonomics initiatives and regional occupational health programs create demand for screening and early intervention. Vendors that partner with local rehabilitation networks and demonstrate reduced sick-leave days find receptive institutional buyers.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in the Nordics
The Nordics combine strong occupational health systems, high digital health maturity, and preventive workplace policies. These markets rapidly adopt tele-rehabilitation, wearable monitoring, and point-of-care ultrasound when cost-effectiveness is shown, and they favor integrated models linking primary care, occupational health, and employers. Successful pilots here scale regionally and set standards for Europe on employer-funded prevention and digital follow-up.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in the Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is heterogeneous, where advanced healthcare pockets rapidly adopt diagnostics, minimally invasive surgery, and digital rehab, while large markets, like China, India, Indonesia balance rising demand with cost sensitivity and variable access. The region’s ageing populations, urban desk-work growth, and expanding private healthcare drive overall market growth. WHO and regional health data highlight rising musculoskeletal need across APAC.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in China
China’s large population, rapid urbanization, and growing middle-class healthcare spending create scale opportunities for screening, conservative devices, and outpatient procedures. However, procurement tends to favour high-volume, cost-effective solutions, and local regulatory pathways require partnership with domestic distributors or manufacturers. Digital-health adoption is strong, presenting an avenue for tele-rehab and employer programs in large enterprises and tech companies. Public health emphasis on ageing and chronic conditions supports rehabilitation services expansion.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Japan
Japan’s ageing population and strong outpatient care infrastructure make it receptive to minimally invasive procedures, precision diagnostics, and home-based rehabilitation. Reimbursement pathways and a conservative approach to new tech favour vendors that demonstrate clear functional benefit and cost-effectiveness for older adults who have higher surgical rates and slower recovery without structured rehab. Japan also shows high adoption of clinical guidelines and registry-based validation.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in India
India presents a mixed picture, where growing private healthcare and large employer sectors in IT and services make employer-driven screening and tele-rehab attractive, while fragmented rural access and cost sensitivity mean low-cost splints and scalable digital solutions win first. Regulatory and reimbursement frameworks are developing, so vendors pilot employer-funded programs or partner with private hospital chains for regional rollout. High population scale offers strong volume potential if pricing and distribution are adapted.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in South Korea
South Korea’s high digital-health penetration and advanced surgical capabilities enable fast uptake of point-of-care ultrasound, minimally invasive techniques, and tele-rehab. Employers and national health programs focused on worker health provide routes for prevention and early intervention, and reimbursement systems support outpatient procedural growth when backed by clinical evidence. Vendors succeed by coupling tech with clinician training and outcome registries.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Taiwan
Taiwan’s efficient healthcare delivery and universal coverage create an environment where diagnostic upgrades and outpatient minimally invasive workflows scale quickly when clinical benefit is demonstrated. Integration with national health insurance processes requires rigorous outcome data, but once validated, adoption across clinics and hospitals becomes rapid.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Indonesia
Indonesia’s healthcare market is fragmented, with urban centers showing demand for diagnostic and telehealth services while rural areas still lack access. Employer-funded programs in larger industrial and service companies pilot scalable screen–triage–treat packages, but nationwide scale depends on distribution partnerships and cost-effective device portfolios. Public health priorities and infrastructure development will shape medium-term growth.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Australia
Australia’s mixed public–private system, strong occupational health programs, and high telehealth adoption create fertile ground for employer prevention programs, point-of-care ultrasound triage, and home-based rehab subscriptions. Reimbursement and hospital purchasing favour proven cost savings and fast return-to-work outcomes, so pilots demonstrating reduced sick leave are particularly persuasive to payers and employers.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in Latin America
Latin America presents patchy access to advanced diagnostics and outpatient surgical capacity, with urban private providers offering the most advanced care. High informal workforce segments and variable occupational health coverage mean employer-driven programs are less uniform; however, multinational employers and large public systems in some countries offer entry points for screening and tele-rehab pilots. Cost-sensitive models and partnership with local distributors are essential.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market in the Middle East & Africa
The Middle East shows pockets of advanced private healthcare that adopt diagnostics and tele-rehab quickly, while many African markets face constrained access and prioritize basic orthopaedic and rehabilitation needs. Regional employer programs in energy and large industrial sectors sponsor prevention pilots. Overall, growth is uneven and driven by private-sector investment, donor programs, and urban healthcare expansion. Partnerships with regional health systems and local suppliers are crucial.
Competitive Landscape
Which Companies Dominate the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Industry and How do they Compete?
The competitive field mixes large orthopedics groups, such as Stryker, Arthrex, CONMED, Integra with specialised device and rehab firms, like MicroAire, Trice Medical, Sonex, Axogen, REH4MAT, AliMed, Medline. Big players leverage broad portfolios, distribution and hospital contracts to push surgical kits and implants, while specialists compete on focused innovations, endoscopic release systems, ultrasound-guided tools, nerve-repair biologics, and rehab wearables.
For example, MicroAire’s SmartRelease endoscopic system targets minimally invasive cubital/carpal procedures. Trice markets Seg-WAY single-portal endoscopic systems for small procedures, and Sonex focuses on ultrasound-guided extremity releases, each carving a niche alongside multi-category giants.
Market Dominated by Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Giants and Specialists
Large medtech firms dominate scale, channel access, and procurement cycles across hospitals and ASCs, using distributor networks and broader orthopaedics suites to win institutional contracts. Stryker’s scale after its Wright Medical acquisition illustrates how giants expand extremities portfolios and push into related niches.
Meanwhile, niche vendors win by offering procedure-specific systems, that reduce OR time and clinic burden, appealing to ASCs and outpatient clinics. Well-funded health systems adopt minimally invasive bundles quickly, while cost-sensitive markets favour low-cost splints and employer prevention programs.
Innovation and Adaptability Drive Market Success
Winning companies combine product innovation with training, service and digital follow-up. MicroAire and Trice emphasise minimally invasive, single-portal systems that shorten recovery and OR time; Sonex advances ultrasound-guided procedures that let surgeons visualise anatomy in real time.
Large firms, such as, Arthrex, CONMED, Integra add breadth through new procedural kits, government/large-buyer contracts, and strategic partnerships that place their systems into operative workflows quickly. Arthrex’s continued product launches and large procedural contracts show how clinical portfolio expansion and service agreements accelerate adoption. These tactics, including device, training and outcome tracking are now core go-to-market plays.
Market Players to Opt for Merger & Acquisition Strategies to Expand Their Presence
Mergers and acquisitions let giants buy niche tech, distribution and clinical evidence rapidly. Stryker’s acquisition of Wright Medical broadened its extremities and biologics portfolio and scale. CONMED acquired Biorez and In2Bones, adding soft-tissue and extremity solutions to expand procedure coverage.
Integra’s acquisition of Acclarent illustrates how firms buy complementary ENT/soft-tissue tech to diversify surgical offerings. For mid-sized specialists, being acquired offers distribution and capital to scale; for acquirers, it’s a fast route to novel procedural IP and access to outpatient channels.
Key Players
-
MicroAire Surgical Instruments
-
A.M. Surgical, Inc.
-
Trice Medical (Seg-WAY / Seg-WAY ECuTR)
-
Sonex Health, Inc.
-
CONMED Corporation
-
Arthrex, Inc.
-
Integra LifeSciences
-
Stryker Corporation
-
REH4MAT
-
North Coast Medical (NC Medical)
-
Medical Designs, LLC
-
Med Spec / Medical Specialties, Inc.
-
Medline Industries, Inc.
What are the Latest Key Industry Developments?
-
2024- MicroAire updated SmartRelease ECTR technical literature and product materials in 2024, reinforcing its position in endoscopic soft-tissue release systems for carpal and cubital procedures and signalling ongoing product support and surgeon engagement to defend market share.
-
April 2024- Integra LifeSciences completed acquisition of Acclarent, expanding ENT and soft-tissue surgical capabilities and signalling strategic diversification into complementary procedural markets and distribution channels that accelerate cross-sell opportunities for peripheral-nerve/soft-tissue tools.
What are the Key Factors Influencing Investment Analysis & Opportunities in the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market?
Investment in the market hinges on two intertwined factors: competitive innovation and healthcare system pressure to reduce cost and downtime. With many unions and workplace health programmes seeking to minimise lost productivity from nerve compression disorders, funding flows are increasingly directed at devices and digital therapeutics that deliver faster recovery, lower complication rates, and remote-care capabilities.
Venture capital and strategic investors are watching closely for startups offering outpatient endoscopic systems, wearable monitoring platforms, and bundled employer-based prevention programmes. These represent high-growth niches within the broader nerve-compression space. Valuations are being shaped by evidence generation, recurring revenue potential, and scale-up opportunities across geographies.
Companies that demonstrate strong clinical outcomes, favourable health-economic profiles, and scalable tele-rehab or subscription models become more attractive investment targets. Meanwhile, regions with mature outpatient surgery ecosystems and high digital-health adoption, such as parts of North America, western Europe and selected Asia-Pacific markets, are emerging as investment hotspots. For investors, the opportunity lies in backing firms that cross-leverage device, software and service models to generate ecosystem-wide value rather than single-product plays.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
Next Move Strategy Consulting (NMSC) presents a comprehensive analysis of the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market, covering historical trends from 2020 through 2024 and offering detailed forecasts through 2030. Our study examines the market at regional and country levels, providing quantitative projections and insights into key growth drivers, challenges, and investment opportunities across all major industry segments.
The market creates multi-level benefits across its stakeholder ecosystem. Investors gain exposure to a steadily growing segment of the musculoskeletal and neuro-rehabilitation market, driven by rising workplace-related nerve injuries and expanding adoption of minimally invasive and tele-rehab solutions.
For customers, patients and healthcare providers alike, the market delivers faster diagnostics, improved ergonomic prevention tools, and less invasive treatment options that reduce recovery time and costs. Policymakers and health authorities benefit through reduced workforce absenteeism, lower surgical burden on public systems, and greater alignment with preventive-care initiatives. Together, these dynamics foster a sustainable value chain where clinical innovation meets public-health priorities and commercial scalability.
Report Scope:
|
Parameters |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 163.67 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 227.84 Billion |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 6.84% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Analysis Period |
2024–2030 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2030 |
|
Market Size Estimation |
Billion (USD) |
|
Growth Factors |
|
|
Companies Profiled |
15 |
|
Countries Covered |
33 |
|
Market Share |
Available for 10 companies |
|
Customization Scope |
Free customization (equivalent to up to 80 analyst-working hours) after purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Approach |
In-depth primary and secondary research; proprietary databases; rigorous quality control and validation measures. |
|
Analytical Tools |
Porter's Five Forces, SWOT, value chain, and Harvey ball analysis to assess competitive intensity, stakeholder roles, and relative impact of key factors. |
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Market Key Segments
By Condition Profile
-
Severity
-
Mild
-
Moderate
-
Severe
-
-
Causes
-
Idiopathic
-
Traumatic or Structural
-
Occupational or Repetitive Stress
-
Metabolic or Systemic
-
-
Demographics
-
Adult Working Age
-
Older Adult
-
Pediatric or Adolescent
-
-
Laterality
-
Unilateral
-
Bilateral
-
By Technology
-
Conventional
-
Minimally Invasive
-
Digital or Telehealth Enabled
By Solution Type
-
Diagnostic Services
-
Physical Examination
-
Electrodiagnostic Tests
-
Imaging
-
-
Non-Surgical Treatment
-
Splinting or Bracing
-
Physical or Occupational Therapy
-
Medications or Injections
-
-
Surgical Treatment
-
In-Situ Decompression
-
Anterior Transposition
-
Medial Epicondylectomy
-
-
Post-Treatment Rehabilitation
-
Outpatient Rehabilitation
-
Home-Based Recovery
-
Tele-Rehabilitation
-
By End-User
-
Primary Care Clinics
-
Specialty Outpatient Clinics
-
Hospitals
-
Ambulatory Surgical Centers
-
Homecare Settings
-
Workplace Programs
Geographical Breakdown
-
North America: U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
-
Europe: U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Netherlands, and rest of Europe.
-
Asia Pacific: China, India, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Indonesia, Vietnam, Australia, Philippines, Malaysia and rest of APAC.
-
Middle East & Africa (MEA): Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Israel, Turkey, Nigeria, South Africa, and rest of MEA.
-
Latin America: Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, and rest of LATAM.
Conclusion & Recommendations
The cubital tunnel syndrome market stands at the intersection of clinical innovation, digital transformation, and preventive healthcare. As diagnostic precision improves and tele-rehabilitation platforms expand access, the market is expected to mature into a more integrated ecosystem combining devices, data, and workplace ergonomics.
Strategic partnerships between device makers, occupational health providers, and digital health platforms define the next phase of competition. The future outlook points to sustained growth supported by technological adaptability, clinical validation, and broader employer participation in preventive screening programs.
Executives focus on scalable, evidence-based solutions that align with occupational health and payer priorities. Investors capitalize on emerging value chains linking diagnostics, rehabilitation, and digital monitoring, while policymakers accelerate impact by incentivizing preventive coverage and ergonomic safety standards. Together, these actions will not only enhance clinical outcomes but also establish chronic elbow pain care as a model for cost-efficient, technology-enabled musculoskeletal management.

















 Speak to Our Analyst
Speak to Our Analyst